Spermatocele Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Spermatocele Definition
- 2 Spermatocele Causes
- 3 Spermatocele Symptoms
- 4 Spermatocele Prevention
- 5 Spermatocele Diagnosis
- 6 Spermatocele Differential Diagnosis
- 7 Spermatocele Treatment and Management
- 8 Spermatocele Follow-up Care
- 9 Spermatocele Complications
- 10 Spermatocele Prognosis
- 11 Spermatocele Recovery Time
- 12 Spermatocele Pictures
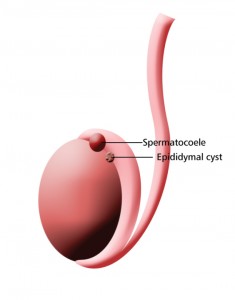
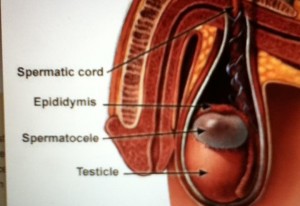
Spermatocele is a cyst or an abnormal sac that grows in the coiled tube situated on the upper-testicle which collects and transmits sperm. This type of cyst is generally filled with clear or milky fluid which may contain sperm. The size of the painless and noncancerous cyst may vary greatly from one patient to another.
These are often referred to as spermatic cysts. They generally do not cause any serious health problems and so, do not require any treatment. But, severe cases of the condition can be treated with surgery.
Spermatocele Causes
The exact causative factors for this condition are still unknown. Possible causes of Spermatoceles include trauma, infection (epididymitis) and inflammation. However, that does not mean that they cannot develop from any other factors other than these two. According to some researches, these cysts can develop from the blockage of the epididymis and some other ducts. Utero exposure to a synthetic type of estrogen named diethylstilbestrol may also be responsible for the formation of spermatic cysts.
According to the ultrasound findings of the scrotum in one study, 35% men develop these cysts following a vasectomy.
A diverticulum originating from the tubules located in the epididymis’s head is also counted among the possible causes of the condition. The diverticulum may increase in size due to spermatogenesis over time, ultimately leading to this cyst.
Spermatocele Symptoms
In most cases, the cysts remain in the same size and do not cause any visible symptoms. However, they may sometimes grow larger and result in the following symptoms:
- Pain and discomfort in the involved testicle
- Feeling a heaviness in the affected area
- Swelling above and behind the affected testicle
- Pain in the lower back, upper thigh and groin regions
- Lower abdominal pain in some cases
In some rare instances, a spermatic cyst may advance and lead to cancer.
Spermatocele Prevention
There is no way of preventing the development of this kind of cyst as the reasons behind its growth are not known. However, performing regular scrotal self-exams can be helpful for detecting any changes in one’s scrotum. Performing the test at least once every month assists in identifying a growth of mass in the area. Early detection of the cyst is generally useful for preventing it from advancing to a harmful stage. It is advisable to consult a physician to learn the correct way of performing this test.
It is ideal to examine the testicles after taking a warm bath as the hot water helps to relax the scrotum which makes it easier to detect any abnormalities.
Spermatocele Diagnosis
Doctors generally perform a thorough physical examination to diagnose this condition. Proper diagnosis is important to understand the size and severity of the cyst as it may lead to more serious health problems and cancer if left untreated. Sometimes, painless malignant tumors are erroneously identified as Spermatoceles and are not treated properly. These tumors can eventually lead to cancer.
The spermatic cysts are generally painless. However, an individual may feel a little discomfort when the doctor examines the mass by palpation. The following diagnostic tests may be used for this purpose:
Transillumination
Sometimes the doctor uses a shining light for illuminating the scrotum to look for any abnormality. A fluid-filled mass is indicated by the light in case the patient has a spermatic cyst.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound may be ordered by a physician for confirming the diagnosis if the transillumination test shows a fluid-filled mass in the scrotum of a patient. In cases where the transillumination fails to clearly indicate the presence of a cyst, an ultrasound helps to determine the exact nature of the mass. This diagnostic test creates images of the affected area by using high-frequency sound waves. It is also helpful for eliminating the possibility of other conditions, like a testicular tumor, that may cause scrotal swelling.
Spermatocele Differential Diagnosis
The following conditions may be confused with this type of cyst as they have similar symptoms:
- Hydrocele
- Varicocele
- Testicular Cancer
- Inguinal Hernia
- Simple Epididymal Cyst
- Neoplasm
- Epididymitis
- Hematocele
- Orchitis
- Tuberculosis of epididymis
- Twisting of the testis
Spermatocele Treatment and Management
Treatment is not necessary in many cases of the condition as these cysts do not usually cause any pain and discomfort. However, proper treatment is required if they grow large in size and cause symptoms like pain and swelling. The available treatment options for curing the cysts are discussed below:
Medication
Non-surgical treatment options include various over-the-counter pain-relief medicines, including acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), that are used for the purpose of managing the pain resulting from the cysts.
Aspiration
Aspiration is a relatively rare procedure used for treating various types of cysts. Here, a small needle is used for puncturing the spermatic cyst and retrieve the fluid inside the sac into a syringe. However, it is not generally recommended due to the chances of epididymal damage which can affect the fertility of the patient.
Sclerotherapy
It is a less commonly used treatment option used for getting rid of this condition. The surgeon begins this procedure by draining the fluid which fills the sac before injecting a certain chemical into the cyst. This chemical contains irritating agents that lead to scarring of the spermatic cyst sac and occupies the empty space resulting from the drainage of the fluid for lowering the recurrence risk of the cyst.
Surgery
Severe cases of the disorder can be treated by operation for removing the cyst. The removal procedure is quite simple and can be performed on an outpatient basis. The surgeon uses general or local anesthesia for carrying out the surgery. An incision is made in the patient’s scrotum to separate the cyst from the epididymis.
Spermatocele Follow-up Care
The patient is generally asked to use gauze-filled athletic supporters after the surgery for applying adequate pressure as well as to protect the incision site. Following are the main follow-up treatments required after undergoing a surgery for removing the cyst:
- Applying ice packs regularly for 2 to 3 days as it helps to reduce the swelling
- Taking the prescribed oral pain medicine for 1 to 2 days to keep the pain in check
- Returning to the doctor around 2 weeks after the surgery for having a follow-up examination
Spermatocele Complications
It does not generally cause any complications. However, in severe cases it is necessary to remove the cyst by surgery which can lead to certain complications. Surgical removal may cause damage to the vas deferens (the tube responsible for transporting sperm from epididymis) or the epididymis which may eventually reduce fertility of the patient.
Sclerotherapy, another treatment option for the condition, may damage the epididymis, reducing the fertility of an individual. This procedure is mainly used for treating men who are already beyond the reproductive years.
None of these two treatment processes can completely prevent the recurrence chances of the spermatic cysts.
Spermatocele Prognosis
Spermatic cysts usually do not cause any short-term or long-term problems. In more serious cases, the prognosis is generally positive with early diagnosis and proper treatment. The condition does not affect the fertility of the patient. Timely treatment allows the patient to live a long and normal life.
Spermatocele Recovery Time
The cyst usually takes 4 to 5 days to heal completely after surgery. The other treatment options take up to one week to cure the condition.
Spermatocele Pictures
Take a look at these images and know how these spermatic cysts appear to view.
Picture 1 – Spermatocele
Picture 2 – Spermatocele Image
Spermatocele is a form of benign cyst that does not cause any health problems in majority of the instances. There are a number of treatment options available to treat these cysts if they cause any serious symptoms and complications. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment allows the patients to live a normal life.
References:
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/spermatocele/DS00619/DSECTION=treatments-and-drugs
http://www.urologyhealth.org/urology/index.cfm?article=117
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/443432-workup#showall
http://www.healthscout.com/ency/1/407/main.html
http://www.mynetpharma.com/spermatocele-a-gist-of-knowledge