Are you suffering from muscular pain, eye problems, fever, diarrhea and skin rashes? All these symptoms together are sure signs of Trichinosis. Read on to know all about Trichinosis disease.
What is Trichinosis (Trichinellosis) ?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Trichinosis (Trichinellosis) ?
- 2 Trichinosis Definition
- 3 How Common Is Trichinosis?
- 4 Is Trichinosis Common In Other Countries?
- 5 Trichinosis Pronunciation
- 6 What Is Trichinosis Caused By?
- 7 How Do You Get Trichinosis?
- 8 Trichinosis Symptoms
- 9 Trichinosis Diagnosis
- 10 How Is Trichinosis Eradicated?
- 11 Treatment of Trichinosis
- 12 What If Trichinosis Goes Untreated?
- 13 Trichinosis Deaths
- 14 Prevention Of Trichinosis
- 15 Temperature To Kill Trichinosis
- 16 Does Freezing Kill Trichinosis?
- 17 Trichinosis and Pregnancy
- 18 Trichinosis Incubation Period
- 19 How Long Does Trichinosis Last?
- 20 Trichinosis Pictures
- 21 Does Trichinosis Go Away?
Trichinosis is a parasitic disease that arises from the consumption of meat products that are not cooked properly. The disease is also known as Trichinellosis or Trichiniasis.
Trichinosis Definition
Trichinosis is actually defined as a food infection caused by trichinae, a parasitic roundworm of the Nematoda group.
How Common Is Trichinosis?
Trichinosis had been first reported in 1966. In the list of countries having people with Trichinosis United States has fortunately a much lower place. The disease peaked in 1948 when 500 people were found to be affected with the syndrome. In recent years, it has not been too active. There have been only 74 Trichinosis USA cases reported between 1997 and 2001. But the disease is occasionally reported in the rural areas.
Is Trichinosis Common In Other Countries?
Trichinosis is more common in among immigrants in South East Asia. This can be attributed to some ways of cooking foods by such people. The disease is also common in Latin America where there is little inspection of meat and regulation on pig consumption.
Trichinosis Pronunciation
Trichinosis is articulated as “tri-ku-no-sis”. It is commonly pronounced as “tri-ki-no-sis” though that is incorrect.
What Is Trichinosis Caused By?
You must have guessed where does Trichinosis come from? As the name indicates, Trichinosis is caused by Trichina – a member of the Trichinella Spiralis family of roundworm.
How Do You Get Trichinosis?
As aforesaid, humans can acquire Trichinosis by due to consumption of undercooked meat, especially pork, which is infected with the Trichinosis roundworm. Most Trichinosis patients in the US get it from eating undercooked meat of infected pigs, bears and other hunted wild animals.
Trichinosis Symptoms
Trichinosis usually gives rise to very few or almost no symptoms whatsoever in case of a minor parasitic infection. Consumption of a small number of larvae does not produce many symptoms. But the entry of a large number of larvae into the intestine can be really harmful. Some of the symptoms of trichinosis are :
Fever
Trichina roundworm infection can raise body temperatures rapidly. The fever may be high or low depending on the extent of the Trichinosis parasite infection.
Skin Rashes
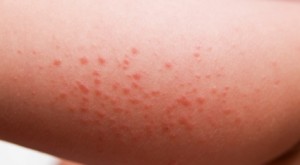
Picture 1 – Skin Rashes
Source – wrinkle-free-skin-tips
In patients of Trichinosis rashes break out in a localized area. These may disappear over time and reappear at some other region of the body.
Muscular Pain
Muscle pain usually arises a few weeks after infection when the parasite spreads to the other parts of the body. Unless quickly treated, a Trichina infection can cause pain in muscles and joints. Even simple activities like eating and talking can hurt a lot.
Respiratory Difficulties
If the parasites infect the respiratory muscles, the person may experience breathing difficulties. Mere breathing of air in and out can cause pain.
Diarrhea
Parasitic infection of the intestinal tract can give rise to diarrheic symptoms. The sufferer experiences intestinal swelling and abdominal pain and passes watery stools. Diarrhea is one of the major symptoms of Trichinosis.
Fatigue
Even little physical activity can make a person with Trichinosis quite tired. This fatigue can impair daily activities of the person. It is one of the main pork Trichinosis symptoms.
Facial Swelling
The condition gives rise to inflammation of the face, particularly around the eyes.
Eosinophilia
This disease is marked by a rise in the number of Eosinophils, a type of white blood cells (WBC), in the blood stream. Eosinophilia arises as a response to Trichina infection in the body.
Trichinosis Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Trichinosis is done by observation, inquiry and testing.
Trichinosis Observation
A swollen face along with fever, nausea and muscle pain is usually an indication of Trichinosis.
Trichinosis Inquiry
A medical professional asks whether the patient had been eating undercooked meat lately. The medical history of the sufferer is also taken into account.
Trichinosis Testing
If the doctor suspects Trichinosis, he/she may advise a blood examination. A blood test shows whether there is a rise in the number of Eosinophils in the bloodstream. A positive result indicates a Trichina infection.
In some cases, a biopsy of a muscle tissue is needed. A sample of the muscular tissue of the sufferer is examined under a microscope in the laboratory to detect the presence of Trichina larvae.
CT Scans are sometimes required to detect the presence of muscle cysts.
Serious cases of Trichinosis lead to neurological and cardiac problems. MRI scans can show any neurological abnormalities. Chest X-Rays can help evaluate if there is any lung involvement.
How Is Trichinosis Eradicated?
There is no specific Trichina cure. Early Trichinosis treatment prevents further development of the condition. Anthelmintics like Albendazole and Mebendazole, if administered within the first three days of infection, can decrease the development of larvae.
Once the infection goes away, steroidal medicines like Pyrantel and Prednisone may be used to provide relief from pain that arises from spreading of larva.
In severe cases of Trichinosis, immediate hospitalization is required. Supportive care is also needed. In people having heart complications due to Trichinosis, pacemaker is needed to bring heartbeats back to normalcy.
Treatment of Trichinosis
Trichinosis patients suffering from diarrhea can drink clear liquids like water, apple juice, sports drinks or weak tea to provide temporary relief to their bowels. One should also drink fluids as often as possible to avoid dehydration.
Diet for Trichinosis sufferers should include soft starchy foods like eggs, bananas, rice, toast, applesauce, plain noodles and gelatin. Food items like alcohol, fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, spicy and fatty items should be excluded.
Pressing hot water bottles and pads against the abdomen can be very effective in providing relief in case of acute pain and cramps in the stomach.
What If Trichinosis Goes Untreated?
Unless treated in time, Trichinosis can cause fatal health complications. There can be serious respiratory difficulties. The condition can result in neurological and cardiologic problems which are, fortunately, not too common. The sufferer may even die due to such complications. Death is, however, rare in cases where there are no such complicated conditions.
Trichinosis Deaths
In serious cases of Trichinosis deaths may happen due to complicated conditions like Encephalitis. Encephalitis is characterized by swelling of the brain tissue. Trichinosis of the brain can also lead to Meningitis. Meningitis results in swelling of the lining of the brain. Both Encephalitis and Meningitis can be very serious and may result in death.
Other Trichinosis complications include Myocarditis, Nephritis, Glomerulonephritis, Sinusitis and Pneumonitis.
Prevention Of Trichinosis
Uncooked meat products are the single most causative factor behind Trichinosis outbreaks. Consumption of thoroughly cooked can help you avoid this disease. Trichinosis Prevention can be done by cooking meat at high heat and storing at extremely low temperatures before eating.
Temperature To Kill Trichinosis
One should ensure that the meat, especially pork meat, is cooked at no less than 140 degree Fahrenheit.
Does Freezing Kill Trichinosis?
Storing infected meat at lower- than – 13 degree Fahrenheit for 10-12 days can kill the parasite.
Trichinosis and Pregnancy
Anthelmintics such as Mebendazole and Albendazole should not be administered to pregnant women as cure for Trichinosis. Trichinosis in pregnancy is not too common. If women have Trichinosis while pregnant, Trichina larvae can enter the muscle tissue of the fecus. In Trichinosis pregnancy can be affected. The unborn child can also be infected by the larvae from the mother. Trichinosis transmission from mother to children is a quite serious case.
Trichinosis Incubation Period
The Incubation Period for Trichinosis usually lasts for 1-2 weeks. After intestinal incubation, the early symptoms include stomach and intestinal disorder due to larval infection in the intestinal wall. If the number of parasites affecting the person is more, incubation period can last up to 45 days.
How Long Does Trichinosis Last?
Mild cases of Trichina infection can last for 3 to 5 days. Serious cases of Trichinosis can stay on for 1 to 2 months. Symptoms like fatigue, discomfort and muscular pain can last for some more months.
Trichinosis Pictures
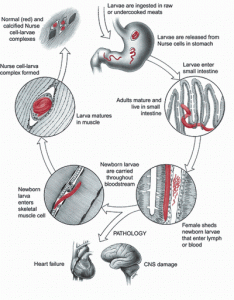
Picture 2 – Trichinosis Picture
Source – medicalook
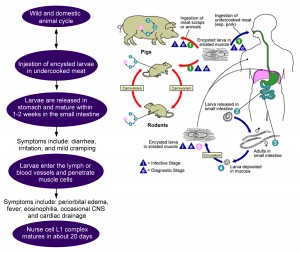
Picture 3 – Trichinosis Image
Source – medscape
Want to know how patients with Trichinosis look like? Check out these Trichinosis photos to get an idea.
Does Trichinosis Go Away?
Proper medical treatment can make Trichinosis go away faster. High doses of corticosteroids for 1-2 days can help reduce the symptoms more rapidly.
If you are experiencing Trichinosis symptoms yourself or have someone suffering from the disorder in your family, it is better to seek immediate medical attention. As aforesaid, early medical treatment can slow down the growth of Trichina larvae. It can also help prevent further health complications like Meningitis and Encephalitis.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trichinosis
http://www.medicinenet.com/trichinosis/article.htm
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/787591-overview
http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/trichinosis/Pages/Default.aspx
http://www.health.state.ny.us/diseases/communicable/trichinosis/fact_sheet.htm
http://www.mdguidelines.com/trichinosis

Trichinosis.
Why do we allow Prosciutto into the USA, when the pork (from Italy) is not cooked or frozen.
Wasn’t there a major flap many years ago with our USDaInoectoirs. I recall that “Prosciutto”
and other products was banned in the US for a number of years. The inspectors finally acquiesced when they learned that there was no trichinosis in Italy as there were no vectors (rats) in the slop.
Thank you,
W.J.Vitale, M.D.