Lesh-Nyhan Syndrome (LNS) is a rare inherited disorder that leads to abnormal muscular movement, behavioral changes and a host of other problems. Read on to know more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of this disorder.
What is Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome?
Page Contents
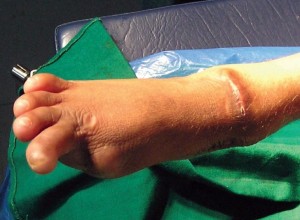
It is a disease characterized by an overproduction and accumulation of uric acid. It generally affects very young children.
The condition is also known by various other names, like:
Picture 1 – Lesh-Nyhan Syndrome
- Nyhan’s Syndrome
- Kelley-Seegmiller Syndrome
- Juvenile gout
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Causes
LNS results from the absence or deficiency of an enzyme, known as hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HGP). HGP is involved in the metabolism of uric acid. It is required by the body to recycle purines in the physical system. The absence of this enzyme leads to an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the body.
LNS is acquired in an X-linked pattern.
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Incidence
The disease affects approximately 1 out of 380,000 individuals. It is mostly found to affect boys.
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Symptoms
The condition typically gives rise to problems like:
- Kidney stones
- Bladder stones
- Behavioral changes
- Abnormal muscle movement
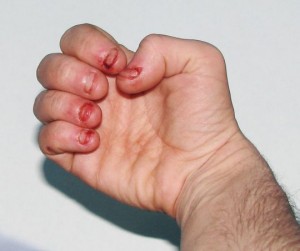
A characteristic feature of the syndrome is self-injury in the form of biting and hand banging.
The symptoms of this syndrome can be categorized into three groups, which are as follows:
Uric acid overproduction
As the disease occurs in infants, uric acid crystals are observed on the diaper of affected children. The overproduction of uric acid can result in kidney or bladder blockage when the crystals get deposited there. Kidney stones may further result in kidney damage. If the crystals get deposited in the joints, they can result in arthritis or other similar problems.
Neurological disability
A number of problems related to the nervous system are observed during the later stages of the disease. These include behavioral changes, loss of muscle control, disoriented behavior, retarded growth and difficulties in walking or speech.
Behavioral abnormalities
The self-injurious tendency, associated with LNS, includes biting of lips and tongue. In the later stages, head banging or other self-harming activities might be noticed. The tendency of causing self-injury is observed in majority of the LNS patients (about 85% males with this condition). It is to be noted that these symptoms are also observed in other mental disorders, such as autism. Aggressive behavior is also observed in patients of this syndrome.
Diagnosis of Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
The diagnosis of LNS is harder in the early stages, as the symptoms are not clear. The diagnostic tests used for detection of this disease involve:
Clinical assessment and behavioral study
The behavior of a child affected with LNS can provide vital clues about the disease. For instance, activities like biting the fingers and lips can be a clear indication of the disease. On the other hand, other self-injurious practices like head-banging are associated with other mental disorders including autism, tourette syndrome and sensory neuropathy. If self-injury is noticed with hyperuricemia and neurological dysfunction, LNS can be confirmed.
Urine Diagnosis
One of the characteristic observed in the disease is elevation of the urate to creatinine ratio in the urine of sufferers. Increase in this ratio is a clear sign of acid overproduction. Although Hyperurecemia cannot be considered as confirmatory test, the genetic mutations of the HPRT clearly confirm the disease.
Tests for protein activity
The confirmatory tests used for LNS involve medical examinations used for measuring protein activity. In this test, a sample of blood or a skin sot is examined in the laboratory to analyze the living cells.
Checking the family history
If the abovementioned tests are positive in a child suspected of having this condition, his family history should be checked for final confirmation. This involves taking the assistance of a genetic counselor who examines past cases of hereditary disorders in a family.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is used for the imaging of the urinary tract.
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of LNS is important to distinguish it from disorders that give rise to similar symptoms, such as cerebral palsy, chorea and other metabolic disorders.
Treatment of Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
The treatment of the disease aims at the management of uric acid overproduction, neurological disability and behavioral problems arising due to this syndrome.
Treatment of uric acid overproduction
The excess production of uric acid, caused by this syndrome, gives rise to gout, kidney problems and renal failure. Increase in uric acid concentration can be managed by a drug called Allupurinol. Allupurinol also helps to control the complications associated with LNS. Another treatment option is to encourage fluid intake by the patient. Drinking a lot of fluids helps wash out the excess uric acid through urine. This is more beneficial in early stages, when there are small uric acid crystals in the body. Proper hydration, along with medication, can be effective in curing the condition. Lithotripsy is another technique used by the doctors to break down the stones to smaller pieces. In case the technique is not helpful, the entire stone should be removed surgically.
Treatment of neurological disability
Drugs like Baclofen, Diazepam and Clonazepam are prescribed by doctors to cure the neurological problems arising due to LNS. The commonly used route of administration is oral. In rare cases, however, the drug might be given through the spinal cord by a pump that is surgically implanted.
Management of Self-injury
For doctors treating LNS symptoms, one of the biggest challenges is to manage the self-injurious behavior in affected children. This can be done by:
Picture 2 – Lesh-Nyhan Syndrome Image
- Keeping harmful objects, like sharp instruments, away from children.
- Using elbow splints to control finger biting.
- Using drugs like gabapentin, carbamazepine and diazepine.
Although these drugs are capable of controlling self-injurious behavior they are not capable of eradicating it completely. Another drug, Resiperdal, is also used by doctors. However, it is associated with side effects like sleepiness.
Finally, parents should also provide proper support to their child and encourage good behavior. If a child tries to harm himself, he should not be scolded or beaten. He should be counseled properly to make him understand the possible accidents. If the above techniques fail to control biting, teeth extraction might be required in children.
If you spot the symptoms of LNS in your child, contact a professional medical care provider at the earliest. Timely treatment and care can prevent the condition from giving rise to severe disabilities in later stages.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lesch%E2%80%93Nyhan_syndrome
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/lesch-nyhan-syndrome
http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/lesch_nyhan/lesch_nyhan.htm
http://rarediseases.about.com/od/rarediseasesl/a/leschnyhan.htm
http://www.patient.co.uk/doctor/Lesch-Nyhan-Syndrome-(LNS).htm
http://www.thirdage.com/hc/c/lesch-nyhan-syndrome-symptoms