What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Page Contents
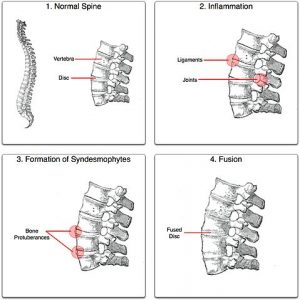
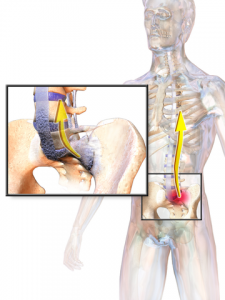
Ankylosing Spondylitis affects the spine and is a type of arthritis that inflates sacroiliac joints and facet joints resulting in spine stiffness, inflexibility and hunched forward position. Sometimes ribs get affected by inflammation and make breathing difficult.
The disease causes calcium accumulation in spine’s discs and ligaments allowing the soft frames to stiffen which fuse together with vertebral bodies and joints. This illness makes the backbone, brittle, laborious and prone to fracture. In advanced cases, swelling develops new bone on the spine leading to abnormality or disfigurement. Ankylosing Spondylitis also stiffens other parts of the body like knees, shoulders, and hips. It affects men more than women, wherein signs and symptoms begin in early adulthood.
Causes
Ankylosing Spondylitis is assumed to be inherited genetically, but maximum patients with this disease have HLA-B27 gene. However, the relationship between this gene and the disease is yet unknown. Several tests have been developed to have a better understanding. However, some additional factors like poor posture and environmental factors intensify the disease.
Symptoms
- Stiffness and Pain: Affects sacroiliac joints, but can gradually influence hips, low back and buttocks.
- Pain in tendons and ligaments: Tendonitis (swelling of tendon) stiffens and causes pain.
- Bony Fusion: Bones overgrow leading to unusual bone joining that affects the back, neck and hips troubling a person to perform regular activities.
- Cardiac Lesions: People experience severe swelling at the base of the heart, near aorta and aortic valve. The stable inflammation results in lesions. Less than 2% of patients suffer from this.
- Cauda Equina Syndrome: Patients sometimes undergo neurological deficits like balance loss, trouble speaking or bladder and bowel incontinence. It results from compression on the nerve in the rear of the spine.
Other Symptoms
- Chest Pain
- Back Pain( Specifically in morning and night)
- Appetite loss
- Morning stiffness
- Stooped shoulders or poor posture
- Low iron levels or anemia
- Weight loss
- Minimum fever level
- Decreased lung function
Symptoms of Other Body Parts
- Bowel Inflammation
- Heart Valve Swelling
- Iris Inflammation
- Headache
- Pain around the eye or eye pain
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
Risk Factors
- Hereditary: People with a family history of this disease are prone to this problem.
- Age: It is unlike rheumatic or arthritic disorders and symptoms might appear in people aged between 20-40 years.
- Ethnicity: Common in Caucasian descent people than African descent or other cultures.
- Related Disease: Present or history of Crohn’s disease, psoriasis or ulcerative colitis increases the chances of developing Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Bacteria: Microbiota are bacteria present in intestines which regulate and develop the immune system, these are believed to develop this disease.
Diagnosis
- Physical Exam: A rheumatologist will perform a thorough exam, and might ask details about the symptoms, pain, etc.
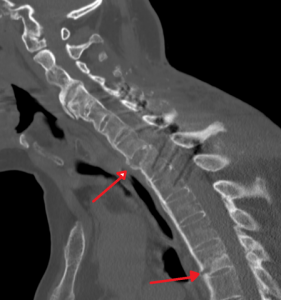
- X-Ray: It helps to know whether there is an erosion of the spine or any joints. However, corrosion is detected when the disease is in the last stage. Experts might also ask for an MRI, but sometimes the results are hard to interpret.
- Blood Test: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a blood test which measures the inflammation. Test for HLA-B27 is also done to evaluate if the protein is present.
Treatment
Therapy can help to minimize the pain and inhibit disability. Timely treatment can diminish symptoms and hinder complications.
Medications
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like naproxen and ibuprofen helps to manage pain and inflammation. These are ideal long-acting drugs for meager complications. Stronger medicines are recommended when NSAIDs do not provide sufficient relief.
Corticosteroids are usually prescriptive for a shorter duration. It is a strong inflammation fighter, and helps to alleviate symptoms and reduces damage around the area.
TNF (Tumor necrosis factor) are medicines that block causes of inflammation and decreases stiffness and joint pain. TNF inhibitors help to aid the progressed condition when NSAIDs are not effective.
In severe cases, the expert provides DMARDs, (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs). These medicines slow down the disease and help to hinder worsening symptoms.
Surgery
In severe cases, deformity or damage of hip or knee joints takes place and replacement surgery is essential. Likely, the osteotomy is performed with lousy posture evoked by fused bones. In this procedure, surgeons realign or cut the bones in the spine to maintain the perfect shape. However, treatment depends entirely upon the severity of the condition and the intensity of its symptoms.
Natural Treatment
- Stretching: Makes bone stronger with flexible joints. It reduces pain through better body movements.
- Exercise: Motion exercises with proper strength training helps to alleviate the signs of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Activities make joint bones flexible and reduce pain. A physical therapist will help to perform the exercises safely and correctly. Deep breathing, yoga practices, swimming, are ideal.
- Posture Training: Spine stiffness results in bad posture which allows the spine bones to fuse jointly in slumping or slouching positions. But patients can reduce this risk easily by practicing good posture.
- Acupuncture: It helps to activate the natural pain relieving hormones.
- Heat & Cold Therapy: Warm shower or heating pads helps to relieve stiffness and pain in the spine or other affected areas. Ice packs can lessen swelling and pain from joints or bones.
- Massage Therapy: Helps to increase flexibility and motion range. To make the therapist aware of the tender points, inform them about the disease.
Complications
- Breathing Difficulty
- Bowel, lung or heart damage
- Eye Irritation
- Contraction of the spine
- Vertebrae might fuse together due to severe inflammation
- Inflammation in tendons and ligaments can worsen flexibility
- Inflammation can extend to shoulders, hips and nearby joints
Prevention
- Retaining a standard body weight
- Healthy diet
- Staying active
- Correct posture
Ankylosing Spondylitis Pictures
Diet
- Include foods full of omega -3 fatty acids, like nuts, fish and oils
- Include different types of green vegetables and fruits
- Yogurt
- Whole grains, like faro and quinoa
Eliminate diet that is rich in sugar, fat and sodium. Processed foods like bagged, boxed, canned foods etc. contain unhealthy ingredients like Trans fats and preservatives which can worsen the inflammation. Limit alcohol intake as it interacts with medicines and makes the situation worse. It doesn’t allow the medication to work and symptoms tend to intensify.