The post Mucus in Urine | Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
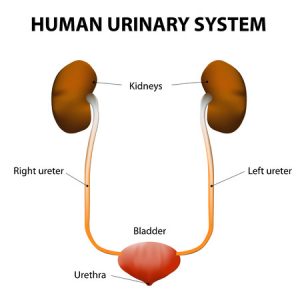
]]>Urine is mostly clear in color but at times it may be amber or straw colored. Moreover, due to presence of mucus it might appear cloudy. Mucus is found in the lining of the urethra and urinary bladder and may be excreted out by getting mixed with urine. The secretions are mostly thin and fluid like.
Mucus is not so common in urine and often considered harmless. However, if found they can be cause diseases in the digestive system, urinary tract, reproductive system and even the immune system. When something goes wrong in the body and several systems are not in sync then only mucus formation is seen in urine.
Types of mucus in urine
There are primarily two types of mucus found in urine:
- Irregular and longitudinal fiber like threads forming bundles that are pale, narrow-ended on one side
- Mucus corpuscles are similar in look to pus cells and are curvy in shape
Common causes of mucus in urine
- Urinary tract infection (UTI) caused by bacterial infection leading to discomfort in urinating and thereby mucus formation
- Urinary tract infection causing pain
- IBS or irritable bowel syndrome
- Inflammatory bowel disease such as Ulcerative colitis
- Obstruction in urinary tract
- Bacterial infection through sexually transmitted diseases like Gonorrhea or Chlamydia
- Bladder cancer with blood in urine
- Kidney stones cause increase in mucus and foul smelling urine with severe pain
Specific Causes of mucus in urine for women
Urinary tract infections have many different factors leading to these diseases:
- Having more than one sexual partner
- Frequent & vicious sexual intercourse
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Dangerous Contraceptives
- Regular intake of antibiotics
- Escherichia Coli Infection
- Harsh cleaners
- Past experience of UTI infection
- Tumors or harmless masses obstructing the urinary tract
- Birth controlling pills
- Staphylococcus infection
Symptoms of Mucus in urine
Signs and symptoms may vary depending on the underlying causes for the formation of mucus. Some of them are as follows:
- Pain in abdomen
- Painful urination
- Discomfort while urinating
- Fever
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Foul smell in urine
Primary symptoms specific to women
- Frequent urges for urinating
- Incontrollable compulsion of urinating
- Amount is quite insignificant at all times
- Urine gets cloudy
- Feeling a burning sensation while urinating each time
- Urine is pinkish, yellowish or Cola colored
- At times, presence of blood in urine
- Urine is pungent smelling
Some other Signs
- Inflammation or pain in the pelvic region
- Restlessness
- Cramps or pain felt at the lower part of stomach
- Discomfort or feeling sick
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Frequent chills
Test for Mucus in urine
- Medical history check
- Thorough physical examination
- Urinalysis for checking the presence of infection
- Urine culture test to know the microorganism behind its cause
Treatment for Mucus in urine
On noticing the presence of mucus in urine, one must undergo medical treatment immediately. Few treatment modalities are mentioned below:
- Antibiotics such as amoxicillin or erythromycin.
- Anti-inflammatory medications in case of membranous inflammation
Natural remedies for Mucus in urine
- Cranberry juice for cleaning out urinary tract infections
- Yoghurt with honey to fight bacteria
- Maintenance of proper hygiene to avoid infections
- Dietary changes
- Avoid gassy foods, wheat, dairy products, and raw vegetables
- Avoid carbonated beverages
- Stop smoking and alcohol consumption
- Include fruits like oranges and apples, salads and green vegetables
- Keep the genital region clean
- Wear cotton underwear
- Use of wipes at intervals
- Drink adequate amount of water at least 10-12 glasses a day
- Keep the body well hydrated with more amount of fluid intake
- Practice safe sex
Homeopathic treatment for mucus in urine
Homeopathic treatment acts quite helpful as they trigger to find the primary cause underlying this symptom of mucus formation and try to cure it. Homeopathic medicines treat the patient and its body as a whole. And also specific medication can be used for particular types of problems according to the symptoms experienced. Effects of these medicines may help to rule out the excess amount of mucus.
Some commonly prescribed medications include:
- Belladonna (if mucus is white)
- Merc (if mucus is red)
- Phosphorus (if mucus is yellow then)
- Causticium or Antimonium Tart if patient feels nausea
- Kali bichrome and Kali Mur
Risk of mucus in urine
A little amount of mucus in urine is however not much of concern. But an excess excretion is alarming and one should pay serious attention to it. Although the mucus may be mild, it may cause high damage to the body if not treated timely. It may cause urinary tract infection, but it may not be much critical as bladder cancer. But this symptom may carry underlying ailments such as abnormalities in the reproductive system, issues of the excretory system and immune system causing an infection.
Prevention steps
The best steps to be followed to prevent further complications are:
- Medical history, the nature, and location of pain all verified
- Consulting the doctor, necessary tests as per recommendation
- Have a healthy diet
- Drink plenty of fluids and water
- Maintain proper hygiene
When to call the doctor?
On noticing excessive mucus accompanied by cloudy urine that is deep yellowish, pinkish or Cola colored carrying a foul smell, make an appointment with the doctor. Some cases might be harmless, but in some conditions, the mucus may be a symptom of an underlying disease that may turn critical. The doctor can quickly determine through the warning symptoms if the mucus is severe or less acute and easily treatable.
The post Mucus in Urine | Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Anuria | Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>Signifying the name itself the word means ‘no urine.’ Uria refers to urine hence Anuria implies no urination or absence of urine. The kidneys do not produce urine in this condition, and it acts as a vital sign for kidney malfunction.
Relation of Anuria to Oliguria
In this medical condition, the urine production becomes less than 500 milliliters per day which is a remarkably low discharge of urine. Anuria is the worst and last stage of Oliguria where the urine output is as less as 100 milliliters per day or even less than that. Anuria is often related to kidney diseases, which develops from the acute stage (Oliguria) and then progresses to its advanced stage (Anuria). Anuria is worse than Oliguria as it damages the kidneys, the urine output becomes dangerously low which turns into kidney failure and if untreated cause death.
Causes of Anuria
There may be several factors underlying this medical condition:
- Uncontrolled diabetes leading to acute kidney failure and then Anuria
- Hypertension damages the arteries around kidneys causing disruption
- Kidney failures
- Prolonged kidney disorder resulting in inability to urinate
- Kidney stones might act as an obstruction in urine discharge along with pain
- Tumors also block the urination output as well as disrupt the kidney functions
- Excessive blood loss, diarrhea, vomiting and loss of fluids may cause low urine outputs
- Allergic reactions to some drugs
- Decreased blood supply to the heart and other cardiac conditions
- Sudden increase of pressure in the abdominal area
- Pancreatitis may cause low urination
Symptoms of Anuria
- Decrease in the urine output
- Excess loss of body fluids
- Irritation or discomfort
- Dizziness
- Loss of appetite
- Lightheadedness
- Rapid pulse
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abnormal urination for 1-2 days
Risk factors
Anuria can affect anyone, but some may be more exposed to the risks. It may include people:
- Suffering from kidney disorders or urinary tract infection
- With enlarged prostate glands
- Who have recently undergone any renal surgery
Complications
It is to be noted that if Anuria is left untreated, then the underlying disease behind its cause is also not treated. It might eventually lead to life risk and several dangerous complications. Some of these complications turn up when:
- Kidney damage that can turn fatal
- Kidney failure resulting in death
- Acute Cardiovascular problems
- Severe dehydration due to excessive fluid loss
- Hematological issues like anemia
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Hyperkalemia
- ECG abnormalities
- Cardiac arrhythmias
Diagnosis
The doctor while detecting may ask about the nature of urinating issues, the presence of blood in urine or fatigue in the patient. On inspection, the doctor must have a closer look at the kidney function by performing the following tests –
- Urine culture
- CT scan of the abdomen
- MRI scan of the kidneys
- Renal Scintigraphy
- Biopsy of a small sample
Treatment of Anuria for adults
Doctors initially analyze the medical history, span and nature of the disorder prior to any treatment for Anuria. The exact condition underlying the decrease in urine output should be detected for proper treatment. Some common treatments include:
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for increasing the urine output
- Discontinuation of drugs and nephrotoxic medications until normal urination
- Antibiotics for urinary tract infection
- Immediate stoppage of Potassium containing medicines
- In extreme cases, surgery for removal of the part disrupting normal flow of urine
- For those unfit for surgery, internal drainage method
- Nephrostomy
- Balancing of fluid input and output
- Retaining the electrolytic balance in the body
- Dialysis in case of kidney disorders
- Urethral stents for collecting urine
- In ultimate instances, a Kidney transplant
- Removal of kidney stones, or any tumors if any
- Surgery, chemotherapy or radiation for tumor removal
Treatment for Anuria in children
Children are more prone to Anuria due to diarrhea and other dehydration issues. Some common treatments are:
- Hydration
- In case of fluid overload, diuretics therapy is done
- Urinary catheterization in case of any postrenal obstruction or stenosis
Home remedies for Anuria
In case there is no severe condition, underlying Anuria then some remedies may be adopted for the easiest and quickest way to cure the disorder:
- Consumption of more amounts of water and liquids
- Reduction of salt intake
- Lowering of potassium intake
- Eat smaller amounts of protein
Alternative ways to get rid of Anuria
Patients may also take homeopathy medicines but again, it depends on the degree of the condition and symptoms. The signs and symptoms gradually get removed. Homeopathy aims at not only in the treating the Anuria symptoms, but also to find out and address the underlying condition. It helps to cure through individualized remedy and treatment procedures. Following medicines may be helpful:
- Aconite
- Apocynum
- Arsenic Album
- Apis Mel
- Belladonna
- Bryonia
- Cantharis
- Camphor
- Colchicum
- Lycopodium, Digitalis
- Kali Bi
- Merc Cor
- Opium
- Stramonium
- Petroleum
- Nitric Acid
Outlook for Anuria
The outlook for Anuria is mainly dependent on the following factors:
- Actual cause
- Early detection
- Easy treatment of the underlying conditions
- Complications in the kidneys
When to see the doctor?
As Anuria relates to several other causes, self diagnosis is a bit difficult. One tends to ignore this condition and tries to solve it through home remedies and self prescribed medicines or treatments. But one must get in touch with a doctor if any changes get noticed in the urine output. Some cases are:
- Even after increased water intakes no improvement is found in the urination
- If oliguria is the underlying condition, the doctor should be informed
- In case of diarrhea if vomiting or a feeling of nausea, lightheadedness, fever, dizziness or fat pulse is observed
The post Anuria | Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Uremia appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>What is Uremia?
This is a toxic disease resulting from kidney disorder that is marked by retention of waste products, usually excreted in the urine, in the blood of sufferers. It is a condition in which the blood urea nitrogen level, which is an indicator of the nitrogenous waste products in the body, is found to be increased. The term is also used to narrowly describe the disorder accompanying kidney failure.
The condition should not be confused with Hyperuricemia, or uricemia, which indicates an accumulation of uric acid in the bloodstream.
Uremia Causes
The condition arises due to any disorder that impairs the ability of the kidneys to filter waste products. The disease may originate due to any disorder that damages the kidney. These renal causes include:
- Surgery
- Injury to the kidney
- Kidney damage from hypertension or diabetes
- Renal artery embolism or occlusion (obstruction of blood flow to the kidney)
- Certain medications, such as high doses of intravenous contrast material or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Kidney disease (including any problem associated to the kidney, such as kidney failure, kidney stones and kidney anomalies)
Uremia may also arise due to various other disorders, which lead to reduced flow of blood or low blood volume. These other causes include:
- Shock
- Burns
- Excessive vomiting
- Excessive bleeding
- Excessive diarrhea
- Congestive heart failure (worsening of the ability of the heart to pump blood)
- Dehydration (deficiency of electrolytes and body fluids, which can be life-threatening when acute and untreated)
Uremia Symptoms
The problems occurring due to this condition are associated to kidney damage that prevents filtration of nitrogen wastes by kidneys. In the absence of proper filtering, the wastes accumulate in the bloodstream and cause poisoning in the body.
The signs and symptoms of this disorder can be categorized into two types:
General symptoms
These include:
- Dry mouth and nose
- Abdominal pain
- Edema (swelling)
- Excessive thirst
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Weakness (loss of strength)
- Fatigue
- Pale skin or pallor
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Confusion or loss of consciousness for even a brief moment
Acute symptoms
These include:
- Low urinary output
- Temporary loss of consciousness or mental confusion
In some cases, the problems can be life-threatening.
Uremia Diagnosis
The conventional diagnostic procedures for this disorder include:
- Routine blood test
- Routine urine test
- Ct scans
- MRI scans
- Ultrasonography
- Biopsy
- Glomerular filtration rate
- Renal function examination
- Blood biochemical examination
Physicians also ask patients whether they are suffering from the following symptoms:
- Weakness
- High blood pressure
- Poor appetite
Doctors also check for presence of Edema and change in amount of urinary wastes. Uremia patients have a pale facial appearance, which also helps in determining the presence of the condition.
Specialized urine or blood tests can help a healthcare provider in diagnosing this condition. Blood area nitrogen tests are useful in determining how effectively the kidneys are functioning. The test measures the amount of nitrogen wastes in the blood of patients. Creatinine tests also help in measuring the amount of creatinine in the body of sufferers. Physicians might also conduct a sodium urine test to assess the amount of sodium in the urine or blood.
Uremia Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this disorder includes making sure that the symptoms experienced by patients are those of Uremia and not those of similar conditions like:
- Acute Renal Failure
- Anemia
- Chronic Renal Failure
- Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1
- Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Uremic Encephalopathy
- Acute Glomerulonephritis
- Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Uremia Treatment
Generally, the disease requires to be cured in hospital. Treatment usually begins with addressing the cause of flow of blood through the kidneys. This is followed up with focusing on removal of nitrogenous wastes from the bloodstream followed by restoring of blood pressure and blood volume. Finally, ongoing treatment may be needed to prevent buildup of wastes and damage to the kidneys as well as addressing their underlying causes.
Acute Uremia Treatment
Cure for the disease usually begins within 24 hours after it is first diagnosed. Immediate treatment is required to stabilize a patient and address the underlying cause of the disorder. Immediate cure may include:
- Blood transfusions
- Blood products
- Fluid therapy
- Hospitalization
- Intravenous fluid
- Hemodialysis (filtering blood outside the body)
- Medicines, such as dopamine, to increase cardiac output and blood pressure
Ongoing Uremia Treatment
Treatment may be continued when doctors have managed to restore blood pressure of patients. Long-term cure may involve use of medications, dialysis and dietary modification.
Uremia and Medications
The medicines that are usually employed for managing the condition are used for controlling related electrolyte and metabolic abnormalities, such as:
- Anemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Iron deficiency
- Hypocalcemia
- Hyperparathyroidism
Other drugs that are used, include:
- EPO for anemia
- Iron
- Phosphate binders
- Calcitriol for hypocalcemia and PTH suppression
- Water-soluble vitamins (such as Vitamin C and Folate)
The choice of drug and usage depends on the medical state of patients, which may change with the severe clinical setting of sufferers.
Uremia and Diet
Dietary changes should be made for Uremia patients only by a dietician who possesses the expertise needed for curing renal conditions, especially in patients who have not yet begun dialysis therapy. Some of the symptoms of this disease may be alleviated with the aid of low-protein diets. A low-protein diet is often recommended to people with mild to moderate cases of renal failure.
However, this approach remains controversial. In studies conducted in this regard, few benefits were found to be associated with this type of diet. There is another problem associated to this disorder; the patients may become malnourished due to deficiency of protein in their diet. A high number of Uremia sufferers are found to die out of malnourishment on starting dialysis.
Uremia Complications
Unless treated properly in time, the disorder can give rise to various acute complications. These include:
- Seizures
- Cardiac arrest
- Coma
- Death
In case of severe Uremia, spontaneous bleeding may occur and may include the following problems:
- Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding
- Spontaneous subdural hematomas
- Increased bleeding from any underlying disorder
- Bleeding associated with trauma
In case of acute underlying abnormalities in electrolyte levels, such as metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia or hypocalcemia, cardiac arrest may also ensue.
Uremia and Acute Tubular Necrosis
Uremia patients occasionally develop a condition, known as Acute Tubular Necrosis. In this disease, the kidney tissues get severely damaged. Patients might eventually suffer from acute kidney failure, a disease characterized by abrupt stoppage of function of the kidneys. Some patients might suffer from convulsions.
Uremia Mortality Rate
The rates of hospitalization and death associated with this condition are quite high, as a result of existing co-morbid conditions like:
- Hypertension
- Coronary artery disease
- Peripheral vascular disease
Uremia Risk Factors
The risk of development of the disorder is increased by a number of factors. These risk factors include:
- Low blood pressure (Hypotension)
- Recent trauma or injury
- Recent surgery
- Recent infection
- Intake of several medicines, like intravenous contrast material or NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
Uremia Prognosis
Unless the condition is treated with the aid of renal replacement therapy (such as transplantation or dialysis), the outcome is poor for sufferers with Uremia of CRF. If treated fast, the condition can be reversed although there is a possibility that the kidneys may suffer permanent damage. The underlying processes that lead to uremia may also result in kidney failure.
Uremia Prevention
The prevention of this disorder includes preventing and managing various kidney disorders that can result in Uremia. Prevention also involves avoiding contact with renal toxicities. The risk for complications can be prevented or minimized by following a proper treatment plan designed by healthcare providers for sufferers of Uremia. The measures for preventing complications include:
Proper rest
Patients of Uremia should have proper nutrition and rest. Sufferers should not take part in strenuous activities that exert them.
Active treatment
Patients should undergo dialysis if the renal functions cannot be reversed. Dialysis therapy involves Hemodialysis and Oral and Peritoneal dialysis. Oral dialysis is only suited for patients of mild cases of Uremia.
Avoiding contact with toxic chemicals
Sufferers should avoid inhalation or skin contact with chemicals that contain cadmium, tetrachloroethylene, chloroform and ethylene glycol. These chemicals can be found in household cleansers, pesticides, paints and vehicle exhausts.
Restricting intake of cadmium-rich foods
Patients should limit the amount of foods that are rich in cadmium, such as unclean vegetables, mussels, halibut, scallops and oysters.
Limiting or giving up smoking
Smoking adversely affects the condition of the kidneys. Naturally, giving up smoking is the best measure to ensure good health of the organs. If that is not possible, smoking should be reduced to a minimum to minimize the risks of Uremia and other ailments of the kidneys.
Uremia Vs Azotemia
Azotemia refers to a problem in blood composition in which some constituents exceed their normal range. An individual suffering from Azotemia suffers from too much nitrogenous compounds in the bloodstream. The disorder usually occurs when the kidney is severely damaged and loses 70-75% of its ability. Uremia mainly refers to a buildup of urea in the blood while Azotemia can refer to an accumulation of urea, creatinine and other nitrogenous wastes in blood. The term Azotemia is generally used when the abnormality can be chemically measured but is not acute enough to produce symptoms. But when the condition begins to produce symptoms (generally at the onset of kidney failure), the accompanying ailments are termed as Uremia.
If you suspect yourself to be exhibiting signs of Uremia, call 911 to seek medical care on an immediate basis. It is important for patients to undergo treatment very quickly to avoid permanent damage to the organs.
References:
http://www.localhealth.com/article/uremia
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/245296-overview
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/glossary=uremia
http://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/uremic-syndrome
http://www.healthocrates.com/Complications-of-Uremia-Prevention
The post Uremia appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Fanconi Syndrome appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>What is Fanconi Syndrome?
Fanconi Syndrome, or Fanconi’s Syndrome, is a rare disorder which affects the proximal tubules of the kidney and does not allow the re-absorption of essential minerals and glucose into blood. Rather, such important nutrients get wasted through urine. After the fluid is filtered, the tubule is supposed to process it but it fails to do that. It can manifest in varied forms and cause a range of complications if not checked on time. It gets its name from the Swiss pediatrician Guido Fanconi, who contributed to the explanation of the disease.
It affects humans as well as dogs, although cats are also affected sometimes.
Fanconi Syndrome Prevalence
This disease has an uncommon occurrence, occurring irregularly as it is evident from the reports. Its inherited forms appear early in children. Caucasian children seem to be at risk of having glycosuria and renal acidoses due to this disease. Accurate information, regarding the prevalence of this disease in any specific population in its acquired forms, is unavailable.
Fanconi Syndrome in Dogs
The occurrence of this disease is not restricted to humans alone. Dogs are equally prone to it. Basenji is the breed that is worst affected by the disorder. It also affects other breeds like Schnauzers and Norwegian Elkhounds.
Due to the onset of this condition, functions of kidney tubules get impaired. Instead of reabsorbing minerals, sugars and essential vitamins to be used in the body, it gets wasted through urine. The loss of solutes causes electrolyte imbalance and dehydration in dogs apart from some more problems.
In Basenjis, the disease is hereditary. In some cases, however, it has been found to be acquired. Differentiating between acquired and genetic cases might not be easy.
In the past, chicken jerky treats for dogs were causing serious concern amongst pet owners. The FDA had issued warnings against it for causing Fanconi-like symptoms in them.
Causes of Fanconi’s Syndrome
In general, this disorder affects the functions of the proximal tubules of the kidney instead of a particular channel. It is different from other tubular conditions like Hartnup disease. It can be caused due to a host of underlying disorders. However, the exact cause of this disease may also remain unknown at times. Genetic link has been established in context of this disorder, when it occurs in children. It can be primary or secondary, on the basis of the process of getting it, through parents or other factors like:
Genetic Defect
In children, it may occur due to genetic factors from Cystinosis. Due to mutation in the gene CTNS, functions of cystinosin becomes faulty. It creates intralysosomal accumulation of cystine, which then leads to severe tubular dysfunction of the kidney in the infant. This condition can be found to exist with other hereditary diseases like Lowe Syndrome and Wilson’s disease.
Drugs
This disease can be acquired by adults, due to certain drug formualtions. Drugs which cause mitochondrial dysfunction have full potential to lead to this disease. Chemotherapy drugs or expired tetracycline antibiotics can be potent causes. Gentamicin, cidofovir, and azathioprine are a few other factors. This condition may also arise as side effects of taking certain medicines or due to having them after expiration. It may become pertinent in patients already suffering from kidney damage. Adefovir and tenofovir drugs can cause HIV patients to get this syndrome.
Multiple myeloma and renal transplants are other factors which may lead to acquisition of this disease. Platinum, mercury, lead and other heavy metals are other agents which cause the acquired form of this disease.
Fanconi Syndrome Symptoms
Certain signs and symptoms start showing when amino acids, phosphates, glucose or other important substances do not get absorbed into the blood. The signs of Proximal renal tubular acidoses include:
- Heightened thirst
- Excess Urination
- Dehydration
- Acidoses
- Retardation of growth
- Hypo-phosphatemia, which manifests as osteomalacia in grownups and rickets in children.
- Hypokalemia
- Hyperchlorema
In case of general proximal tubular dysfunction, glucose, protein and phosphates are found in urine.
Fanconi Syndrome Symptoms in Dogs
Some of these common symptoms are noted in dogs:
- Excessive thirst leading to overconsumption of fluids.
- Excess urinating
- Loss of weight
In severe cases, the following problems can be caused:
- Metabolic acidoses
- Electrolyte imbalances
Fanconi Syndrome Diagnosis
Bicarbonate wasting, accompanied by Hyperchloraemic metabolic acidosis, may signal the need for testing the patient for Fanconi’s syndrome. Evaluation is also done when a patient is found to be affected by a certain medical condition related to this syndrome.
To diagnose this disease, a series of tests have to be conducted to assess the excess loss of substances like phosphate and glucose, through urine. Tests are basically determined after consulting the medical history of a patient and performing a thorough physical checkup. Laboratory tests are conducted for checking the levels of amino acids, phosphate, uric acid, sodium, bicarbonate, potassium etc. Blood and urine tests are done for clinical diagnosis.
There seems to be no significance of radiological evaluation in this case. In very rare cases, rickets caused due to mineral wasting may be reported.
Fanconi Syndrome Treatment
The treatment of this syndrome is based on the correct diagnosis of the underlying disease which is primarily responsible for it. Substances that are meant to be utilized by the bloodstream get lost into the urine. Treatment plan basically centers on the replacement of these lost substances comprising electrolytes and fluids that are essential to the body.
Know about some of the ways by which the disorder is treated:
- To normalize levels of serum phosphate, it should be given to the patient in small dosages. To avert symptoms like gastric, the amount is subsequently increased over time.
- IV solutions or oral intake is advised to check dehydration in these patients, which results due to polyuria.
- In such conditions, diuretics are advised to control volume expansion though it leads to loss of potassium. In order to check this loss, supplement of potassium including potassium bicarbonate, acetate and citrate, are given.
- Liver failure may occur due to Wilson disease, for which a liver transplant can be done. It is usually successful in managing the abnormalities resulting in the renal tubes.
- To cure metabolic acidoses, sodium bicarbonate is administered in right doses. Alkali helps in rectifying this problem.
- Replacement of uric acid, amino acids or glucose is not important as they seldom lead to symptoms.
- Enzyme insufficiency also results in this syndrome. Proper diet should be consumed by these patients. Those with Wilson disease should be fed with diet having less copper.
- If cystinosis results in kidney failure, kidney transplant can be done.
- To improve strength of the muscles, carinitine supplements are sometimes administered. However, they may not offer satisfactory results all the time.
Fanconi Syndrome Treatment in Dogs
No definite treatment for this disease exists as yet. Management is the key to endow a healthy life to the affected dog. Dehydration can be checked by making fresh water available to it. To maintain the solute levels, some supplements can also be given. Routine urine checkup for Basenjis can be done to ensure early detection which minimizes chances of kidney impairment.
Fanconi Syndrome Diet and Activities
As already indicated, deficiencies in enzyme often causes different forms of this disease. These enzymes are entrusted with the metabolism of fructose, galactose, tyrosine, phenylalanine and other nutrients. Symptoms associated with the kidneys usually go away when these substances are excluded from the diet. No restrictions have been put on the activities of the patients with Fancony syndrome. Due to the risk of organ failure, muscular strength can be severely affected which certainly restricts stressful physical activities.
Fanconi Syndrome Life Expectancy
The death rate associated to this condition is related with the metabolic abnormalities which can be caused in the patients. It usually does not affect the normal lifespan of an individual if serious kidney failures have not taken place. Studies show that dogs with idiopathic form of this syndrome can have normal lifespan.
Fanconi Syndrome vs Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi anemia (FA) should be distinguished from Fanconi syndrome as both are separate diseases. FA is rare disorder of the blood that causes failure of the bone marrow. Whereas Fanconi’s syndrome is related with the kidneys and children are more susceptible to it.
Fanconi Syndrome vs. Fanconi Bickel Syndrome
Fanconi Bickel syndrome results due to mutation in the GLUT2 gene which leads to carbohydrate metabolism. This rare disease causes kidneys and liver to enlarge by the second year of life, giving rise to life-threatening consequences.
Fanconi Syndrome Prognosis
The prognosis of this syndrome seems to be reasonable. However, the outcome depends on the underlying disease. Along with the treatment plan, the time of diagnosis plays a role in influencing the outcome to a great extent. If it is an acquired form, it will subside within a specific period. However, the inherited ones can lead to organ failures and pose a lot of problems related to growth. Kidney failure, neurologic disorders, visual impairment, ovarian dysfunction, mental retardation and hypotonia are some of the ailments which can be caused due to late diagnosis and enhanced severity. Naturally, it is important to detect and treat the syndrome on an early basis.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fanconi_syndrome
http://www.fanconisyndrome.net/Fanconi-Syndrome-Causes.html
http://www.uspharmacist.com/content/d/health_systems/c/28622/
http://www.healthline.com/galecontent/fanconi-bickel-syndrome
The post Fanconi Syndrome appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Azotemia appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>Azotemia Definition
It is a disorder marked by the presence of unusually high level of compounds such as creatinine and urea that contain nitrogen.
Azotemia Types
Based on its origin or underlying cause, this disease is classified into three types. Although distinct, these types have a few features that are common.
The three main types of this condition are:
Prerenal Azotemia
It is marked by the presence of high amounts of nitrogen-containing compounds in the bloodstream resulting from limited flow of blood to the kidneys. It may also occur as a result of low blood pressure and irregular pumping action of the heart.
Primary Renal Azotemia
It is also referred to as Intra-renal Azotemia. It is characterized by an elevation in the level of nitrogen-rich compounds in blood, usually due to damaged kidneys. This type of the condition may also arise as a consequence of conditions like Pyleonephritis and diabetes.
This form has also been found to result from the use of some drugs, like Mitomycin, Cisplatin and Gentamycin. If taken in excessive amounts, these medications may cause degeneration and degradation of the linings of the kidney. This can automatically heighten the risk of development of this disorder.
Postrenal Azotemia
The disorder leads to an elevation in the level of nitrogen-rich compounds in blood due to obstruction in the pathways within the kidney. This obstruction may occur in the urethra or ureters. In some cases, the blockage may also be observed in the pathways through the bladder.
This type commonly arises due to kidney stones. Development of stones is the cause of obstruction in the kidneys. This form of the disorder also results from enlargement of the prostate gland (in men) and swelling of the kidneys (in both sexes).
All three types of this disorder can lead to a dangerous elevation in the amount of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and various other compounds that are discharged into the urine.
Azotemia Causes
The disorder is mainly associated to inadequate filtering of blood from the body by the kidneys. In healthy individuals, the kidneys expel waste products from the body in the form of urine and filter blood. However, in some people, the organs are unable to remove creatinine, urea and other nitrogenous compounds from the blood adequately. This improper functioning of the kidneys may arise as a result of:
- Low blood pressure
- Irregular cardiac pumping action
- Use of certain drugs
- Kidney stones
- Damage to the kidneys
Azotemia Symptoms
The nitrogenous compounds, the presence of which gives rise to this disorder, are quite toxic in form. Naturally, an accumulation of these substances in the body gives rise to a number of health issues in sufferers.
The symptoms of this condition tend to vary from one sufferer to another based on the type of the disorder that a person is having. Generally, an individual with any of the three forms of the disease suffers from problems like:
- Rapid heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Fatigue, even during rest
- Frequent vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Mental confusion
- Reddish or blackish urine
- Lightheadedness
- Reduced urinary output
There can also be paleness of skin and inflammation of joints. Some affected individuals experience pain and tenderness in the lower back and the abdomen. Inflammation near the elbows and the ankles can be an indication of excessive buildup of nitrogen-rich compounds in the bloodstream of patients.
The condition often has an acute onset. In other words, the symptoms arise all of a sudden although certain cases tend to worsen progressively over a course of several weeks or even months.
Azotemia Diagnosis
A person experiencing more than one symptom mentioned above should get in touch with a physician without any delay. Doctors typically carry out a physical examination of suspected patients and also ask them about the health issues that they are experiencing. In most cases, blood and urine samples are collected and sent to laboratory for analysis. Detection of low levels of nitrogen in urine samples and high levels of BUN in blood samples can confirm the presence of Azotemia.
In some cases, imaging tests are conducted as a part of additional diagnosis. Such exams, like sonograms, can be assistive to physicians in pinpointing the underlying cause of problems in the kidney.
Azotemia Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this disorder should aim at making sure that the symptoms experienced by patients are a consequence of Azotemia and not of other similar conditions like:
- Acute Tubular Necrosis
- Uremia
- Nephritis, Interstitial
- Obstructed Megaureter
- Glomerulonephritis, Chronic
- Chronic Renal Failure
- Glomerulonephritis, Acute
Doctors should also take other factors into consideration that can cause an increase in the levels of creatinine or BUN. These involve:
- Gastrointestinal hemorrhage
- Ketoacidosis
- Large protein meal
- Steroids
- Total parenteral nutrition
Azotemia Treatment
The disorder is commonly treated with the prescription drug Amifostine. This drug helps lower the ill-effects resulting from the use of Mitomycin and Cisplatin and thus, decreases the possibility of the development of Azotemia. However, this treatment option can only be useful when there is risk of development of Primary Renal Azotemia due to the usage of the medications mentioned above.
Other common treatment measures for this disease include use of insulin and administration of loop diuretic drugs. These are useful in preventing the buildup of nitrogenous compounds in the bloodstream of sufferers.
People affected with this disorder are often at risk of being dehydrated. This is countered by hospitalizing such individuals and administering them with intravenous fluids. If an Intrarenal form is detected, physicians should make use of a dialysis machine to take over the process of blood filtration temporarily (to compensate for the improper functioning of the kidneys) and assessing the underlying cause of the renal problems.
Azotemia Prognosis
Many individuals affected with prerenal and postrenal forms of Azotemia manage to recover with drugs that reduce swelling, regulate blood pressure and open narrowed blood vessels. In case medicines fail to remove an obstruction or if there is a complete impairment of the kidneys, operative procedures may be required.
Azotemia in Dogs
In dogs, this condition is manifested by symptoms like:
- Dehydration
- Weakness
- Uremic breath
- Stupor
- Hypersalivation
- Ataxia
- Poor quality of coat
- Uremic stomatitis
The outcome depends on the underlying cause of the disorder. Complete recovery is possible if pre-renal and post-renal forms are effectively managed. However, if acute enough or if left untreated for a long time, the conditions can cause permanent damage to the kidneys.
Azotemia Vs Uremia
Azotemia is often confused with Uremia, although the two are completely distinct conditions. Azotemia is characterized by an increase in the levels of serum creatinine and Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN). Uremia, on the other hand, is marked by the abnormal retention of urine and other waste matters and nitrogenous wastes (urea) in the bloodstream.
Azotemia Complications
All three forms of this disorder can give rise to various complications, which can be life-threatening for sufferers. In the Prerenal form, conditions such as atherosclerosis may arise – characterized by reduced flow of blood to the kidneys. The Intrarenal form is basically kidney failure as the kidneys are impaired in themselves. The Postrenal form arises due to obstructed flow of urine following discharge of waste materials from the kidneys.
It is essential to visit a doctor and seek immediate professional medical care in case of manifestation of more than one symptoms of Azotemia. As aforesaid, this is a dangerous condition that can give rise to fatal complications in sufferers. Naturally, timely treatment and proper management is essential to cure this disorder in time and increase the chances of a swift recovery for patients.
References:
Organ Failure: Deaths from Organ Failure, Heart Failure, Renal Failure, Chronic Kidney Disease, Acute Liver Failure, Paul Tsongas by Books, LLC
The Washington Manual of Nephrology Subspecialty Consult by Steven Cheng and Anitha Vijayan.
The post Azotemia appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Adrenal Insufficiency appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>What is Adrenal Insufficiency?
It is a condition in which the adrenal glands are unable to manufacture hormones in normal quantities, especially Cortisol. The disorder was described for the first time in 1855 by Thomas Addison.
The disorder is abbreviated as AI.
Adrenal Insufficiency ICD 9 Code
The ICD 9 Code for this condition is 255.4.
Adrenal Insufficiency Types
AI is differentiated into three major types:
- Primary AI
- Secondary AI
- Tertiary AI
Secondary AI is found to be the more common type of the disorder.
Adrenal Insufficiency Incidence
The first type of the disorder, Primary AI, affects 1-4 out of every 100,000 individuals. It has been found to affect people of both sexes and all age groups.
What Happens in Adrenal Insufficiency?
The condition arises when the adrenal glands, which are situated above the kidneys, do not manufacture enough steroid hormones – chemicals that regulate the function of organs. This happens when the glands are damaged due to an infection or an underlying cancerous condition. In some cases, the disease may also arise if the adrenal glands are removed during a surgery.
The human body comprises of two adrenal glands, each of which is situated above each kidney. These glands manufacture hormones that are needed by the body for proper functioning. Two important hormones that are produced by this gland are:
Aldosterone
It is also known as Mineralocorticoid and mainly helps maintain the level of salt in the human body. In the absence of this chemical, there can be a severe drop in blood pressure due to dehydration. Unless treated on time, patients may suffer from low salt and potassium levels in the bloodstream. This can result in changes in cardiac rhythm as well as drowsiness and fatigue.
Cortisol
Also referred to as Glucocorticoid, it is important for the body for various reasons. The chemical helps in a number of ways, such as:
- Maintaining sugar levels
- Maintaining blood pressure
- Controlling appetite
- Providing strength to the muscles
- Combating stress
A deficiency in cortisol level may lead to a number of health issues, such as:
- Weakness
- Tiredness
- Loss of weight
- Upset stomach
Such problems can be extremely serious in the absence of treatment and may even lead to the death of sufferers.
Adrenal Insufficiency Causes
Know about the main causes of the various types of AI:
Causes of Primary AI
The majority of cases of this type occur due to Addison’s Disease, an autoimmune condition. Autoimmune disorders are the most common cause of this disorder. The defense system of the body turns against and destroys the tissues of the body itself.
The remaining cases are the result of a tumor of the adrenal gland (adenoma) or a disease known as Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia.
It also occurs when the adrenal glands are damaged in some way. Some other causes of the condition are:
- Infections
- Surgical removal of the adrenal glands
- Inherited conditions
- Bleeding in the glands
Causes of Secondary AI
In healthy individuals, the pituitary gland is able to produce the ACTH hormone which instructs the adrenal gland to produce cortisol. But in people affected with Secondary AI, the pituitary gland fails to secrete and send the Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) hormone to the adrenal glands due to a pituitary disorder. In the absence of the ACTH hormone, the adrenal glands are unable to produce cortisol.
Secondary AI often occurs in people who take steroids for a long time and then stop using them all of a sudden. It can also be a result of:
- Pituitary adenoma or microadenoma
- Sheehan’s Syndrome
- Hypothalamic tumor
Some of the factors responsible for this type are temporary while some are permanent. Taking a few medicines, such as Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone or Prednisone, may temporarily give rise to Secondary AI. The permanent causes may be:
- Damage to the pituitary gland due to radiation or surgery
- Hormonal problems, present at birth
- Infections or tumors in the pituitary gland
Causes of Tertiary AI
It originates as a result of Hypothalamic disease and a reduction in the level of CRF (Corticotropin Releasing Factor).
Adrenal Insufficiency Symptoms
The disease primarily gives rise to health issues like:
- Muscular pain
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Poor appetite
- Loss of weight
- Dizziness while standing
Adrenal Insufficiency Diagnosis
Physicians generally begin the diagnosis of this disorder by observing and asking about the symptoms as well as analyzing the medical history of AI patients. During detection, doctors usually check the level of potassium, sodium, glucose, cortisol and other hormones to understand the underlying cause of the disease. They also look at the pituitary gland or the adrenal glands with the aid of imaging tests, such as:
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- X-rays
- Ultrasound
The medical exams that can be necessary for detection of this disorder are:
- Short ACTH Stimulation Tests
- Prolonged ACTH Stimulation Tests
- ACTH Secretion
- Cortisol Secretion
- CRH Stimulation Test
Adrenal Insufficiency Treatment
Doctors generally rely on medications for curing this disorder. Patients are advised to take a cortisol replacement through oral means, one or two times a day. Some other commonly prescribed drugs for this disorder include:
- Prednisone
- Hydrocortisone
- Dexamethasone
Those deficient in the hormone aldosterone should take a type of medications known as Fludrocortisones. Patients tend to feel better when they take a proper dose of the drug. These are steroid medicines and can give rise to various side-effects, such as:
- Acne
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Weight gain
- High blood pressure
However, it is Synthetic glucocorticoids that are mainly used for the treatment of this disorder. These must be taken every day, in proper dosage and at the right times, to maintain bodily equilibrium. People who are affected with the disease (and are sick or suffering from physical stress) should take glucocorticoids to ease their stress levels. However, one needs to consult a good doctor about the requirement of having proper glucocorticoid replacement if he/she is:
- Vomiting
- Sick with fever or diarrhea
- Having major dental work
- Undergoing surgery
A person suspected of having this disorder should be admitted to a hospital on an emergency basis. If possible, the patient should be administered a saline infusion to stabilize his/her condition before shifting. Patients who have been conclusively detected with AI need to be treated by an adrenal hormone replacement therapy, as advised by an endocrinologist.
Adrenal Insufficiency Complications
Some of the possible complications of this disorder include:
Pregnancy issues
Pregnant women who are suffering from the disease may experience nausea or vomiting in the early stages of their maternity. If this interferes with an oral intake of medicines, injecting hormones into the body of affected women may become necessary.
Illness
If patients suffer from other ailments along with AI, the oral dosage of glucocorticoid may need to be adjusted to resemble the normal adrenal gland response to this stress. Severe injury or fever may necessitate triple oral dosage. Once patients recover from the stressful situation, dosage may be returned to normal to maintain levels. Those affected with AI should have a proper knowledge of how to increase dosage of medicines during stressful periods. If diarrhea, vomiting or acute infections arise, medical attention should be sought on an immediate basis. This is due to the reason that such health issues may precipitate Addison’s Disease.
Surgery
Cortisol is a stress hormone. Due to this reason, individuals affected with Chronic AI (who require any surgery involving general anesthesia) must be treated with saline and glucocorticoids. Intravenous treatment usually starts and continues until patients are completely awake and are able to take the medicine orally. The dose of the medication is restored to that of pre-operative stage as the patient recovers.
Patients who are not presently taking glucocorticoids but have taken the drugs for a long time until some months before, should inform their physician prior to surgery. Such individuals may have enough ACTH to sustain normal events but may require intravenous treatment to cope with the stress resulting from operation.
Physical stress, resulting from surgery, ailments, accidents or infections, may abruptly worsen the symptoms of AI. A severe condition, known as Adnreal crisis, may occur as result. If left untreated, the problem may even lead to the death of patients. It mainly arises in people affected with Primary AI.
Some of the major warning signs of AI are:
- Diarrhea
- Low blood pressure, leading to loss of consciousness
- Acute nausea
- Vomiting
- Abrupt pain in the legs, abdomen or back
During an adrenal crisis, you need to be immediately injected with Glucocorticoids (medications that replace cortisol). You also need to visit a hospital to receive further treatment.
Adrenal Insufficiency Management
You should inform your friends and family members about what they need to do in case of an adrenal crisis. You should also always wear a medical alert tag or bracelet. The tag should read “Steroid Dependent” or “Adrenal Insufficiency” based on your health status. You may also include any other disorder that you may have, such as “diabetes,” to help medical professionals be more informed in case of a medical emergency. You should also carry an ID card that should contain information about your contact number and address, your physician and a list of medicines that you are using currently.
You should also remember to carry an extra set of medicines while you are travelling. In case you are delayed for some reason, these might come in handy. You should also keep a set of clean syringes and vials of medicines that you must inject yourself. You may find them essential in case you have been severely hurt or not close to a hospital or emergency medical care facility. These should be properly labeled with your doctor’s prescription.
Adrenal Insufficiency Prognosis
The outcome of the disorder is quote good in most AI patients who are treated and monitored properly. Most affected individuals are found to have a normal life expectancy and lead an active life. Children affected with AI who are cured and managed properly can have a normal development and have puberty without experiencing any difficulties.
Adrenal Insufficiency Support Groups
AI patients or their family members can approach any of these organizations for more information about the disease and also to receive proper support:
Pituitary Foundation
Email id: [email protected]
Website: http://www.pituitary.org.uk
Telephone: 0845 450 0375 (Mon-Fri: 9AM to 5 PM)
Addison’s Disease Self-Help Group
P.O. Box 1083
Guildford
Surrey
GU1 9HX
E-mail: [email protected]
Website: http://www.addisons.org.uk
If you suspect yourself to be an AI sufferer, get yourself diagnosed on an immediate basis. It is never advisable to ignore treatment when you have a disease that has a potential to worsen as much as AI. It is recommended that you get yourself tested and treated as soon as possible, if you feel you are suffering from Adrenal insufficiency.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_insufficiency
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/adrenal-insufficiency-addisons-disease-beyond-the-basics
http://www.drkaslow.com/html/adrenal_insufficiency.html
http://endocrine.niddk.nih.gov/pubs/addison/addison.aspx
The post Adrenal Insufficiency appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Definition
It is a common kidney disorder characterized by disturbed water-balance in the body. In this type of ailment, a small defect in the tubule of the kidney causes a person to release large amounts of urine. Such small tubes remove water in large quantities which dehydrates the body and causes excessive thirst, especially in hot weather. This disorder is related to a hormone, known as ADH- Antidiuretic Hormone. Though Diabetes Insipidus Nephrogenic is a type of diabetes mellitus, both the disorders have separate reasons for their cause.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus ICD9 Code
The ICD9 code for this condition is 588.1.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Incidence
NDI is an uncommon ailment. Compared to its hereditary form, Acquired Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus occurs more frequently among the patients. Approximately it is found to arise in 1 in every 25000 inhabitants of the US.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Types
This progressive disorder can be categorized into two major forms:
Picture – Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
- Congenital NDI
- Acquired NDI
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Causes
NDI occurs when the small tubes of the kidney fail to respond to a chemical compound in the body, known as ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone, also known as Vasopressin). The main function of this hormone is to send special signals to the kidney. In people with NDI, the kidneys discharge large amounts of water into the urine making it more diluted.
The cause for the development of this disorder can depends on the type of the condition that a person suffers from.
Acquired NDI
The main causes for its occurrence are:
- Hypokalaemia
- Idiopathic
- Hypercalcaemia
- Post-obstructive uropathy
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Drugs (such as Foscarnet, Clozapine, Antifungals, Antineoplastic agents, Lithium2, 3 and Antiviral medications)
Congenital NDI
It is triggered by:
- Irregular NDI, along with intracerebral calcification and mental retardation.
- X-linked mutation in the V2 ADH-receptor gene.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Symptoms
Patients suffering from NDI have an uncontrollable thirst for water, particularly ice water. The urine production in such patients is around 3-15 liters per day.
A few patients try to avoid drinking large amounts of water to evade excessive urination. Such individuals suffer from severe dehydration due to lack of enough fluids in their body. The symptoms that indicate the presence of NDI include:
- Sunken eyes
- Dry mucous membranes
- Sunken fontanelles in newborns
- Dry skin
There are a number of other symptoms that can occur due to the absence of adequate fluids in the body. These problems, which serve as warning signs for patients and indicate the presence of NDI to physicians, include:
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Weight Loss
- Muscle pains
- Headache
- Fast heart rate
- Low body temperature
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis of this syndrome is essential for doctors to determine the intensity of the condition and provide patients with appropriate treatment for it. The necessary diagnostic tests for NDI include:
- Urine specific gravity
- Urine 24 hour volume
- Urine concentration test
- Serum Sodium
The above-mentioned tests help display a number of symptoms characteristic of the disorder, such as:
- ADH level
- High urine flow, irrespective of the amount of fluid consumed.
- Low urine osmolality
- High serum osmolality
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Treatment
The main objective of treating NDI patients is to monitor the level of fluids in their body. This disease can be successfully treated by drinking large volumes of water. The fluid intake should be equal to the total amount of urine produced in the body. Intake of water should be accompanied by a healthy low sodium diet.
In a few cases, this disease may arise due to certain medicines and drugs. Such medications should immediately be stopped after consulting a doctor, to avoid further complications arising out of this disorder.
Medicines, such as Hydrochlorothiazide, may help reduce the occurrence of NDI symptoms and prevent any damage to the urinary tract due to dilatation. This is done by minimizing the production of urine by up to 50% through hydrochlorothiazide drug therapy. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as Indomethicin, can also be used to enhance the concentration of urine in patients.
Dehydration, caused by NDI, can be cured by drinking lots of water. During extreme dehydration, intravenous fluids are administered to affected individuals to stabilize their condition.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Prognosis
If enough fluids are consumed and the electrolyte balance is maintained, NDI does not have any severe impact on the water balance of the body. Not drinking enough fluid can make a patient suffer from multiple physical complications.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Complications
The numerous complications arising in an NDI affected patient, due to improper treatment or absence of cure, include:
- Dilation of the ureters and bladder
- Severe dehydration
- High blood sodium (hypernatremia)
- Shock
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Risk Factors
The presence of a number of other factors can increase the risk of having NDI. These include:
Heredity
A genetic defect can make a permanent change in the ability of the kidney to make the urine concentrated.
Being male
The disorder is found to afflict males more than females.
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Prevention
There is no possible option to prevent the occurrence of Congenital NDI. In a few cases, however, the acquired form of the disorder can be prevented from worsening with medicines under the guidance of a health care provider.
NDI is a rare but a complicated diabetic disorder. Unless managed in time, the condition can destabilize the balance of water in the body and give rise to complications. If you or any of your family members experience excessive thirst or any other symptoms of this disorder, consult a professional medical care provider immediately.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephrogenic_diabetes_insipidus
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001540/
http://www.patient.co.uk/doctor/Nephrogenic-Diabetes-Insipidus.htm
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/nephrogenic-diabetes-insipidus
The post Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Proteinuria appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>Proteinuria refers to the medical condition in which the urine of a patient has very high abnormal content of proteins.
This condition in most cases develops as the result of another underlying body condition that affects the functioning of the kidneys.
What are proteins?
Proteins refer to the body building blocks including the bones, hair, muscles and nails.
The proteins are also needed by our bodies for very important functions and purposes including the protection from infection, helping in blood coagulation as well as maintaining the circulation of the proper amounts of fluids in the body.
What happens so that a person can develop Proteinuria?
In the healthy person, as the blood passes through the kidneys, it is completely filtered of all the waste products which are then eliminated through urine while leaving the vital elements like proteins in the blood so that they can continue to circulate in the body and perform the already stated vital body functions.
Unless the kidneys are damaged, most proteins will be retained in the blood because they are generally big and they cannot pass through the filters of the kidney (glomeruli). However, the small sized proteins like the globulin and the albumin can pass through the filters of the kidney and so they can be found in the urine of the healthy person.
The function of albumin in the body is retaining of fluids in the blood. It soaks up fluid from the tissues of the body. Proteinuria will thus arise when there is a problem of the filtration of blood such the large proteins pass through the glomeruli and they are thus eliminated in urine as waste.
Proteinuria in children
Children and teens may develop orthostatic proteinuria that does not necessarily signify problem of kidneys. This proteinuria in children develops because of the activities of the kid of standing for long hours during the day.
In most cases, benign orthostatic proteinuria in children does not need medication but the child should be put on the recommended diets that improve the functioning of kidneys like drinking a lot of water and taking a lot of fruits and vegetables.
What are the causes of Proteinuria?
There are various factors which acting singly or simultaneously may cause or aggravate the problem of proteinuria. Generally speaking, any condition that may lead to the inflammation of the kidney filters (glomeruli) can lead to development of proteinuria. In medical terms inflammation of the glomeruli is referred to as nephritis or glomerulonephritis.
These factors include
Infection of the kidneys/ Urinary tract: Infection of the kidneys is in most cases caused by bacteria, yeast, fungi or even virus.If proper medication for the infection is not sought as soon as possible, the glomeruli may become very inflamed leading to proteinuria.
Chemotherapy Side Effects: drugs like the Streptozocin can cause proteinuria even when they are taken as recommended. In the US, this drug is approved by the FDA for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic islet cells cancer. It has a very high toxicity risk in that it directs affects the pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin. Generally speaking, Streptozocin rarely cures the metastatic pancreatic islet cells cancer so it is only used in those patients whom the cancer cannot be treated by surgical procedures.
Some Biologic therapies: Some therapies like Interleukin-2 (IL-2) can lead to glomeruli problems leading to this problem. Interleukin-2 is approved in the FDA for use in treating Renal Cell Carcinoma that is metastatic. Note that Il-2 is not just a drug; it is a natural component of the body immunity system. It fights cancer by simulating growth of body immunity. The IL-2 drug side effects in the kidneys may lead to proteinuria.
Chronic diseases and conditions: The direct effects and symptoms of some chronic diseases or conditions may cause problems of the kidneys. The side effects of the medications that are used to treat these diseases and conditions may also cause serious side effects to the kidneys leading to proteinuria.
These diseases and conditions include:
High blood pressure: Elevated levels of blood pressure may interfere with the proper functioning of the kidneys. The kidneys may become inflamed and the end result will be development of proteinuria.
Diabetes: Diabetes refers to the condition in which the body is unable to regulate the levels of sugar in the blood. Diabetic patients pass out urine that is especially very high in albumin. The elevated and unregulated levels of blood sugar may lead to severe proteinuria and kidney failure.
Multiple myeloma. This refers to certain cancer that affects the plasma cells. The plasma cells are a type of the body white cells. This condition can cause the presence of M-protein in urine. The protein that presents in urine as a result of this condition is also referred to as Bence-jones protein or myeloma protein. Proteinuria associated with Bence- jones protein is called Bence- jones proteinuria.
System Lupus Erythematosus: this is a condition that occurs when the body immunity system for reasons that are not clearly known begins to attack the healthy body cells. This causes inflammation of various body organs among them the kidneys. Inflammation of the kidneys because of this condition (that is medically referred to as lupus nephritis) may cause proteinuria.
What is Orthostatic proteinuria?
Postural or orthostatic proteinuria refers to the increased urinary protein excretion during day time related to upright position and increased activity.
What is Tubular proteinuria?
Tubular proteinuria occurs due to the failure of re-absorption of low molecular weight proteins by proximal tubules.
What is Nephrotic range proteinuria ?
When more than 3- 3.5 mg of protein is excreted from the body in 24 hours, it is referred to as nephrotic proteinuria.
What is the latest news on the recent medical research on proteinuria?
The recent medical research tends to show that the type and level of proteinuria; that is, whether the proteins in the urine is albumin only or other proteins, strongly determines the kidney damage extent. It also determines whether the patient is at the risk of developing kidney failure that is progressive.
Recent research also tends to show that the people that suffer from this condition have an active cardiovascular disease or they are at risk of developing it in the future. The damage of the blood vessels can lead to the failure of the heart, kidney failure or stroke.
A study that was conducted in 1996 under the sponsorship of the American National Institutes of Health (NIH) came to the conclusion that proteinuria is a precursor to the development of progressive kidney failure in those patients suffering from type II diabetes. In the view of these findings, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and National Kidney Foundation (NKF) advise that all people suffering from type II diabetes should undertake very frequent proteinuria testing.
What is the medical advice for proteinuria patients?
Doctors advise that once you are diagnosed with proteinuria you should seek the proper advice and guidelines on what to do and what not to do so that you prevent any further development or complication of the proteinuria condition itself as well as the other underlying conditions that caused it.
Various health organizations also recommend that people that are at risk of the disease should have the levels of proteins in their urine checked very often. Detection of the proteinuria condition early enough before it has progressed can help prevent kidney failure.
Who is at the risk of developing proteinuria?
People that are HYPERTENSIVE, DIABETIC or those who suffer from other chronic conditions that have damage to the kidneys are at very high risk of developing proteinuria. Diabetes is the leading cause of proteinuria in the US. Diabetes patients should be very vigilant and watch out for the early symptoms of the disease. Hypertension is the second leading cause of kidney failure that may lead to severe proteinuria.
Medical research shows that AFRICAN AMERICANS are higher risk (in fact about 20 times) of developing kidney problems that lead to proteinuria than the Native Americans. The African Americans can develop proteinuria even when there blood pressure is not very much elevated or even when the blood sugar levels are not extremely unregulated.
Other people that are at high risk include:
- Overweight and obese
- The elderly people
- Hispanic problems
- American Indians
- Pacific Islander Americans
- The people that are related to people that suffer from kidney problems in general and proteinuria in particular
What are the symptoms of proteinuria?
Unless there has occurred damage to the kidneys, people with an active proteinuria condition may not present any proteinuria symptoms and they may not actually notice that they have any problem, of the kidneys.
When the proteinuria symptoms present, they are in most cases be accompanied by the symptoms of underlying conditions. If for example the proteinuria is caused by diabetes, it will be accompanied by diabetes symptoms like blurred vision, headache, fatigue, body weakness, frequent urination, thirst, hunger and such related diabetes symptoms. If the proteinuria is caused by high blood pressure (HBP), the patient may experience headache, dizziness, vertigo, sweating and such related HBP events.
At its advanced stages, proteinuria causes urine to appear foamy. Because of the excess removal of the proteins from the body, the patient may also begin to experience and show symptoms of swelling of the abdomen, hands, feet and face.
These proteinuria symptoms do not conclusively show that one is suffering from proteinuria. They may be experienced because of only the underlying disease or condition. Undertaking Urine or kidney function test is the surest way of confirming or ruling out proteinuria.
Effect of Proteinuria in pregnancy
Proteinuria in pregnancy causes a serious condition called proteinuria preeclampsia, where the pregnant woman becomes hypertensive, with associated symptoms like swelling of feet, hand and limbs.
Diagnosis of proteinuria
To confirm or rule out proteinuria, the doctor will need to conduct:
URINE TEST: This is the simplest test for proteinuria. The urine of the patient is collected and then placed in a container. The tester will use paper that is chemically treated to perform the treat. It will change color if there is too much protein in urine. More specific tests are required to find out the smaller amounts of proteins in the urine.
KIDNEY FUNCTION TEST: The doctor will check for the levels of urea nitrogen and Creatinine in the blood. If the levels of these chemicals is very high then that indicates that the kidneys are not working properly or they have failed. Healthy kidneys completely remove these chemicals and substances from blood. The doctor may also conduct an X-ray or ultra sound of the kidneys to ascertain the extent of damage.
What is the treatment for proteinuria?
Since proteinuria is a condition that develops as result of another condition or disease in the body, it is treated by controlling or treating that which is causing or aggravating it. The proteinuria treatment will thus involve the diagnosis of what is exactly causing the condition.
If the proteinuria is as a result of urinary tract infection (UTI), then the doctor may prescribe antibiotics if the UTI is caused by bacteria. If the cause of proteinuria is diabetes, the doctor may prescribe insulin injections or other oral diabetes medications.
The doctor may also prescribe medications for lowering blood pressure if the cause of proteinuria is elevated blood pressure. The proteinuria treatment thus depends on the underlying condition or disease.
What are the recommended proteinuria diets for patients?
All proteinuria patients are advised to strictly follow the RENAL DIET that is very low in protein, potassium, sodium and magnesium. In addition to this, they should also limit the intake of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates increase the levels of sugar in the blood and that may increase the diabetes complications. The carbohydrates are also in most cases converted in fats and so they may increase the proteinuria symptoms and complications.
The patients should avoid artificial sweeteners, caffeine, sugar and other sugary and sweet beverages and drinks. They should also avoid taking junk foods; this is to avoid the increase in weight and obesity that has been proven to increase the proteinuria risks and complications. The proteins should be taken in limited quantities.
The proteinuria patients are further advised to take lots of fruits and vegetables. The fruits and vegetables are very rich in natural fiber and they help boost body immunity and the functioning of body organs. The patients should also limit or avoid the intake of the oils and the saturated fats.
References:
http://www.aafp.org/afp/20000915/1333.html
http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/pubs/pdf/proteinuria.pdf
The post Proteinuria appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Hyperphosphatemia appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>What is Hyperphosphatemia?
It is a condition marked by an unusually high level of phosphates in the bloodstream. Generally, the phosphate level is significantly higher than the usual range of 0.84 to 1.58 mmol in each liter of serum.
Hyperphosphatemia Symptoms
Some of the main symptoms of Hyperphosphatemia are :
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism (SHPT)
It makes the Parathyroid glands secrete excessive Parathyroid hormone (PTH) as a response to Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels in bloodstream) as well as associated hypertrophy of the glands. This condition is particularly seen in individuals suffering from Chronic Renal Failure. The hormone mobilizes calcium from the bones and increases its concentration in the bloodstream. If this condition persists, it may result in discomforting symptoms like
- Pain and fractures due to acute bone weakness
- Crystallization of calcium and phosphate in the heart, wall of the vessels and in the bloodstream
- Acute arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- Poor circulation
- Strokes
- Heart attacks
Renal Osteodystrophy
It is a bone disorder that is marked by fibrous degeneration and softening of bone as well as the development of cysts in bone tissue. It results from Chronic Renal Failure.
Ectopic calcification
It refers to a pathologic calcium salt deposition in the tissues.
Hyperphosphatemia may also lead to the accumulation of crystals in the skin of a person, resulting in acute itchiness. Acute hyperphosphatemia usually result in the sudden development of problems like :
- Tetany – It is a neurological syndrome that is marked by seizures as well as cramps and twitching sensations in the muscles.
- Hypocalcemia – It is characterized by unusually low amount of calcium in the bloodstream of a suffering individual.
- Ectopic or metastatic calcification – It results from pathologic calcium salt deposition in tissues that were previously undamaged.
Hyperphosphatemia Causes
Some of the main causes of Hyperphosphatemia are:
Impaired kidney function
Defective function of the kidneys is one of the most common causes of this disorder. An impairment of kidney function can make it difficult to eliminate certain salts from the bloodstream.
Hypoparathyroidism
This disorder is characterized by reduced level of Parathyroid hormone (PTH). Usually, this hormone suppresses reabsorption of phosphate by the kidneys. In the absence of enough PTH, the reabsorption of phosphate is higher.
Chronic renal failure
A chronic failure of the kidneys results in higher retention of phosphate in the human body. This leads to Hyperphosphatemia.
Osteomalacia
This condition is supposed to arise from insufficient vitamin D in the diet as well as other factors like malabsorption, renal disorders or lack of sunlight. It may also be a causative condition for this disorder.
Drugs
Oral Sodium Phosphate solutions are used to prepare bowels of children prior to Colonoscopy. Oral intake of these solutions can lead to the development of Hyperphosphatemia.
Phosphate levels can also increase due to use of certain medications and some childhood disorders. Too much phosphate may also lead to an imbalance of electrolytes in the bloodstream. This occurs as the body finds it difficult to correct the problem rapidly with fresh electrolytes being introduced constantly.
Hyperphosphatemia Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this condition involves differentiating it from discomforting symptoms arising out of
- Imbalance or excess in diet
- Toxins
- Lipemia
- Icterus
- Hemolysis
- Physiologic hyperphosphatemia in animals of young age
Hyperphosphatemia Treatment
The first step in curing Hyperphosphatemia is to determine the condition causing it. Once the cause is diagnosed, cure or management can begin while caregivers work on bringing stability in the electrolyte levels of the patient. This can be done by encourage elimination of waste products through the kidneys by using a diuretic and supplemental water.
Patients having this condition as a result of kidney injury can be cured by reducing the absorption of phosphate from gastrointestinal tract as well as lowering its intake. Sufferers must avoid food items that are rich in phosphate content. Antacids comprising of calcium must be taken along with meals to make the calcium bind to the intestinal phosphates and not get absorbed. Prolonged stimulation of parathyroid glands can lead to Hyperparathyroidism, making surgical removal of glands necessary.
Treatment for acute Hyperphosphatemia involves administering phosphate binding salts such as Aluminum, Magnesium and Calcium. However aluminum is not administered in patients with renal failure. This is because there can be a deposition of Aluminum. It is preferable to use Calcium in such cases.
Reduced dietary intake of phosphate and Phosphate Binders can help avoid increase of this salt in the bloodstream. Moderate exercise and drinking lots of fluids can help one get rid of imbalance in the bloodstream by utilizing excess phosphates. If these methods are found inadequate in improving the situation, doctors may use binding agents.
Hyperphosphatemia Prevention
Individuals suffering from disorders causing this condition are at high risk of suffering from Hyperphosphatemia. They should be regularly screened with the aid of blood tests and a complete electrolyte panel. This can allow care providers to detect problems quickly, before non-treatment results in complications. This disease may also be diagnosed while a routine blood panel is being carried out for identifying other conditions.
Hypercalcemia and Hyperphosphatemia
An overactive parathyroid gland (Hyperparathyroidism) is often responsible for the development of both Hypercalcemia and Hyperphosphatemia in the same individual. Hyperparathyroidism results in excessive secretion of Parathyroid hormone which results in an unusually high level of calcium in the human bloodstream. This can have an impact on many systems of the human body, particularly resulting in Osteoporosis and Bone Resorption.
Vitamin D toxicosis is also responsible for inducing both Hypercalcemia and Hyperphosphatemia.
Hyperphosphatemia is seen as serious when the level of Phosphate is greater than 7 mg/dL in children as well as adolescents and 5 mg/dL in adults. In a normal adult, the range is 0.81-1.45 mmol/L (2.5-4.5 mg/dL). Phosphate levels are 30% higher in children and 50% greater in infants due to effects of growth hormone.
References:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/767010-overview
http://www.unitedhealthdirectory.com/diseases-and-conditions/hyperphosphatemia/
http://www.ccmtutorials.com/misc/phosphate/page_08.htm
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/causes-and-treatment-of-hyperphosphatemia
The post Hyperphosphatemia appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>The post Flank Pain appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>Flank Pain Definition
Medical researchers define flank pain as a discomforting sensation arising in the flank. Flank refers to the region lying between the hip and the last rib.
Pain in the flanks may be any of these two types:
- Unilateral – Pain in right or left flank
- Bilateral – Flank pain on both sides
Flank Pain Location
The pain arises in the flank, the region of the body that is above the Ilium and below the rib. Usually, it begins in a posterior fashion or in the middle part of the axillary line. It results from the stimulation of specific nerve endings upon stretching of the renal capsule or ureter.
Flank Pain Causes
Some of the main causes of Flank pain are:
Kidney problems
Pain in the flanks may arise due to diseases and other problems affecting the kidney, such as kidney stones, renal infection (Pyelonephritis), polycystic kidney disorders, abscesses and renal infarction. In some cases, flank pain may be a symptom of cancerous conditions in the kidney. In case of kidney cancer, there can be blood in the urine along with flank pain.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
Approximately 10% patients of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) are seen to develop painful symptoms. The aneurysm is supposed to be a result of stretching or trauma of the nerve plexus surrounding the celiac axis as well as other aortic arterial branches that stimulate the nerves. The aneurysm can lie immediately beside the ureter and give rise to Hematuria from local ureteral trauma or irritation.
Back ailments
A pain in flanks may also arise in case of a traumatic strain in the back muscle due to intense physical activity. A herniated or slipped disc can put pressure over the adjoining regions and result in origin of pain on one side of the human body.
Patients of acute back conditions, such as Spinal Arthritis, frequently experience pain between the back and the abdomen.
Pyelonephritis
This condition is generally characterized by a pain that is milder in intensity than a typical renal colic ache. The condition is characterized by highly discomforting symptoms, such as
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stiff neck
- Headache
The condition also gives rise to tenderness in the flanks that is often more acute in intensity than in renal colic patients.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Aches in the flank area may also arise due to problems in the gastrointestinal system, such as
- Pancreatitis
- Stomach ulcers
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Food poisoning
The problem may also originate due to stomach infections such as Diverticulitis that result from entrapment of bacteria in the colon. Other digestive problems may also lead to pain in flanks. In such cases, pain is usually accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting.
Gynecological problems
In women, pain in the flanks may arise due to presence of an Ovarian Cyst.
Renal abscesses
This condition usually gives rise to pain that is more intense than Pyelonephritis patients can experience. This is due to the fact that inflammation and edema stretches the renal capsule to an even greater extent. In some cases, it gives rise to palpable lumps on flanks. This may be accompanied by other symptoms like irritation of the diaphragm.
Blood clots
Sometimes, blood clots can obstruct the uterus and become responsible for an acute renal colic attack. These blood clots may arise due to underlying medical problems like
- Renal pelvis tumors
- Parenchymal tumors
- Hemophilia
- Glomerulonephritis
- Sickle cell disease
- Angiomyolipoma
These can also originate as a consequence of percutaneous renal biopsies. Use of streptokinase medications has been found to produce successful results in some cases.
Herpes Zoster Infection
The Herpes zoster is a type of virus that gives rise to a viral infection. A Herpes infection can give rise to a mild burning pain, generally in the region surrounding the flank. Generally, the pain arises prior to the occurrence of skin changes characteristic of this infection. With time, vesicles arise over the affected region, making it possible for doctors to easily diagnose the condition.
Treatment of this viral infection depends on the symptoms, with antiviral agents and analgesics being the medications of choice.
Radiculitis
This condition arises due to trauma (injury) of the roots of the lumbar thoracic nerve. It can result in pain in the flanks. A pain characteristic of this condition may also develop due to a trauma to the costovertebral junctions. The pain is similar to Renal Colic when there is pain in the 10th, 11th or 12th ribs. The pain arising due to this disorder is is often found to be an acute one. An injury or scarring of the intercostal nerve can be the main source of the pain.
Flank Pain Symptoms
The condition, as the name indicates, is characterized by a pain in the flank region. The ache usually worsens with movement. The intensity of pain varies from moderate to acute and generally depends on the underlying causative condition. The side where the pain is felt indicates which kidney has been affected. A right flank pain indicates a problem in the right kidney whereas left flank pain suggests a pain in the left kidney. A minor cause may give rise to a moderate pain that can advance with increased body movements, usually unaccompanied by other signs. In acute cases, the pain may be acute and piercing without showing any sign of enhancement or reduction with movements. The pain may spread in a downward direction and result in testicular pain (in men) and labial pain (in women). Acute flank pain may be accompanied by other discomforting symptoms, such as
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Muscular tenderness
- Nausea
- Pain and discomforts while passing urine
- Vomiting
- Pink or Red Urine (due to small amounts of blood in the urine)
Flank Pain Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this problem is usually done by physical examination that involves medical tests like:
- Abdominal CT scan
- Cytoscopy
- Retrograde ureteropyelography
- Ultrasound examination of the abdomen or the kidney
- Intravenous pyelography (IVP)
- Lumbosacral spine x-ray
- Urine Culture
- Urinalysis
- Voiding Cystourethrography
The medical history of the patient is taken into account white determining the cause of the painful symptoms. Physical examination helps in diagnosing the exact cause of the pain. Laboratory tests such as X-rays and blood test are also conducted.
Flank Pain Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this disease involves distinguishing it from other disorders, such as:
- Diarrhea
- Chronic Digestive Conditions
- Appendicitis
- Food poisoning
Flank Pain Treatment
Treatment for flank pain, which usually depends on the underlying cause, includes:
- Hydration
- Analgesics (pain medications)
- Antibiotic medicines
Doctors recommend patients to get enough rest for treatment of mild flank pain. This should be followed by exercise and physical therapy for complete cure. Patients of Spinal Arthritis are prescribed anti-inflammatory medicines. Antibiotic medications are used for treatment of infections in the urinary tract and kidneys. Analgesics (pain relieving medicines) and high intake of fluids can help in case stones are diagnosed in kidneys.
In case of acute flank pain, immediate hospitalization may be required.
Flank Pain Prevention
Pain in the flanks can be prevented by following a healthy lifestyle which involves:
- Daily intake of healthy foods
- Drinking enough fluid to keep the body hydrated
- Exercising regularly
Right Flank Pain
Pain in the flank in the right side of the body may arise due to infections in the urinary tract and the bladder, kidney problems as well as gynecological disorders. Individuals suffering from arthritis or diabetes may also suffer from this pain. It may also originate due to muscle pull or injury in the lower back area. In women, Ovarian Cyst development may be one of the major causes of right flank pain.
Left Flank Pain
The flank in the left side of the human body can pain due common problems like muscular spasms or severe cases of infections like acute Pyelonephritis. Gastrointestinal Disorders, Kidney Problems, Urinary Tract ailments and Diverticulitis may also give rise to this pain. If stones develop in the left kidney, there can be a left-sided flank ache in sufferers.
Lower Left Flank Pain
Pain in the lower left region of the flank is usually dull and stabbing in nature. It can arise due to problems in the viscera or the internal organs of an individual. Pain may also originate due to structures external to the abdomen. Lower left pain maybe harmless or acute. Lower abdominal pain that arises rapidly may be a sign of a serious underlying condition and can be treated by an experienced medical professional.
Left Flank Pain after Eating
Many individuals experience a stabbing pain in the left side of the abdomen just after having food. The pain can be acute enough to make it difficult to perform daily activities. Patients usually feel an overwhelming urge to lie down while moving about.
The pain may arise due to problems in organs like gallbladder, pancreas, appendix and liver. CT Scan, Ultrasound examinations, Endoscopy, Colonoscopy and blood or urine tests can help diagnose these problems.
Intermittent Flank Pain
Many patients of Irritable Bowel syndrome (IBS) are found to suffer from intermittent pain in the flanks. The problem can also arise in sufferers of Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK). Pain may arise during waking hours as also in times when a patient is asleep. Dull pain may cause discomforts while sharp flank ache may actually disrupt sleep and compel sufferers to sit up. Flank muscle pain due to trauma encountered during sports activities may also be a cause of this problem.
Chronic Flank Pain
Chronic cases of this condition may arise due to persisting kidney problems like:
- Kidney stones
- Kidney abscesses
- Kidney tumors
- Kidney cysts
- Kidney Infection (Acute Pyelonephritis)
- Glomerulonephritis
The causes of flank pain may be different in men and women. In men, pain in the left flank may arise due to problems like :
- Spermatic cord disorders
- Testicular disorders
- Sexually transmitted diseases (such as Gonorrhea)
Left flank pain in women may be a result of problems like:
- Mid-cycle pain (Mittleschmerz)
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
- Miscarriages
- Ovarian Cysts
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Endometritis
- Ectopic pregnancy
In both men and women, painful symptoms may arise due to other reasons like :
- Constipation
- Splenic flexure syndrome
- Colon Cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease (such as Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s disease)
- Diverticulitis
- Ischemic/Microscopic colitis
- Diverticulosis
- Appendicitis
- Infected or enlarged spleen
Severe colicky flank pain that radiates to the groin, scrotum and the labia may be a result of Acute Renal Colic. Renal Colic pain commonly arises when a small stone passes down the ureter, the tubular structure connecting the kidney to the bladder.
Flank Pain During Pregnancy
Many pregnant women are also found to suffer from pain in their flanks during pregnancy. Approximately 200,000 pregnant women in the U.S have been estimated to have this problem every year. This can occur due to the presence of conditions like
- Ureteral Obstruction
- Ovarian Tumor
- Renal Calculus
- Ovarian Torsion
- Placental Abruption
- Strain or rupture of the abdominal muscle
Flank Pain ICD 9 Code
The ICD 9 code for flank pain is roughly 789.07, which falls under “other symptoms involving abdomen and pelvis”. However, this does not specify the exact point of origin of the pain.
If you are suffering from a persisting pain in the flanks, immediately get in touch with an experienced health-care provider. A good doctor will ascertain the underlying cause and treat the condition accordingly. An early diagnosis and treatment can help you make an early recovery from the disorder. So if you are having flank pain, do not delay treatment.
References:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1958746-overview
http://ad2004.com/Biblecodes/Hebrewmatrix/colic.html
http://www.healthcentral.com/chronic-pain/h/chronic-flank-pain.html
http://www.medhelp.org/posts/Urology/Flank-pain-only-during-sleep-upon-waking/show/3538
http://stomach-pain-after-eating.net/stomach-pain-after-eating-lower-left
The post Flank Pain appeared first on Prime Health Channel.
]]>