Are you undergoing frequent anxiety pangs or unintentional weight loss of late? If yes, you are most probably suffering from Hashitoxicosis. Read and know more about this rare condition, including its incidence, symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment.
Hashitoxicosis Definition
Page Contents
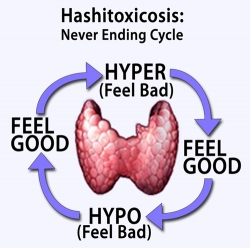
It is a condition of the thyroid gland where affected individuals display frequent episodes of hyperthyroidism. This hyperthyroid phase is usually transient. It is generally considered to be an autoimmune condition where the thyroid gland produces increased amount of thyroid hormone. Inflammation of the thyroid gland is abrupt during this condition.
Hashitoxicosis Incidence
Picture 1 – Hashitoxicosis
It commonly affects the middle-aged population, especially women who are undergoing menopause. It may also affect children between 3 to 12 years of age.
Hashitoxicosis Symptoms
Some of the main signs and symptoms of this condition are:
Anxiety
Patients may have an unusual feeling of nervousness and restlessness, which is a very common symptom observed during this condition. They may also suffer from irritability and depression.
Panic Disorder
It is a type of anxiety disorder where patients may undergo sudden attacks of intense fear and always have a sense of some terrible event that they feel may occur soon.
Mania
It is manifested by elevated mood or energy levels. Individuals suffering from this disorder may become excited and behave in an abnormal manner.
Hyperactivity
Patients tend to be abnormally active during the transient phase of hyperthyroidism.
Weight Loss
High thyroid hormone levels in the body increase the rate at which food is metabolized, causing unintended weight loss despite increased appetite.
Weakness
Increased levels of thyroid hormone in the body may lead to chronic tiredness and listlessness.
Intolerance to heat
Hyperthyroidism can lead to increased or profuse sweating in affected people, typically accompanied by unusual heat intolerance. Patients may feel hot and sweat even during cold conditions.
Menstrual Irregularities
Women with this inflammatory thyroid condition may suffer from irregular menstrual periods and vaginal bleeding.
Mood swings
Affected patients may easily get agitated and feel stressed and impatient.
Insomnia
Hyperthyroidism can cause sleeplessness in some patients.
Tremors
Mild muscular tremors, especially in the hands and tongue, are quite apparent in affected patients.
Palpitations
Accelerated heart or pulse rate under normal conditions may occur due to shortness of breath.
Lightheadedness
It is an unpleasant sensation of dizziness that is recurrent in patients with elevated levels of thyroid hormone.
Nausea
Acute discomfort in the abdominal region generates an involuntary urge to vomit in patients.
Diarrhea
Higher levels of thyroid hormone in the body may result in Diarrhea in certain patients. Frequent bowel movements, along with abdominal cramping, may also lead to reduced appetite.
Visual distortion
During hyperthyroid phase, certain patients may complain of eye irritation or blurred vision. They may exhibit blood shot or red eyes, accompanied by intense pain and visual problems.
Loss of libido
Low thyroid hormone levels may lead to decreased sexual libido in both men and women during this condition. Such patients may have little or no interest in sexual activities.
Photophobia
In some patients, light sensitivity or intolerance may develop. Such people may suffer from extreme discomfort in eye on exposure to bright lights or glare.
Noise Sensitivity
Mild irritation or intolerance towards any form of noise or sound may cause headache and annoyance in a few patients.
Patients of this disorder may experience several symptoms that change over time and may eventually develop into Permanent Hypothyroidism.
Hashitoxicosis Causes
Causes of this specific disorder are found to be nearly similar to other Hyperthyroid conditions, leading to abnormal increase in thyroid hormone levels. Some of the main causative factors of this ailment include:
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
It is an autoimmune disorder that causes excess secretion of Thyroid hormone and is normally associated with this hyperthyroid phase. In this condition, the body is not able to recognize the thyroid gland and attacks it by a variety of cell-antibody-mediated immune processes. Affected patients may experience phases of hyperthyroidism before the onset of hypothyroid phase. These hyperthyroidism spells are known to cause Hashitoxicosis. Medical experts believe that a certain virus or bacterium may trigger this autoimmune response. However, this theory remains unexplained as yet.
Graves’ disease
It is another autoimmune condition where the thyroid gland becomes overactive, producing excessive amount of thyroid hormones. It causes serious hormonal imbalance where thyroid autoantibodies (TSHR-Ab), activating the TSH-receptor (TSHR) is released in excess. This further stimulates thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion. It is also manifested by intense thyroid growth.
Heredity
Genetic conditions may also lead to an abnormal secretion of thyroid hormone that is unwittingly transmitted from generation to generation.
Hashitoxicosis Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disorder normally begins with an extensive physical examination. Physicians simply observe the major symptoms of this condition such as weight loss, high pulse rate and sluggishness. This is generally followed by few diagnostic tests in order to detect the exact condition.
Hormone test
This is a simple blood test conducted to monitor the levels of thyroid hormone. Elevated hormone levels indicate abnormality in the thyroid gland.
Antibody test
This diagnostic technique can help detect whether Hashimoto’s disease is the cause of this disorder. Increased levels of antibodies, produced in blood as a reaction to enhanced thyroid secretion, confirms the presence of this disorder.
Biopsy
Hurthle cells present in the thyroid gland undergo modification due to an over-activity of the thyroid gland. During a thyroid biopsy, physicians can determine whether the thyroid cells have enlarged in size.
Hashitoxicosis Treatment
Hyperthyroidism, if left untreated for a prolonged duration, may lead to Osteoporosis in the middle-aged population. Naturally, it requires professional medical treatment. This involves use of:
Picture 2 – Hashitoxicosis Image
Medication
Lower doses of beta-blockers or anti-thyroid drugs are usually administered to affected patients for a short duration. Some patients are also given anti-anxiety medications for the treatment of anxiety disorders, such as Benzodiazepines and anti-depressants.
Thyroidectomy
It is the total or partial removal of the thyroid gland by surgical means. It is a common procedure and is generally recommended by physicians when long-term use of medications becomes ineffective. Post-surgery however, there could be several potential complications including permanent voice change or deficiency in calcium levels.
Thyroid ablation
It is a radioactive iodine treatment that is normally conducted after complete thyroidectomy to destroy any remaining thyroid tissues. In certain cases, the entire thyroid is completely excised or ablated. Ablation usually depends on the degree of severity of the condition.
Hashitoxicosis is only a temporary inflammation of the thyroid gland that does not lead to any major complications. Patients can always go back to living a normal and healthy life by undergoing appropriate treatment procedures under an experienced health expert.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hashitoxicosis
http://elaine-moore.suite101.com/hashitoxicosis-update-a121050
http://jim-lowrance.suite101.com/conditions-related-to-hashimotos-thyroiditis-a137630