Mastoiditis is an acute rare condition of the ear. Read on to know all about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of Mastoiditis.
What is Mastoiditis?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Mastoiditis?
- 2 Mastoiditis in Children
- 3 Mastoiditis in Adults
- 4 Chronic Mastoiditis
- 5 Mastoiditis Complications
- 6 Bilateral Mastoiditis
- 7 Coalescent Mastoiditis
- 8 Masked Mastoiditis
- 9 What Causes Mastoiditis?
- 10 Mastoiditis Symptoms
- 11 Mastoiditis Diagnosis
- 12 Mastoiditis Treatment
- 13 Mastoiditis Prognosis
Medical researchers define Mastoiditis as a form of ear infection that affects the mastoid bone located in a segment of the skull that is positioned posterior to the external ear.
Mastoiditis in Children
This condition usually affects children. Acute cases of this disorder are quite frequent in children. In kids, Mastoiditis presents itself as a dangerous condition. Children affected with this disease are found to have their affected ear protruding out to an extent and mildly pulled down. This occurs due to moderate inflammation of the soft tissues and skin posterior to the ear over the mastoid region.
Most kids with this disorder need immediate hospitalization. Antibiotics and middle ear drainage is required for cure. An abscess that is present rear to the ear must be surgically drained out. If this does not improve the infection, a Mastoidectomy surgery needs to be done.
Mastoiditis in Adults
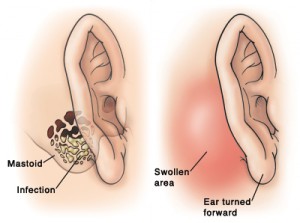
Picture 1 – Mastoiditis
Source – mountnittany
This disease mainly affects children but can also be seen in adults. In grown up individuals, the condition may be characterized by symptoms like:
- Intermittent ear drainage
- Irritability
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Ear lobe inflammation
- Tenderness behind the ear
- Redness behind the ear
In acute cases of this disorder, there can also be drooping and bulging of ears in adults. The syndrome may arise due to the development of a skin cyst known as Cholesteatoma in the middle ear. This can obstruct drainage of the ear and lead to the development of this condition.
Chronic Mastoiditis
It is an infection of the mastoid bone and the middle ear. The condition is also known as Chronic Suppurative Mastoiditis. The disorder gives rise to very discomforting symptoms like persistent drainage from the eardrum. It is an acute infection that can damage the middle ear structures and the mastoid bone. It can also result in various intracranial complications. Some of these can create life risks.
This disorder arises when a chronic inflammation known as Chronic Otitis Media affects the mastoid. It is generally characterized by a puncture in the eardrum, with sporadic drainage of infected material through the eardrum aperture. There is no bone destruction in this condition unlike Coalescent Mastoiditis. However, there may be thickening and inflammation of the lining within the mastoid bone. The disorder may also arise due to a condition known as Cholesteatoma that obstructs the linkage between the mastoid bone and the middle ear.
Mastoiditis Complications
Some of the main complications of Mastoiditis are :
- Mastoid Bone destruction
- Vertigo or Dizziness
- Epidural abscess
- Spread of infection throughout the body or to the brain
- Facial paralysis
- Meningitis
- Partial or total loss of hearing
Bilateral Mastoiditis
This is a type of Mastoiditis characterized by the development of swollen lumps on the back of the head. Sufferers experience blockage in their ear for days and months without any apparent pain.
Coalescent Mastoiditis
It is actually an Acute Otomastoiditis that arises when mucoperiosteal disease spreads to involve the mastoid bone. This leads to a reabsorption of the septae that normally separates one mastoid air cell from the other. This change is only easily appreciated on thin section bone-algorithm through the temporal bones.
Masked Mastoiditis
It refers to an Acute Mastoiditis complication that fails to resolve with antibiotic treatment and leads to the development of Granular Osteitis of low intensity in the mastoid bone. This disorder is characterized by pain in the head and the ear as well as a general ill-feeling. However, the disease is generally asymptomatic and lurks silently. It can lead to the formation of abscess as well as other complications.
What Causes Mastoiditis?
This condition is generally caused by an untreated condition known as Acute Otitis Media, which is actually a Middle Ear Infection. The infection may spread to the mastoid bone of the skull from the ear. Acute Otitis Media leads to an accumulation of the mastoid bone with infected substances.
Acute Otitis Media most frequently occurs in children and can give rise to acute health risks if left untreated. Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Haemophilus Influenzae are other Mastoiditis causes.
Various other microbes are responsible as causes of Mastoiditis causes. These are
- Porphyromonas
- Bacteroides
- Pseuodomonas aeruginosa
- Prevotella
- Fusobacterium
- Escherichia coli
- Proteus
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Klebsiella
Mastoiditis Symptoms
Know about some of the symptoms of Mastoiditis when there is an infection of the mastoid bone. These include
- Low grade fever
- Headache
- Inflammation of the Tympanic membrane of ear
- Profusion of thick, pus-filled fluid draining from ear
- Redness in bone posterior to the ear
- Erythematous (Unusual redness of the skin caused by dilation of blood vessels)
Mastoiditis Diagnosis
This disorder is diagnosed by an examination of the skull. This is usually carried out with the aid of physical examination as well as medical imaging tests like CT scan of the head and the ear and an X-Ray examination of the skull. These tests can effectively show any unusual defect of the mastoid bone. Blood Tests may also be conducted to detect this syndrome.
In some cases, doctors may carry out a culture of the drainage from the sufferer’s ear to detect any bacterial presence. However, the results for this bacterial culture may be found negative if the sufferer has already started taking antibiotics for cure. If all other diagnostic methods fail to show results, an Exploratory Surgery may be conducted as a last resort.
Mastoiditis Treatment
Antibiotic medicines are most frequently used in the treatment for Mastoiditis. However, surgical drainage and operation may also be used in some cases for curing acute cases of this condition. Antibiotic drugs may be administered over a prolonged duration, particularly if there is a high progression of this infection. Even though the type of drugs used vary in nature, the initial treatment is usually carried out with the aid of a broad spectrum of antibiotics. In some individuals, antibiotic can be used after performing a bacterial culture.
This health syndrome may be difficult to cure. This is due to the fact that the drugs may be unable to reach into the depths of the mastoid bone. Long-term or repeated cure of this disorder may be required in such cases. The infection may be cured with the aid of injected and oral doses of antibiotics.
Mastoiditis Surgery
If an antibiotic therapy is unsuccessful in treating the infection, a type of surgery needs to be conducted for Mastoiditis cure. This operative procedure is known as Mastoidectomy and involves drainage of the Mastoid bone as well as surgical removal of a part of it. Another surgery, known as Myringotomy, is also carried out for its treatment and involves drainage of the mid-section of the ear through the Tympanum (eardrum).
Mastoiditis Prognosis
This condition can be cured with treatment. However, it is difficult to treat this syndrome completely and it may recur after an interval.
If you or anyone in your family is suffering from a persistent ear infection that fails to improve with treatment, you should immediately get in touch with a healthcare professional. Prompt treatment of this disease has often been found to be highly effective in curing this disorder. Early diagnosis and cure will help in achieving a faster recovery from this disorder.
References:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001034.htm
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/784176-overview
http://www.umm.edu/ency/article/001034.htm
http://www.hearinginfo.org/DiseasesDisorders/mastoiditis.htm

I was going for my medical records at home because we are getting ready to move and I started reading newspapers and into thousand and 10 I had a MRI done of my brain without contrast and then with contrast and it showed that I had bilateral mastoid congest changes I didn’t even realise I had this until now I sometimes when I blow my nose I certainly will have something drop out of my sinuses into my mouth and I’ll choke and cough it out and I don’t know what it is but it something that’s rotten it smells rotten it’s nasty I don’t know what ideas so I really don’t know what’s going on and I do have drainage from my ear what do I do? Help me please and right now we have no insurance.