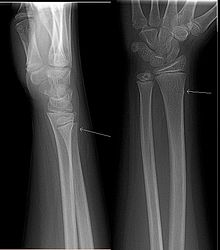
Greenstick fracture is a broken bone condition that affects many infants and young children. Read on to know what Greenstick fracture is as well as its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Greenstick Fracture Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Greenstick Fracture Definition
- 2 Greenstick Fracture Meaning
- 3 Greenstick Fracture Symptoms
- 4 Greenstick Fracture Causes
- 5 Greenstick Fracture Diagnosis
- 6 Greenstick Fracture Treatment
- 7 Greenstick Fracture Surgery
- 8 Greenstick Fracture Prognosis
- 9 Greenstick Fracture in Forearm
- 10 Greenstick Fracture in Tibia
- 11 Greenstick Fractures in Children
- 12 Greenstick Fracture Pictures
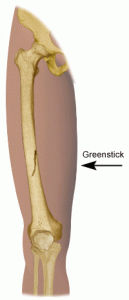
Picture 1 – Greenstick Fracture
It is a form of mild bone fracture that is characterized by bending or partial breaking of soft bones. It is also referred to as Buckle fracture or Torus fracture. The condition is often seen in young children.
Greenstick Fracture Meaning
When a young twig is bent and broken, part of it breaks while the other side remains stressed but unbroken. “Greenstick Fracture” owes its name to this analogy.
Greenstick Fracture Symptoms
Certain features of this type of fracture are similar to those seen in standard long bone fractures. A standard fracture of this type gives rise to problems like,
- Pain in fractured region
- Redness
- Bruises
- Inflammation
The condition typically results in bending of the bone as opposed to distinguishable deformities such as breaking. These are stable fractures as a section of the bone remains unbroken. Acute pain and deformities typical of other fractures is usually minimal or absent in this condition.
Greenstick Fracture Causes
This fracture is commonly a result of a fall which may lead to the bending of a bone. It may also be caused due to a blunt injury, such as a blow. The condition is most common in childhood when kids are likely to suffer a fall the most while participating in sports or playing.
This fracture mostly affects the arm bones due to the natural human impulse of extending the arms for supporting the body during a fall.
Greenstick Fracture Diagnosis
It is difficult to diagnose this fracture as it does not lead to the same symptoms as other broken bone conditions. Furthermore, it is quite hard to differentiate it from soft-tissue injuries, such as a bad bruise or a sprain.
Medical imaging tests like CT scans or X-rays are often used to detect this problem. In some cases, doctors also use X-ray images of the uninjured limb to compare it with those of the injured one. This can help reveal any abnormalities that might go undetected otherwise. Sometimes, Greenstick fractures in the soft bones of a child do not show up well in X-rays. In such cases, a Computerized Tomography (CT) scan or an Ultrasound scan may render better images.
Greenstick Fracture Treatment
Treatment of a Greenstick Fracture requires subjugating the fracture. This is typically done by mildly pulling the bone apart a bit and then pushing it into position to help it straighten as before. The affected limb is then put by doctors into a cast and immobilized. This helps the bone grow back and ensures complete healing of fractures.
Casts are the standard method of restricting bone motility. However, doctors may also recommend a removable splint if they feel that it can provide the same benefits. A splint is a better option in that a child can easily take it off during a shower or a bath. In children suffering from Greenstick fractures of the distal radius, removable splints are also found to yield better results. Traditionally, Buckle fractures are put in casts that are made either above or below the elbow.
Nowadays, most casts are manufactured by using a water-resistant material. These are available in various colors and designs. However, a child with a fractured limb should not swim unless the cast lining is also waterproof.
Greenstick Fracture Surgery
Most torus fractures heal entirely after being subjugated and put into a cast. However, the fracture fails to heal properly in some individuals. A surgery is needed for treatment of such cases. An operative approach is highly rare, particularly in cases where the fracture is addressed very quickly and the bone is kept free from stress (such as bearing weight) while it heals.
Greenstick Fracture Prognosis
The healing time for this condition is often very quick. Once this condition subsides, it is not generally as painful as some other types of fractures. Bones of children tend to heal faster than those of adults. However, the splint or cast of children may be replaced or removed with a smaller cast in as little time as three to four weeks.
Greenstick Fracture in Forearm
Greenstick fractures commonly affect the forearm region. The fracture extends through a section of the bone and causes it to bend on the other side. The bone cracks only on one side and the other slope remains intact. Greenstick forearm fractures are unique to children and hardly ever seen in adults. This forearm fracture can appear extremely crooked and requires some effort to be straightened.
Greenstick Fracture in Tibia
In young kids, these fractures often affect the Tibia (shin bone). The fractures usually occur due to a fall while playing or indulging in sports activities. A child with a fractured tibia is unable to walk or stand for several weeks. The area is put in a cast. It generally requires about six weeks for healing.
Greenstick Fractures in Children
This condition is very common in children. This is due to the fact that the bones of a child are much more flexible than adult bone and more susceptible to damage due to their softness. In children, these are often mistaken for soft tissue injuries that occur after a trauma. In children suffering from these fractures, the cause is often revealed to be a traumatic force implemented to the area. The trauma can result from a direct hit or due to a fall. This usually gives rise to discomforting symptoms like,
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Inflammation
- Restricted movement of the region
Very young children, who are unable to express the cause of their discomfort, may cry uncontrollably in case of Buckle fractures.
Greenstick Fracture Pictures
Here are some Greenstick Fracture photos that will help you get a visual idea about the condition. You may find these Greenstick Fracture images quite useful for your reference.
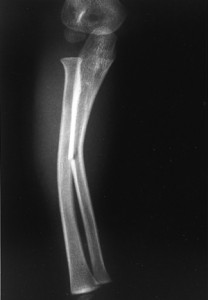
Picture 2 – Greenstick Fracture Image
If your kid has got a Greenstick fracture, immediately get in touch with an orthopedist and seek appropriate medical care. Timely care and treatment will help your child make a faster recovery and let the fractured area heal without much discomfort.
References:
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/greenstick-fractures/DS00817
http://www.bonesfracture.net/index.php/2011/09/greenstick-fracture/
http://www.kidsfractures.com/forearm/
http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=a00039