Synovial Cyst is a cyst on the surface of some joint that occasionally causes mild to severe pain. Read on to find out all about the symptoms, treatment options and etiology of this cyst.
What is Synovial Cyst?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Synovial Cyst?
- 2 Synovial Cyst Etiology
- 3 Synovial Cyst Causes
- 4 Synovial Cyst Risk Factors
- 5 Synovial Cyst Symptoms
- 6 Synovial Cyst and Ganglion Cyst
- 7 Synovial Cyst Diagnosis
- 8 Synovial Cyst Differential Diagnosis
- 9 Synovial Cyst Treatment and Surgery
- 10 Synovial Cyst Complications
- 11 Synovial Cyst Prognosis
- 12 Synovial Cyst Recurrence Risk
- 13 Synovial Cyst Prevention
- 14 Synovial Cyst Pictures
It is a type of ganglion cyst that occurs due to some spinal degeneration. Fluid secretion from the adjacent joint into the nearby tissues generally causes this cyst. It can affect different joints in the human body, including:
- Spine
- Knee joint
- Hip joint
- Ankle joint
- Wrist
- Finger joint
- Shoulder joint
- Elbow joint
The cyst is also known as Myxoid Cyst and Mucous Cyst.
Clinical appearance of the Synovial Cyst often occurs along with osteoarthritic symptoms. The cyst is bluish or reddish in color and secretes a gelatinous fluid if punctured. It sometimes leads to Spinal Stenosis in lumbar spine.
Synovial Cyst Etiology
These cysts have a prevalence of less than 0.5% throughout the world. They generally occur in people with a history of back pain. People aged above 60 years are most likely to develop this condition. However, it can also be seen in people who aged around 40 years. In some very rare cases, Myxoid Cyst occurs in children.
Synovial Cyst Causes
The body produces a type of fluid that keeps the joints lubricated. Sometimes, this fluid may accumulate at one point to form this cyst. Some kind of erosion in facet joint located in the lumbar spine leads to these cysts. This process typically occurs in lumbar spine and grows at L4-L5 level in majority of cases. In some rare instances, however, it may also develop at the L3-L4 level.
The pain due to the cyst results from the blood flowing in the veins around the spinal nerves that are unable to drain when the spinal canal is closed. This leads to irritation and pain of the nerves. Sitting down reduces the pain by allowing the venous blood to drain and relieving the pressure.
Synovial Cyst Risk Factors
The factors that increase the risks of development of these cysts include:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Acute or chronic trauma
- Joint instability
- Various overuse injuries
Individuals who take part in repetitive activities like keyboarding and playing some musical instrument have an increased risk of having Myxoid Cysts.
Synovial Cyst Symptoms
Spinal Stenosis caused by this cyst leads to pain and inflammation in the hips and lower back that progress towards the legs. Sometimes, the symptoms caused by Synovial Cyst may resemble those of Spinal Stenosis even if the condition is not present.
Generally, patients do not experience any pain while sitting as the spinal canal is opened up in the seated position which relives the pressure on the adjacent spinal nerves. However, standing up and walking closes down the spinal canal, putting pressure on the nerves and causing pain.
Synovial Cyst and Ganglion Cyst
Both these cysts are formed by the accumulation of different fluids. The Synovial Cysts are sacs filled with the fluid that is secreted for lubricating the joints while Ganglion Cysts are formed by various fluids.
Synovial Cyst Diagnosis
Radiology is used for diagnosing their presence. Magnetic Image Resonance scan or MRI scan of the spine can detect the presence of these cysts. The MRI reports display the cysts as lesions with similar signal intensity like water.
X-rays, including flexion or extension motion x-rays can be used for ruling out the possibility of any spinal instability. Checking for spinal instability is important as the joint is suffering from degeneration. In many cases, a degenerative spondylolisthesis is associated with the condition. The degenerative spondylolisthesis indicates the instability and incompetency of the joint.
Detecting any instability of the joint before performing the surgery for treating the Synovial Cyst is very important as failing to identify and cure instability during a surgery may even require a second surgery in the future.
Synovial Cyst Differential Diagnosis
The following conditions are sometimes confused with Synovial Cyst as they are characterized by similar symptoms:
- Arthritis conditions (particularly Rheumatoid Arthritis)
- Tendon rupture
- Fracture
- Tumors nodules (particularly rheumatoid nodules)
- Tumor (malignant and benign)
Physicians should ensure that patients are actually suffering from Synovial cysts and not any of the above mentioned disorders.
Synovial Cyst Treatment and Surgery
No treatment is required for these cysts unless they are causing pain and irritation. However, it is important to keep them under observation to detect any sign of deterioration. If an individual experiences just a mild irritation, he or she should restrict the activities that are mainly causing the discomfort. There are various injections and medications that help to relieve the pain within a short time. Other conventional pain relief options like physical therapy and chiropractic can also reduce the pain. One can consider the following treatment options if the pain is too severe to carry out the daily activities.
Aspiration
Sometimes, doctors recommend draining the Synovial Cyst with a needle for relieving the pain and discomfort. Generally, neuroradiologists perform the process of aspiration. This process depends on the size and location of the cyst. The aspiration procedure is not used if the cyst is too large in size. In some instances, aspirating a lumber spine Myxoid Cyst provides only temporary relief. In these cases, a patient should seek further treatment for the condition.
Steroid Injections
This is another useful treatment option for alleviating the pain and irritation of this cyst. The steroid medication is injected into the joint where the cyst has formed. But, it is just a temporary treatment option and may not work in some cases. The maximum number of steroid injections recommended by most physicians is three per year.
Removal Surgery
Physicians may recommend a Synovial Cyst removal surgery if a patient is found to be suffering from extremely severe symptoms that cannot be treated successfully by the above treatments. Sometimes, the surgical resection involves fusing the affected joint after the initial operation because of recurrent cyst formation. This is also done when a surgeon is concerned about the spinal stability of patients. Movement of the joint can be restricted by the fusion which prevents any formation of the cyst in future. The cyst has a very low rate of recurrence after a successful surgery with or without the fusion process.
Synovial Cyst Complications
Neurological deficits like muscle weakness and numbness can cause various complications at the recovery stage of Synovial Cyst that involves the spine. Complications include poor wound healing, anesthesia and infection if surgical excision is required for treating the cyst. In some rare cases, a lumbar cyst may even require further surgery for stabilizing an unstable spine.
Synovial Cyst Prognosis
The prognosis of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms. Aspiration and corticosteroid injection successfully cures the pain and irritation in around 35% of cases while surgical excision has a 95% success rate. In most cases, the pain and irritation subsides after a patient receives proper treatment. In case of cancerous Synovial Cyst, the outcome depends on the type of cancer and how much it has spread.
Synovial Cyst Recurrence Risk
Treating Mucous Cysts by steroid injections and aspiration process has a high recurrence risk. There is 10% risk of recurrence of the Myxoid Cysts if they are removed by surgery.
Synovial Cyst Prevention
There are no known ways of preventing the formation of these cysts. However, some people believe that performing specific exercises can help to keep the joints lubricated and prevent the fluid build-up.
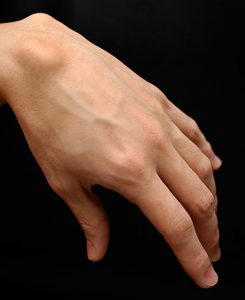
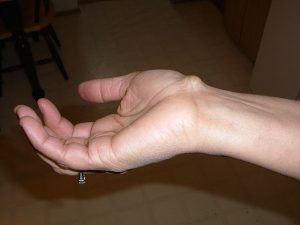
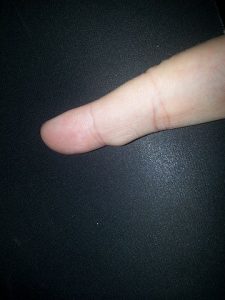
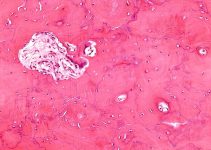
Synovial Cyst Pictures
The Following pictures show how these cysts look like.