Leukoplakia is a discomforting condition that affects around 3% of the world population. Read and know what is Leukoplakia as well as all about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
Leukoplakia Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Leukoplakia Definition
- 2 Leukoplakia Types
- 3 What is Homogeneous Leukoplakia?
- 4 Leukoplakia Symptoms
- 5 Leukoplakia Causes
- 6 Leukoplakia Diagnosis
- 7 Leukoplakia Differential Diagnosis
- 8 Leukoplakia Treatment
- 9 Leukoplakia Prognosis
- 10 Leukoplakia Prevention
- 11 Leukoplakia Home Remedies
- 12 Leukoplakia and Cancer
- 13 Leukoplakia Pictures
It is a health condition that is characterized by the development of rough, hard lesions in the mouth, on the mouth or the inner side the cheek as a response to long-standing irritation.
Leukoplakia Types
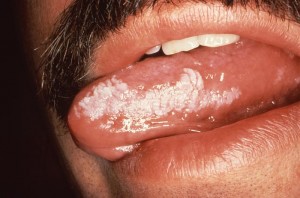
Picture 1 – Leukoplakia Tongue
Some of the main types of Leukoplakia are:
Hairy Leukoplakia (HL)
People with weakened immune system due to medications or underlying disorders (such as HIV/AIDS) suffer from a form of Leukoplakia that is known as “Hairy Leukoplakia (HL)”. In such cases, the lesions appear as white, fuzzy patches and arise on the tongue. These are usually painless and look similar to ridges or folds on the sides of the tongue. The condition is often mistaken for oral thrushes that are common in individuals affected with HIV/AIDS. Oral HL may also be indicative of a failure of anti-retrovial therapy.
Oral Leukoplakia (OL)
It causes development of white plaques or patches that are difficult to be rubbed off. It is not what causes this disease. It arises in less than 1% of the world population and is viewed as a rare syndrome. However, it is supposed to be a potentially malignant disorder. It is more likely to affect men than women.
Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia (PVL)
It is an uncommon type of progressive multifocal Leukoplakia. In most cases, it undergoes a malignant change to turn into a verrucous carcinoma or squamous cell cancer. The condition has a high possibility of recurrence.
Laryngeal Leukoplakia (LL)
It is characterized by the presence of keratin on the epithelial surface of the vocal cord. As per some medical studies, the condition arises from smoking, Laryngopharyngeal reflux, alcoholism and industrial pollution. Dysplasia (abnormal development of cells or organs) in the Laryngeal Leukoplakia is suggestive of a potential malignant transformation.
Cervical Leukoplakia (CL)
This variation gives rise to ulcers in the cervix of the vagina. These are white in appearance with a maximum diameter of 1 cm. They are mainly caused due to endocrinal disorders (marked by rise in estrogen levels) and are usually removed by freezing. This condition indicates a strong possibility of cancerous or malignant developments in future.
Idiopathic Leukoplakia (IL)
The syndrome is marked by persistent white lesions in the oral plaques. Patients with this disease suffer from a high risk of suffering from cancerous developments in future. It is supposed to be a precancerous Leukoplakia. Studies reveal that approximately 4-17% IL sufferers have malignant transformation of their ulcers in less than 20 years.
What is Homogeneous Leukoplakia?
It refers to a Leukoplakia lesion that is mainly white in color and uniformly thin and flat in appearance. The bumps have a smooth, folded or wrinkled surface that may display shallow cracks.
Leukoplakia Symptoms
The disease primarily affects the mucus membranes of the mouth. As aforesaid, the condition gives rise to hard bumps on the oral region of sufferers. The lesions usually arise in areas like,
- Roof of the mouth
- Tongue
- Gums
- Lips
- Inside of the cheeks
In females, the lesions may also arise on the outer genital region.
The bumps typically arise as open sores and are white or gray in color. In some patients, these may be red in appearance and referred to as Erythroplakia, a condition that may result in cancer. In most patients, the lesions are thick and slightly elevated in appearance. These have a firm surface that is difficult to scrape off. In some cases, however, the bumps have a flat or an irregular surface.
Though visually disturbing and uncomfortable to sufferers, these are usually painless and do not produce any discomforting symptoms. If the lesion develops into a blister and suffers rupture over the skin surface, inflammation and infection may occur. Painful symptoms can arise in such cases.
Leukoplakia Causes
The exact cause of this condition is unknown. However, any type of irritation in the mouth is supposed to give rise to this disorder. Oral irritation may occur due to problems like,
Prolonged smoking
Long-term smoking (especially of pipes) often gives rise to Smoker’s Keratosis, a condition marked by an overgrowth of horn-like skin layers in the mouth.
Rough teeth
Rough surface of crowns, fillings or dentures may also give rise to this problem.
Tobacco use
Prolonged chewing of tobacco puts the mouth at higher risk of getting this condition. Regular use of tobacco snuff may also lead to the problem.
Alcohol intake
Consumption of alcohol may not be a causative factor for this disease. However, it can aggravate the oral lesions and worsen the problem.
Some other possible causes of Leukoplakia are:
Age
The condition can be related with age as it is found to affect many elderly people across the world.
HIV/AIDS
Hairy Leukoplakia is mostly seen in individuals found to be HIV-positive. In HIV-affected people, it is often regarded as one of the first signs of infection and arises in approximately 25% sufferers.
Low immunity
People with weakened immunity can also fall prey to this condition. Those who have a low-functioning immunity, such as in the days following a bone marrow transplant, are vulnerable to this disease.
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
This virus, though not harmful itself, may also give rise to this ailment. Once it enters the body, it can remain inside for life. It is usually dormant but can get reactivated if the immune system gets weakened due to some underlying disorders or side effects of certain medications.
Leukoplakia Diagnosis
The early diagnosis of this condition involves a physical examination of the lesions. A dentist may perform a biopsy of the lump to differentiate it from more serious problems, such as cancer. Biopsy may either involve removal of a small part of the lesion with a tiny spinning brush (as in Oral Brush Biopsy) or complete excision of the blister (as in Excisional Biopsy). Laboratory analysis of the sample helps a pathologist detect the presence of any abnormal cell.
Generally, Oral Brush Biopsy is used first to take out and analyze a lesion sample. If the biopsy result comes as positive, Excisional Biopsy may be performed to remove the sore entirely. If the sore is found to be too large for excision, an oral surgeon may be needed to conduct a full operation.
Leukoplakia Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this disorder involves distinguishing it from other conditions that produce similar symptoms. These include,
- Hyperkeratosis
- Dysplasia
- Squamous carcinoma
- Lichen planus
- Candidosis
- Lupus erythematosis
In some cases, a complete oral mucosal test needs to be carried out to rule out other possible causes of white lesions on the oral region. Tests are also required to check for Lymphadenopathy of the neck and the head.
Leukoplakia Treatment
Treatment for this condition aims at getting rid of the lesions. This involves removal of the lesions themselves as well as the source of oral irritation that acts as the cause of development of the bumps.
Removal of lesions requires a surgical operation, which is generally carried out under the effects of local anesthesia in a physician’s office. Patches may be removed with the aid of scalpels, laser or a very cold probe that eradicates cancerous cells by freezing (Cryoprobe). If the sores recur, as is common, follow-up visits may be needed.
Removal of the source of irritation involves,
- Cessation of smoking
- Stopping use of tobacco products, as snuff or in any other form
- Cessation of alcohol consumption
In most sufferers, stopping smoking and alcohol intake helps resolve the condition. People having the disease due to rough oral surfaces require immediate treatment of dental problems like rough teeth, fillings and irregular denture surface.
Hairy Leukoplakia usually does not require treatment. If cure is needed at all, it may comprise of
Topical medications
Tretinoin (Retinoic Acid) and Podophyllum resin solution are the standard topical medicines used for curing Leukoplakia patches. Topical application of these drugs can bring about an improvement in the appearance of the patches. The lesions may, however, recur as soon as topical therapy is stopped.
Systemic medications
Systemic therapy involves the use of antiviral medicines like Famciclovir (Famvir) and Valacyclovir (Valtrex) which prevent replication of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV). However, this therapy is also unable to remove the patches. Once the therapy is stopped, the lesions often make a recurrence.
Leukoplakia Prognosis
This is usually diagnosed to be a harmless condition. Its symptoms generally resolve within a few weeks or months on successful treatment and removal of the source of irritation. It can become cancerous, but only rarely. Cancerous lesions are cured by surgery as well as use of preventive measures that stop dispersion of cancer to other regions of the body.
Leukoplakia Prevention
In most cases this syndrome can be prevented by:
Restricting or avoiding alcohol intake
Alcohol can be a trigger factor for Leukoplakia as well as oral cancer. A combination of smoking and alcohol makes it easier for the toxic chemicals present in tobacco to penetrate the oral tissues.
Avoiding all tobacco products
Tobacco, taken in any form, can cause Leukoplakia and aggravate its symptoms. Regular use of tobacco products may also lead to oral cancer. Leukoplakia patients should keep away from all types of tobacco products.
Beta-carotene
Intake of 150,000 IU Beta-carotene, twice every week, can also help keep the problem at bay.
Following a Mediterranean-style diet
Mediterranean diets comprise of high amounts of fresh vegetables, especially tomatoes, as well as fish oil, olive oil and citrus fruits (such as lemon, grapefruit and oranges). These food items contain high amounts of antioxidants that are supposed to prevent damage to human cells.
Leukoplakia Home Remedies
The natural treatment of Leukoplakia is possible at home. It involves use of
Green Tea
Daily consumption of a mixture of 3 grams of whole green tea, green tea pigments and green tea polyhenols can help in improving the lesions. Applying the mixture on the bumps can also allow faster healing.
Fresh vegetables and fruits
Fruits and vegetables such as orange, green fruits, pumpkin, carrots, spinach, squash and cantaloupe contain high amounts of antioxidants like beta carotene that deactivate toxic oxygen molecules before they can destroy tissues. Leafy vegetables like spinach, lettuce and cabbage are also believed to provide maximum protection against cancer. An ideal diet for patients of this disease should be high in potatoes, wholegrains and wholemeal bread.
Vitamin supplements
Daily consumption of 28, 500 IU Vitamin A and 800 IU Vitamin E has been found to yield effective results in curing the lesions caused by this disease. Vitamin C, when taken along with Vitamin E and beta-carotene, has also been found to be an effective remedy.
Avoiding exposure to sunlight
Sunlight can aggravate lesions arising on exposed regions of the body. Hence, it is necessary to protect lips from exposure to sunlight.
Leukoplakia and Cancer
This is generally found to be a benign condition. However, around 4% of people with this disease can go on to suffer from cancer, which is one of the worst possible complications. The risk of cancer is greater in some forms of the disease, especially Idiopathic Leukoplakia. Approximately 5 out of every 100 individuals with this condition can suffer from oral cancer in the later stage of life. The risk is especially greater in patients who smoke or chew tobacco on a regular basis.
Hairy Leukoplakia, unlike traditional forms of the disease, does not usually lead to oral cancer. Poor-fitting dentures are not responsible for development of cancerous conditions.
Leukoplakia Pictures
Check out these Leukoplakia photos to know how the condition looks like. You will find these Leukoplakia images quite useful to get an idea of the physical appearance of patients of this syndrome.
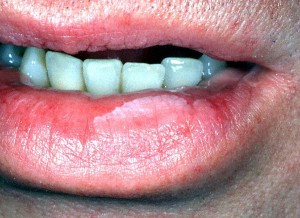
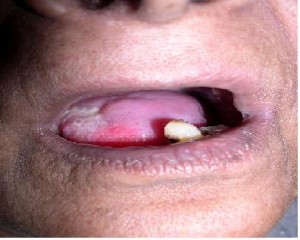
Picture 2 – Leukoplakia Image Picture 3 – Leukoplakia Photo
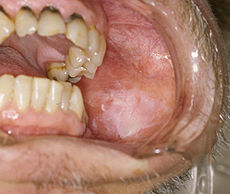
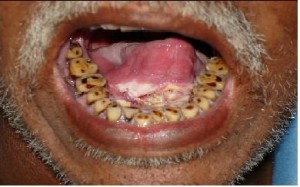
Image 4 – Picture of Leukoplakia Image 5 – Photo of Leukoplakia
If you notice any lesions similar to Leukoplakia or Hairy Leukoplakia, do not nglect them. Get in touch with a physician and undergo a through checkup. Timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease can help you make a faster recovery and even check possible cancerous complications at an early stage.
References:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001046.htm
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/leukoplakia/DS00458
http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/dental-health-leukoplakia
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/853864-overview
