Are you experiencing a sharp or gnawing pain in your ribs? Chances are that you might be suffering from a musculoskeletal disorder known as Costochondritis. Read and know all about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of this disorder.
What is Costochondritis?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Costochondritis?
- 2 Costochondritis ICD 9 Code
- 3 Costochondritis Incidence
- 4 Costochondritis Types
- 5 Acute Costochondritis
- 6 Chronic Costochondritis
- 7 Costochondritis Symptoms
- 8 Costochondritis in Children
- 9 Costochondritis Causes
- 10 Costochondritis and Fibromyalgia
- 11 Costochondritis Diagnosis
- 12 Costochondritis Differential Diagnosis
- 13 Costochondritis Treatment
- 14 Costochondritis Prognosis
- 15 Costochondritis Risk Factors
- 16 Costochondritis Home Remedies
- 17 Costochondritis Prevention
It is a condition marked by the swelling of the cartilage that joins the rib to the sternum or breastbone, a junction referred to as the costosternal joint.
Costochondritis ICD 9 Code
The ICD 9 Code for this condition is 733.6.
Costochondritis Incidence
This condition is a common cause of chest pain in adolescents and children. According to doctors, approximately 650,000 cases of chest pain arise every year in young people of age group 10-21 years. The peak age for the occurrence of this disease is 12-14 years.
Costochondritis Types
The condition is usually classified into two types:
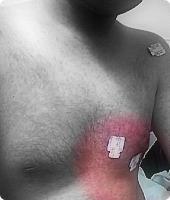
Picture 1 – Costochondritis
Inflammatory Costochondritis
It is characterized by inflammation or swelling of the region. The cause of inflammation in sufferers is unknown.
Infectious Costochondritis
This form can arise due to a bacterial or fungal infection of the affected spot. It may also arise as a post-surgical or a post-traumatic infection which can occur months after a surgery on the area or an injury to the affected region.
Acute Costochondritis
It is a form of Costochondritis that often arises after an upper respiratory infection or chest surgery. When it develops after surgery, a bacterial infection is the most possible cause. The condition responds to antibiotics in such cases. When it arises after a viral respiratory infection, the condition is most likely to resolve on its own in a matter of few weeks.
In some individuals, the problem follows a specific trauma or injury to the chest area. In a few cases, such as in athletes and sportsmen, it may develop after a series of minor traumas. Acute cases of Costochondritis, arising after trauma, also resolve in 4-6 weeks even in the absence of a specific treatment.
Chronic Costochondritis
It is defined as the swelling of the bones and cartilage of the chest wall that gives rise to chest pain. The inflammation does not have any definite cause. Chronic cases of this condition are too difficult to diagnose. Doctors often mistake the painful symptoms as effects of depression and end up prescribing anti-depressants to patients. They refuse to believe continual complaints of pain from sufferers. The disorder is also often mistaken for Tietze’s Syndrome.
In this condition, patients may suffer from painful symptoms in the sides of the ribs, the sternum or the frontal region of the chest.
Costochondritis Symptoms
The disease is usually characterized by tenderness and pain in the costosternal joint. In the majority of sufferers, the pain is acute although it can be dull and gnawing in some people. The disorder may affect any of the seven costo-chondral joints. The pain is found to arise in more than one area in 90% cases. The painful sensations usually arise more frequently on the left region of the breastbone although these may be experienced on either side of the chest.
In some individuals, the pain may radiate to the abdomen or the back. The fourth, fifth and sixth ribs are the most common spots where pain can be experienced. Pain tends to increase on taking deep breaths or while the trunk is moved. The painful sensations decrease as the breathing becomes slower or when the trunk movement is stopped.
Some other less common signs and symptoms of this disorder include:
- Pain during coughing
- Breathing difficulties
- Tenderness on pressing the rib joints
Pain is usually experienced in reclining or sitting postures. Stress is known to worsen the sensation. In Costochondritis, there is no inflammation in the affected region. This is where it differs from Tietze’s Syndrome, another condition that is similar to Costochondritis in all respects except the fact that the former involves inflammation. When Costochondritis is associated with Tietze’s Syndrome, pain is generally accompanied by inflammation and/or redness in the most tender regions of the body. The discomforting sensations may linger all though the life of an individual when the condition is related with autoimmune disorders like PBC.
Costochondritis in Children
As aforementioned, this condition is a common cause of chest pain in children. It is said to account for 10-30% of all cases of chest pain in kids. Usually, chest ache in children arise after an upper respiratory infection or minor trauma (injury). Affected children usually suffer from pain and other discomforting symptoms in the heart and lungs.
If painkillers, medications, changes in lifestyle and other non-invasive measures fail to improve the condition, doctors may recommend surgical ablation of a sore cartilage. Medical attention should be sought on an emergency basis if a child with this condition begins to suffer from respiratory problems, high fever, palpitations and an acute increase in pain.
Costochondritis Causes
As already said, the condition arises due to swelling of the joints located between the cartilages that attach the ribs and the breastbone (sternum). Generally, it is not clear why the inflammation occurs. However, some possible causes of this condition are believed to be:
Physical strain
Too much physical effort, in the form of heavy lifting and strenuous exercise, has been linked to the development of this condition. Severe coughing has also been considered to be a possible cause.
Trauma
An injury in the chest in the form of a blow or strike could also give rise to this problem.
Joint infection
An infection of the rib joint by microbes, such as bacteria, fungi or virus may also lead to the problem. Conditions like Aspergillosis, Syphilis and Tuberculosis are common examples of rib joint infection.
Tumors
The condition may also arise due to cancerous and noncancerous tumors. Cancer may shift to the rib joint from any other area such as the lung, breast or thyroid.
Arthritis
In some individuals, the development of this disorder has been associated to particular problems like Ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Costochondritis and Fibromyalgia
Chronic cases of Costochondritis commonly develop as a symptom of Fibromyalgia, a rheumatic condition characterized by widespread muscular pain. About 60-70% of all patients of Fibromyalgia suffer from this disorder at some point of their lives. Fibromyalgia patients may suffer from episodic pain and other discomforting symptoms of Costochondritis that persist for an indefinite period all through their lives.
In cases where the disease arises from Fibromyalgia, chest pain can vary from a gnawing discomfort in the rib cage to acute aches in the region close to the upper sternum (frequently on the left side). Patients usually feel soreness while touching their ribs. Repetitive activities, such as sitting before a computer, are believed to aggravate the condition.
Costochondritis Diagnosis
The condition is usually diagnosed by a physical examination of the tender and painful region. During exam, doctors touch the areas along the breastbone to sense any swelling or tenderness. They also ask patients to move their arms or rib cage in certain ways that can help trigger the symptoms in sufferers.
Costochondritis Differential Diagnosis
The painful sensations arising due to this condition are often quite similar to the aches related to osteoarthritis, gastrointestinal problems, lung disease and heart disease. Differential diagnosis of this disorder involves carrying out various tests, such as an electrocardiogram or a chest X-ray, to rule out such problems. There is no specific imaging test or laboratory exam to confirm a diagnosis of this disorder.
Costochondritis Treatment
The condition generally resolves on its own and does not need any treatment. In some cases, however, the disease persists for several months or even more. Treatment usually aims at relieving pain in sufferers. This can be done with the aid of:
Medicines
Many people use over-the-counter pain relievers to manage aches. If that does not help, a visit to doctors is necessary. Physicians may recommend use of medications like:
NSAIDs
Doctors might prescribe Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like naproxen (Aleve) and ibuprofen (such as Motrin or Advil). Lighter strengths of these medicines can be purchased over-the-counter while stronger varieties need to be purchased by prescription.
Antidepressants
These classes of drugs include Tricyclic antidepressants like Amitriptyline that are often used to manage chronic pain — particularly those that make patients unable to sleep at night.
Anti-seizure drugs
The epilepsy medication Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin and others) has also be proven effective in managing chronic pain in sufferers.
Narcotics
In case of severe pain, doctors might prescribe narcotic drugs that contain codeine, such as Oxycodone (Roxilox,Percocet and others) or Hydrocodone (Vicodin, Lortab, others). However, use of narcotics is not generally recommended as patients may get addicted to these drugs.
Therapy
The condition can be effectively treated with the aid of physical therapy, which might involve:
Nerve stimulation
This is actually a process known as Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), in which a weak electrical current is sent by a device through adhesive patches on the skin close to the painful region. This may block out or disrupt painful signals, thus preventing them from reaching the brain.
Stretching exercises
In some patients, gentle range-of-motion workouts may be effective in bringing about an improvement.
Operative techniques
If conservative measures fail to improve the symptoms, physicians may suggest directly injecting a corticosteroid and a numbing medication into the joint that is painful.
Costochondritis Prognosis
With proper treatment, the condition usually subsides or even resolves within a few days or weeks.
Costochondritis Risk Factors
The condition frequently arises in women and in individuals aged over 40 years. People suffering from infections and those lifting heavy objects on a daily basis are also highly susceptible to this disorder.
Costochondritis Home Remedies
It can be really depressing for patients to know that medical treatment can do little to cure this condition. However, there are some self-care measures that can add to the comfort of patients and help them manage the condition in a much better way. These include:
Picture 2 – Costochondritis Image
Over-the-counter pain relievers
Naproxen (Aleve), Ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) can be effectual in managing the symptoms of this disease.
Ice or Heat
Application of ice or heat on the painful region of the body can help relieve the symptoms. Pressing a heating pad or application of hot compresses to the painful region for several times a day may be effective in improving the condition.
Rest
Avoiding activities that worsen the painful symptoms can be effective in relieving the discomfort. Providing ample rest to the injured region can be quite helpful in help patients manage the symptoms much better.
Costochondritis Prevention
There is no specific way to prevent this condition, as it exact cause is often unknown. Some evidence suggests that children who carry heavy school bags, particularly over one shoulder, are more prone to this disorder. The condition is also linked to strenuous exercise, heavy lifting and upper respiratory infections.
The risk of getting this condition is also likely to be avoided by following some general preventive steps like:
Adjusting school bags
Adjust the weight of the bag of your child to make it as less heavy as possible. A heavy bag or satchel makes the shoulders slump and can give rise to this condition. Teach child how to carry his/her bag in the most appropriate way to avoid this problem.
Avoid trigger activities
Certain physical activities are found to trigger painful symptoms in chest or worsen an already existing ache. Ask your doctor about safety measures that should be practiced while lifting or performing exercises to prevent chest tenderness and pain resulting from physical exertion.
Maintaining good health and hygiene
The condition is also believed possible to be kept away by avoiding infection. Practice good hygiene to avoid development of a respiratory infection. Wash your hands frequently and thoroughly. Avoid sharing clothes, utensils or drinking glasses with others. Limit your exposure to infected people to avoid contracting the ailment.
Costochondritis is generally harmless and goes away after sometime even without medical treatment. However, you should seek emergency medical attention in case of severe and persistent chest pain or discomfort in yourself or any family member. Make a list of all the symptoms, medicines that you may be taking and other possible causes of the disease that might help doctors diagnose the condition more easily. The clearer you describe your symptoms, the better it will be for your doctor to diagnose and treat your condition.
References:
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/costochondritis/DS00626
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/costochondritis/article_em.htm
http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/costochondritis
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000164.htm