Sialolithiasis is the abnormal formation of stones or salivary calculus in the salivary glands of a person. It is most commonly found in the submandibular salivary gland and duct followed by the parotid gland and its duct. Sublingual glands that are found beneath the tongue are the least affected.
Major and Minor Salivary Glands
Page Contents
- 1 Major and Minor Salivary Glands
- 2 Functions of Salivary Glands
- 3 Sialolithiasis Salivary Duct Stones
- 4 Submandibular Sialolithiasis
- 5 The Wharton Duct
- 6 Sialolithiasis Causes
- 7 Sialolithiasis Symptoms
- 8 Diagnosis of Sialolithiasis
- 9 Sialolithiasis Treatment
- 10 Possible Side Effects of Sialolithiasis Treatments
- 11 Preventions of Sialolithiasis
The salivary glands are composed of different types of minor and major glands.
- Major glands include the parotid, submandibular gland, and the sublingual gland.
- Minor glands are composed of several glands that may be located along our upper aerodigestive tract, mucosa of the oral cavity, hard palate, pharynx and our lips
Functions of Salivary Glands
The role of salivary glands is very important in the process of digestion. Some of its specific functions include enzymatic degradation of food substances, lubrication, production of certain antibodies, hormones and other reactive substances associated with blood groups, antimicrobial protection and mediation of taste. Thus, any alteration or malfunction on one of these glands will definitely affect the overall function of the digestive system and the other organs.
Sialolithiasis Salivary Duct Stones
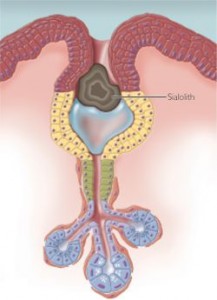
Picture 1 – Sialolithiasis
Source – drugster.info
This is a type of sialolithiasis wherein the salivary ducts are the ones which are affected. It is the accumulation of phosphate or calcium crystals in at least one of the salivary ducts of an individual. These may include either the parotid, sublingual or submandibular glands. Anyone who experiences sialolithiasis salivary duct stones will suffer from lower water content of saliva due to the stone formation in one of the ducts as well as higher risks for dehydration. Several factors may increase the risk of possibly acquiring this disease which includes medications like diuretics, anti-histamines and anti-depressants.
Submandibular Sialolithiasis
Submandibular Siolothiasis is the formation of stones particularly in the submandibular glands of an individual. The submuandibular gland is considered as the second largest if we are referring to the major salivary glands which weigh approximately 10 grams. This is located in the submandibular triangle of our neck.
Persons who are suffering from submandibular sialolithiasis find themselves having stones that form in their submandibular gland which are found beneath the floor of our mouth. The result of this stone formation is obstruction in our Wharton’s duct, which lies in between our hypoglossal and lingual nerves.
The Wharton Duct
Wharton Duct was first described by Thomas Wharton, an English anatomist where it also got its name. The purpose of this duct is to drain the saliva from submandibular and sublingual glands as well as sublingual caruncle which is located at the base of the tongue. It does so by exiting the gland from a deep lobe, then allowing it to pass through the floor of the mouth and eventually opening in close to the proximity of the lingual frenulum.
Sialolithiasis Causes
The cause of sialolithiasis remains unknown until now but there are some researchers who argue that this may be triggered by the food that an individual eat, just like the one mentioned above. More over, other factors which may result to this condition EW a follow:
- Salivary stagnation
- reduced food intake
- dehydration which also results to a higher viscocity in our saliva
- decreased production of saliva caused by constant medication of anti-psychotic, anti-hypertensives and anti-histamine drugs which really affects the manufacture of saliva of the mouth
- precipitation of calcium salts
- epithelial injury which may have occurred near the duct resulting to unwanted sialolith formation
Sialolithiasis Symptoms
Common sialolithiasis symptoms include swelling and discomfort in the affected salivary gland. The pain increases during meal time and other cases wherein more saliva may be needed for the preliminary process of digestion.
Other symptom which individuals may fear if they have sialolithiasis includes an unusual taste or gritty feel with their own saliva. The pain and discomfort while eating may also become too severe it becomes exposed to sour or acidic foods.
In worst cases, the patient may even experience a bacterial infection of the gland which will make it extremely swollen, and very painful and even tender to touch which may also result to fever.
Diagnosis of Sialolithiasis
Diagnosis of Salivary gland stones are done by medical history and physical examination. The stones can often be felt by fingers. Confirmation of sialolithiasis is done by Xrays.
Sialolithiasis Treatment
Before any form of sialolithiasis treatment, your health care provider will request that you undergo x-ray just to confirm their earlier diagnosis based on medical history and physical examination. After confirming your condition, the following sialolithiasis treatment may be recommended:
- Hydration
- Warm compresses
- Gland massage
- Use of antibiotics to stop the spread of infection
For severe cases where surgery is needed the following treatment options may be applied:
- Trans Oral Ductotomy
This is the opening of the Wharton Duct for it to be cannulated and dilated so the stone can be completely removed through trans-oral approach.
- Excision
In some case involving deep entraparenchymal stones also known as multiple stone, the glands may be required to be excised on an elective basis.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
This is also referred to as ultrasonic lithotripsy. It uses ultrasound waves to help break up the stones which formed in one your ducts or salivary glands and allowing it to pass through the same duct as well. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of this sialolithiasis treatment is yet to be validated so it is rarely recommended by doctors.
Possible Side Effects of Sialolithiasis Treatments
People who will undergo sialolithiasis treatment should be prepared to experience scarring in the duct opening, especially when an excision is made. Additional stone formation may also arise and infection may spread to other ducts so it is best to follow all the drug medications and medical advises of your doctor to avoid unwanted complication in the future.
The most severe type of side-effect which you may experience due to sialolithiasis treatment is paralysis especially if the entire salivary gland needs to be removed due to several complications which involves nearby nerve. If this happens, you will feel loss of sensation in the face and tongue area.
Preventions of Sialolithiasis
If you do not wish to suffer from sialolithiasis then you should make it a point that you drink a minimum of eight glasses of water a day. Massage your salivary glands every after meals to help clear thickened saliva. Moreover, it would also be helpful if you will refrain from using over-the-counter drugs and instead stick with prescribed drugs given by doctors.
Reference :
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC403356/pdf/canmedaj00143-0061.pdf
http://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/medical/issues/sag-01-31-2/sag-31-2-17-0002-4.pdf

Thanks it’s a nice note,