Anaplasmosis Definition
Page Contents
Anaplasmosis, also referred to as Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (HGA), is a bacterial disorder transmitted by a species of bacteria named Anaplasma phagocytophilum. The condition was earlier referred to as Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis (HGE). Humans get infected by the bacteria if they are bitten by the black-legged tick (Ixodes scapularis) or deer tick (Ixodes dammini). These ticks are also responsible for transmitting another serious disorder named Lyme disease.
Anaplasmosis Causes
The main cause of HGE is the bite of a tick infected with Anaplasma phagocytophilum bacteria.
Anaplasmosis Transmission
The disease is generally transmitted to humans by the bite of black-legged ticks carrying the HGA bacteria, rickettsial parasites of ruminants. Ticks acquire the infection when they bite wild rodents carrying the A. phagocytophilum bacteria. Humans get affected by it if they are bitten by an infected tick. The ticks can transmit the bacteria to animals like dogs, horses, cats, goats and sheep.
Anaplasmosis Symptoms
Most people affected by this bacterial infection experience mild symptoms. In some cases, however, the symptoms can even be life threatening. The severity of the condition depends on the age and overall health of the patients. The onset of the symptoms occurs within the first week after a tick-bite. The white blood cells, especially the granulocytes, are affected by the Anaplasma bacteria. The common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Muscle pains
- Fatigue
- Severe headaches
- Malaise
- Chills
The less frequent signs of HGA are:
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Cough
- Weight loss
- Joint pain
- Diarrhea
- Change in mental state
- Confusion
- Hemorrhage
- Rash
Anaplasmosis Prevention
This infectious disorder can be prevented by taking certain precautions for avoiding tick bites. One should take the following preventive measures to stay away from ticks in areas where they are likely to be present:
- Avoiding entering areas with tall grass and brush or any place where ticks may be present
- Wearing light-colored clothes
- Wearing long pant, long sleeved shirt and socks
- Tucking the pant into boots or socks and the shirt into the pant
- Applying pest repellants with DEET on the skin
- Spraying permethrin-containing tick repellents to the boots and clothing
- Checking thoroughly for any ticks on the body after returning from outdoor activities
The ticks need to stay attached to the body for a considerable amount of time before they can infect a person. Naturally, the above mentioned precautions can effectively prevent the condition by removing any ticks attached to the body as soon as possible.
At present, no vaccine is available for preventing HGA. However, the occurrence of this bacterial disease can be prevented in cattle through the use of the Anaplasmosis vaccine.
Anaplasmosis Diagnosis
The initial diagnosis of HGE is done depending on the signs and symptoms present in a patient. Doctors perform a detailed physical examination to detect the disorder. Various laboratory tests are also used for this purpose. Blood tests are very useful for making this diagnosis as they help physicians detect a low WBC count, an increase in the levels of certain liver enzymes and a low platelet count.
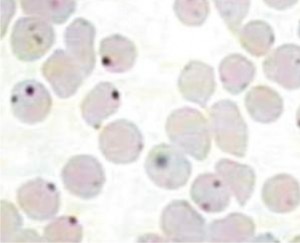
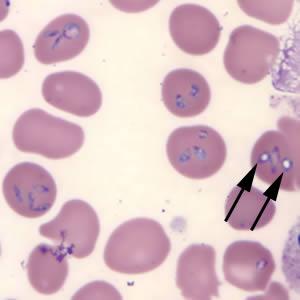
Blood smear in another useful diagnostic test that helps to detect the characteristic morulae of A. phagocytophilum bacteria in the affected blood cells. However, the diagnosis can only be confirmed by performing a Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR examination or by the immunostaining methods.
Anaplasmosis Differential Diagnosis
Its differential diagnoses can vary according to symptoms and severity. Usually, the diagnostician has to rule out the following disorders while making the diagnosis:
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Mononucleosis
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Hematologic Malignancy
- Cholangitis
- The early stage of a hepatitis A infection
Anaplasmosis Treatment
People infected by the HGA bacteria are generally treated with tetracycline antibiotics for ten to fourteen days. The antibiotic medicine named Doxycycline is commonly used for the purpose. The recommended Doxycycline dosage for adults is 100 mg per 12 hours. Children with body weight lower than 45 kg are given the antibiotic at a rate of 2.2 mg/ kg body weight, twice every day. In some cases, the symptoms of weakness, headache and malaise may persist for several weeks after the treatment is complete. Serious conditions like renal failure and respiratory difficulty also require proper management.
Alterative antibiotics are necessary for treating the infection in individuals with serious allergies to Doxycycline. Research shows that another antibiotic drug named Rifampin can effectively fight the bacteria responsible for HGE.
Palliative care, meaning management of the symptoms, may also be necessary. HGE patients often suffer from flu-like symptoms such as headache, fever and joint pain which can be treated by medications as well as certain natural remedies. Non-strenuous activity and bed rest are also important treatment measures for these patients.
Anaplasmosis Prognosis
HGE usually has an excellent prognosis with patients recovering completely after receiving proper antibiotic treatment. A small number of individuals may suffer from a recurrence of the disorder. The recurring cases are completely curable and do not generally lead to any long term effects.
Anaplasmosis Complications
The possible complications of HGE include damage of various organs including the heart, lungs and kidneys. The following life threatening complications may arise in some very rare instances:
- Kidney failure
- Severe Anemia
- Respiratory failure
- Sepsis (blood tissue infection)
- Secondary infections
- Nerve damage
- Neurological symptoms
Older patients and individuals with weak immune systems are more likely to develop these serious health problems.
Anaplasmosis Pictures
Here are some images of the ticks that transmit the disease into humans.
Picture 1 – Anaplasmosis
Picture 2 – Anaplasmosis Image
Anaplasmosis is a serious, although curable condition associated with ticks that requires early diagnosis. Prompt treatment allows patients to return to their normal daily routine within a very short time. Individuals with the serious complications of HGE can also attain recovery after receiving proper treatment.
References:
http://www.aldf.com/Anaplasmosis.shtml#top
http://www.cdc.gov/anaplasmosis/symptoms/index.html
http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/ehrlichiosisanaplasmosis/Pages/complications.aspx
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-anaplasmosis.htm
http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/idepc/diseases/anaplasmosis/basics.html#treatment