What is Sporotrichosis?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Sporotrichosis?
- 2 Sporotrichosis Prevalence
- 3 Sporotrichosis Types
- 4 Sporotrichosis Causes
- 5 Sporotrichosis Symptoms
- 6 Sporotrichosis Diagnosis
- 7 Sporotrichosis Differential Diagnosis
- 8 Sporotrichosis Treatment
- 9 Sporotrichosis Complications
- 10 Sporotrichosis Prognosis
- 11 Sporotrichosis Prevention
- 12 Sporotrichosis in Animals
- 13 Sporotrichosis Pictures
Sporotrichosis is a disease caused by infections of the Sporothrix schenckii fungus. This fungal disease generally affects the skin, although there are other rare forms that can affect the bones, joints, lungs and also the brain. The condition is also known as the “Rose gardener’s disease” or “Rose-thorn disease” as it can spread through roses.
Sporotrichosis Prevalence
Although the exact figures relating to the prevalence of this condition are not known, it is estimated that only 1 or 2 individuals in per million populations are affected by it, making Sporotrichosis a very rare disease.
Sporotrichosis Types
Based on the areas that are affected, various forms of this disorder exist. These include:
Skin or Cutaneous Sporotrichosis
The most common variant of this disease affects the skin or the cutaneous surface. They are most frequently found in the fingers, hands and arms.
Pulmonary Sporotrichosis
This form of the disease occurs when an individual inhales the S. schenckii spores. Patients of this disease are susceptible to pneumonia or tuberculosis.
Disseminated Sporotrichosis
When the infections of the Sporothrix schenckii fungus spread from their primary site to the secondary sites, it develops into a very rare, critical form known as disseminated Sporotrichosis. It can spread to the joint and bones (osteoarticular Sporotrichosis) or to the brain and the central nervous system (Sporotrichosis meningitis).
There are also certain other forms of the disorder, such as Endophthalmitis and Chorioretinitis.
Sporotrichosis Causes
The disorder occurs due to infections caused by the fungus called Sporothrix schenckii. It is found mostly in vegetation. Infections commonly occur when the skin gets broken while handling the plant materials like briars, rosebushes, or mulch-rich dirt.
For people involved in professions like horticulture, farming, rose gardening or maintenance of plant nurseries, Sporotrichosis can develop as a job-related disease. The fungus can enter the body through small abrasions and cuts to cause infections. Widespread or disseminated Sporotrichosis can occur in individuals having compromised immune systems as they inhale the dust that is filled with spores.
Sporotrichosis Symptoms
The infections of Sporotrichosis progresses slowly. It may take anywhere between 1 to 12 weeks for the first signs to appear after the initial contact with the fungus, although the average duration is 3 weeks. If the organism affects the skin, nodular bumps or lesions mat appear around the point of entrance as well as along the lymph nodes and blood vessels. The lesions start off as painless and small, and may range in color from being pink to purple. The lesions can become larger if left untreated and resemble boils. Small quantities of pus may come out of the lesions and nodules on an occasional basis. More lesions will start appearing, eventually developing into a chronic ulcer. Mycetomas might form under certain circumstances. These are areas where the sinus tracts are created from lymph to skin surface and they discharge granules that contain masses of organisms responsible for causing the infections. The symptoms associated with pulmonary Sporotrichosis include excessive coughing, fibrosis, cavitations and nodules of the lungs, as well as swelling of the hilar lymph nodes.
Body-wide or systemic Sporotrichosis can give rise to lung and breathing difficulties, arthritis, bone infections, as well as infections of nervous system. The tissues that surround the brain may get affected in a condition known as fungal meningitis. The disease spreads to various other parts of the body in patients who have an already compromised immune system. In such cases, the condition can prove to be life-threatening and become difficult to treat.
Sporotrichosis Diagnosis
Diagnosing Sporotrichosis can be difficult as many other conditions show signs and symptoms similar to it. A physical examination will reveal the typical sores. Commonly, a swab or a tissue sample is obtained from the infected site and is sent to lab for fungal culture. The tissue sample can be stained by using Grocott’s methenamine silver (GMS), PAS digest or Gram stain. Tissue samples are generally obtained from the skin, the sputum, the synovial fluid, or the cerebrospinal fluid. Serological tests are of little value to the diagnosis of this disorder due to its limited sensitivity and specificity.
Sporotrichosis Differential Diagnosis
A number of health conditions show signs and symptoms similar to that of Sporotrichosis. Hence, it should be differentiated from such similar disorders while determining the diagnosis of this particular condition as this will help in effective medical management. The differential diagnoses of Sporotrichosis include taking into account health disorders like:
- Yaws
- Pinta
- Syphilis
- Leprosy
- Tularemia
- Sarcoidosis
- Candidiasis
- Nocardiosis
- Tuberculosis
- Leishmaniasis
- Blastomycosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Fungal Pneumonia
- Erythema Nodosum
- Bacterial Pneumonia
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Paracoccidioidomycosis
- Staphylococcal Infections
- Mycobacterium Marinum
- Ulceroglandular tularaemia
Sporotrichosis Treatment
The treatment of this condition depends on the areas of the body that are affected as well as the severity of the disease. A number of treatment options are proposed for it, which include the following:
Saturated solution of potassium iodide
Although doctors are not sure how it does work, applying potassium iodide in a droplet form has been found to heal cutaneous Sporotrichosis. This generally takes anywhere between three to six months of treatment.
Antifungal drugs like Fluconazole and Itraconazole (Sporanox)
At present, the drug Itraconazole is more prevalently used to treat this disorder instead of Fluconazole. Patients having low tolerance for Itraconazole should be treated with Fluconazole.
Amphotericin B
The antifungal medication Amphotericin B is delivered intravenously. Several patients, however, find it difficult to tolerate Amphotericin B because of its potential after-effects like nausea, vomiting and fever. Lipid formulations of the Amphotericin B are generally recommended instead of the Amphotericin B deoxycholate due to its lower risks of causing any adverse effects. Severe infections occurring during pregnancy can be treated with Amphotericin B. Children having disseminated or severe diseases can be initially treated with Amphotericin B deoxycholate which can then be followed by itraconazole. Patients of Sporotrichosis meningitis can be treated with a combination of 5-fluorocytosine/Flucytosine and Amphotericin B.
Newer forms of triazoles
Posaconazole can be used as an alternate form of therapy for Sporotrichosis as its in-vitro activity is similar to the drugs itraconazole and amphotericin B. However, the correlation between clinical response and in vitro data is still insufficient to recommend drugs like Posaconazole and Voriconazole for the treatment of Sporotrichosis.
Surgery
Surgery might become necessary if there are bone infections or cavitatory nodules within the lungs.
Sporotrichosis Complications
Sporotrichosis can progress to give rise to other diseases, depending on the status of the immune system. The various health complications that may arise from this condition include:
- Arthritis
- Cellulitis
- Discomfort
- Sarcoidosis
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Bone infections
- Lung and breathing difficulties
- Secondary skin infections like staph or strep
Affected individuals may also suffer from side effects of medications like Amphotericin B. Infections of joints and the central nervous system have been recorded but are quite rare.
Sporotrichosis Prognosis
The outcome for patients infected with this disease is normally good with treatment. It might take several months or even years to get rid of the infections and the affected areas might get scarred. Disseminated Sporotrichosis can be more difficult to manage and might require chemotherapy drugs. Individuals having a weak immune system can experience fatalistic implications if they are affected by Disseminated Sporotrichosis.
Sporotrichosis Prevention
Most cases of this disorder occur when the responsible organism enters the body through a wound or a cut in the skin while attending to vegetation containing these fungal spores. This disease can be prevented by wearing gloves and long sleeves to protect the hands while working with the soil, rose bushes, hay bales, sphagnum moss and pine seedlings.
Sporotrichosis in Animals
This fungal disease can also affect domestic as well as wild mammals such as cats, dogs and horses. Cats are normally affected by a severe form of skin Sporotrichosis, and medical personnel and other individuals should take protection while handling them to avoid catching the infection.
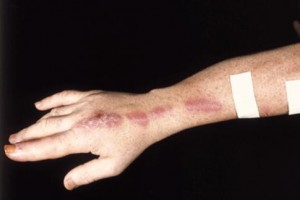
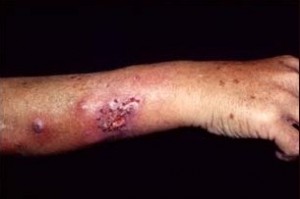
Sporotrichosis Pictures
These images show the condition of the skin after being affected by this disease.
Picture 1 – Sporotrichosis
Picture 2 – Sporotrichosis Image
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sporotrichosis
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001338.htm
http://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/communicable/sporotrichosis/fact_sheet.htm
http://www.mycology.adelaide.edu.au/Mycoses/Subcutaneous/Sporotrichosis/