Are you suffering from regular muscle stiffness or having partial memory loss? You could be suffering from Adrenoleukodystrophy. Read and know more about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment and life expectancy of this disorder.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Adrenoleukodystrophy Definition
- 2 Adrenoleukodystrophy Types
- 3 Adrenoleukodystrophy Incidence
- 4 Adrenoleukodystrophy Symptoms
- 5 Adrenoleukodystrophy Causes
- 6 Adrenoleukodystrophy History
- 7 Adrenoleukodystrophy Diagnosis
- 8 Adrenoleukodystrophy Treatment
- 9 Adrenoleukodystrophy Support groups
- 10 Adrenoleukodystrophy Life expectancy
It is a rare condition that belongs to a group of genetic disorders known as Leukodystrophies that causes damage to the myelin sheath (an insulating membrane that covers the nerve fibers in the brain). In this fatal condition the adrenaline glands, responsible for releasing stress hormones in the body, often become dysfunctional. The damage to the brain, adrenal gland and peripheral nervous system is due to the excess accumulation of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) in those regions.
The disorder is also known by other names, such as:
- ALD
- Siemerling-Creutzfeldt Disease
- Addison-Schilder’s Disease
Adrenoleukodystrophy Types
ALD can be classified according to the different age groups it affects and on the basis of the onset of the symptoms that it produces.
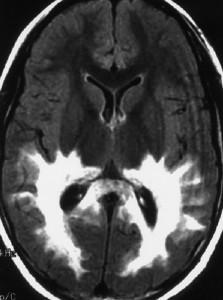
Picture 1 – Adrenoleukodystrophy
Childhood-onset ALD
This is the most severe form of ALD that usually affects males between 4 and 10 years of age. Nearly, 35% of the patients with ALD develop this severe classic childhood form. Symptoms are rapidly progressive and lead to severe disability due to degeneration of the white matter of the brain.
Adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN) or Adult-onset ALD
It is a less severe and common form of this genetic condition. Typically, all patients suffering from ALD normally develop this form after reaching adulthood. It is generally seen in males between 21 and 35 years of age and slowly progresses into deterioration of the brain.
Addison disease
In this form, the adrenal glands are not able to produce sufficient amount of steroid hormone and suffer from adrenal insufficiency. Neurological symptoms are evident in 10% of the population with ALD but are generally seen in nearly all patients.
Mild Adrenomyeloneuropathy
Female carriers may develop symptoms of adrenomyeloneuropathy. Development of neurological disorders and adrenal insufficiency is rare.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Incidence
ALD occurs all over the world and is not limited to any particular race or ethnicity. It generally occurs in about 1 in every 20,000 males during birth. However, some females also act as carriers of this condition and exhibit its symptoms.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Symptoms
Each form of ALD is manifested by an individual set of symptoms. If left untreated, these may turn severe. Know about the symptoms of each type of ALD.
Childhood-onset ALD Symptoms
The primary signs of this form include:
- Behavioral changes – Children may have mood swings and aggressive behavior. They often undergo irritation and personality changes.
- Poor memory – Mental stamina of the children may become very weak and they may find extreme difficulty in remembering or recalling anything that is seen, read or heard.
- Visual loss – Damage to the brain often leads to visual impairment that can either be partial or complete.
- Learning disabilities – Affected children have a poor school performance and face difficulty in following anything that is taught to them. There is a decreased understanding of verbal communication and deterioration of handwriting.
- Seizures – Patients may have frequent episodes of epileptic attacks or fits due to disturbed brain activity, causing changes in behavior.
- Poorly articulated speech – There is difficulty in speaking or expressing, using correct words or sentences.
- Difficulties in swallowing – Neurological damage may weaken the throat muscles, causing difficulty while eating. Patients often choke or cough while attempting to swallow. They may even get a sensation of food particles being stuck in the throat or entering the windpipe or nose.
- Deafness – Neurological degeneration may cause auditory impairment to a point where patients suffer from total hearing loss.
- Deterioration of the nervous system – Progressive damage to the brain decreases the motor activities of the muscles that disturb the movement and coordination in patients. In severe cases, paralysis or coma may occur.
- Fatigue – Patients may encounter physical exhaustion after a period of prolonged activity. Weakness and lethargy are some of the common problems that they experience.
- Hyperpigmentation of skin – Patches of skin become darker in color than the normal surrounding skin, due to excess accumulation of the skin pigment known as Melanin. Impaired adrenal function along with neurological damage may lead to this condition.
- Progressive dementia – Neurodegenerative disorder causes memory loss that begins gradually and worsens progressively over a period of time.
Adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN) or Adult-onset ALD Symptoms
It is characterized by:
- Progressive stiffness – In this condition, patients suffer from muscle spasms and tremors, causing progressive neurodegenerative disorder. There is numbness and rigid movement in the neck, arms and legs.
- Paralysis of the lower limbs – A loss of function in the muscles of the lower limbs is a very common symptom of AMN.
- Ataxia – Patients have poor coordination and unsteadiness due to failure of the brain to regulate the posture and movement of the body.
Addison disease Symptoms
It is manifested by signs like:
- Coma – Malfunctioning of the adrenaline glands, combined with neurodegenerative conditions, may lead to a prolonged state of unconsciousness in patients.
- Decreased appetite – Loss of appetite may result in unintentional weight loss.
- Muscular weakness – Nervous system disorder prevents transmission of electrical impulses to the muscles of the body. Due to this condition, patients tend to lack strength in muscles all over the body or in only one side of the body.
- Nausea – Patients may experience discomfort in the abdominal region with an involuntary urge to vomit.
Mild Adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN) Symptoms
In this form, patients display symptoms identical to AMN. However, there are some additional problems like:
Moderate sensory loss – Patients have decreased ability to respond to stimuli that affect the senses like sound, touch, taste or vision.
Excessive muscle tone – Abnormal increase in muscle tension reduces ability to stretch muscles. Maintenance of posture and passive movement becomes quite difficult, causing a hunchback.
Mild peripheral neuropathy – Nerves that are located exterior to the brain and spinal cord and constitutes the peripheral nervous system (PNS) suffers damage in this form of ALD.
Urinary problem – Some patients may have urinary incontinence where moderate amounts of urine starts leaking without any warning. Sneezing, coughing, laughing and exercising may also cause accidental leakage of urine. Neurological damage also leads to incomplete emptying of the urinary bladder, causing acute pain and discomfort.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Causes
This condition is inherited in an X-linked pattern. Here, a mutated gene that causes this disorder is located on the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes present in each cell. Females generally have two copies of the X chromosome unlike males who have only one X-chromosome. In this condition, the mutated gene resides only on one copy of the X chromosome in females that lead to less severe or no symptoms. Hence, they are regarded as carriers of ALD. Males, on the other hand, develop this condition easily as the only X chromosome is present with this defective gene. The signs and symptoms of X-linked ALD tend to appear at a later stage in females than in males.
This genetic condition causes the myelin sheath to wear out. Due to this, affected individuals begin to lose their body functions gradually. This leads to severe cases of paralysis. Myelin loss generally occurs due to an overload of the very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs), which are not easily disposed off by the human body.
Adrenoleukodystrophy History
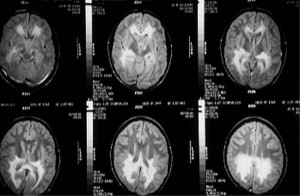
Picture 2 – Adrenoleukodystrophy Image
In 1910, two physicians, Haberfeld and Spieler reported the first case of ALD in two boys who were brothers. The elder brother, who was already suffering from movement disorder, died when only 8 years old. Later, the younger brother started developing a bronzed skin tone, partial vision loss and mental disability when around 6 years of age. A year after that he began to experience difficulties while walking. He lost the ability to speak and died after a few months of hospitalization. In 1913, Paul Ferdinand Schilder, examined the brains of both the brothers and discovered severe loss of myelin. A decade later, Ernst Siemerling and Hans Creutzfeldt came across a boy with a similar condition. It was then documented that this disorder has an adverse effect on the adrenal glands. The disorder was then named “Siemerling-Creutzfeldt Disease” or “Schilder’s disease” after these three physicians.
In 1952, physicians Adams and Kubic suggested that the condition should be placed in the same category as multiple sclerosis, since both the disorders share the same trait of myelin loss, although they noted that ALD showed more degeneration. By 1963, researchers noticed that males are more prone to this disorder than females and considered it as an X-linked recessive inheritance. The term “adrenoleukodystrophy” was introduced in 1970, owing to the progressive brain degeneration along with adrenal insufficiency that characterized this disease.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ALD is generally based upon certain characteristic features and an array of laboratory tests.
Blood test
Patients with ALD have high levels of VLCFAs in the blood that can be easily diagnosed by a simple blood test. This method is generally accurate in males but may give a false negative test in females who are carriers. This procedure may also be used to evaluate the adrenal glands and detect the amount of adrenaline in the blood.
Genetic testing
Physicians often collect blood samples of patients in order to directly identify any mutation or defect in the X chromosome. This diagnostic test is used for carrier screening, prenatal testing, and newborn screening.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head
This imaging technique helps detect the damaged white matter of the brain. Physicians can view the detailed images of the brain to detect any developmental or structural abnormalities.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Treatment
Specific treatments that can cure ALD completely are generally not available. However, there are some procedures that can be followed before its symptoms arise and cause irreversible damage. Physicians normally advise patients to eat a diet low in VLCFAs in order to prevent its further increase in the body.
Adrenal insufficiency treatment
Patients having adrenal insufficiency must go for a regular adrenal gland testing. In most cases synthetic steroids are administered to the patients, due to reduced production of the natural hormone. However, these artificial steroids may produce some negative effects, such as dehydration and low blood pressure.
Lorenzo’s Oil
Some medical experts suggest the use of a mixture of oleic acid and euric acid, known as Lorenzo’s oil, which can lower the levels of VLCFAs in the blood. However, this oil only delays or reduces the symptoms and does not cure this disorder.
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
It is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood. If diagnosed at an early stage, this particular process can help prevent or delay the progression of ALD. Umbilical cord blood stem cell transplant is generally performed in those patients for whom a matched stem cell donor is not found. This method is not recommended for patients with very severe symptoms as it may cause fatal complications in them.
Medication
Lovastatin is a very commonly used anti-cholesterol drug that may help in lowering the levels of VLCFAs and inhibit further damage to the brain. Docosahexanoic acid (DHA) is used in the treatment of neonatal ALD that relieves the patients of symptoms like stiffness and seizures.
Physical therapy
Patients with muscle strains and spasms often benefit from physical therapy. This technique utilizes a variety of modalities such as ultrasound, electric stimulation, massage, and thermal therapy to relieve the symptoms.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Support groups
There are some support groups all over the world for patients and their families who are affected by ALD. These organizations give practical support and advice to the patients and raise funds for their treatment. March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation, Children Living with Inherited Metabolic Diseases, Australian Leukodystrophy Support Group Inc are some of the organizations towards this cause.
Adrenoleukodystrophy Life expectancy
ALD is usually severe and can cause disability and death within 2 to 4 years of age, due to complications such as pneumonia. Patients with AMN can develop cerebral demyelination that could be life-threatening.
Adrenoleukodystrophy needs early diagnosis and proper attention to be cured. It is curable as long as the possibility of occurrence of this condition is predicted by patients. If you are undergoing any form of paralytic attacks, seek medical attention immediately.
References:
http://www.x-ald.nl/clinical-diagnosis/facts-on-x-linked-adrenoleukodystrophy/
http://www.mayoclinic.org/adrenoleukodystrophy/types.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenoleukodystrophy#Genetics
http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/adrenoleukodystrophy/adrenoleukodystrophy.htm