What is Hyperthermia?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Hyperthermia?
- 2 Difference between Hypothermia & Hyperthermia
- 3 Hyperthermia often confused with fever
- 4 Stages of Hyperthermia
- 5 Causes of hyperthermia
- 6 Symptoms of hyperthermia
- 7 Who are at risk?
- 8 Diagnosis of hyperthermia
- 9 Treatment for hyperthermia
- 10 Home remedies for hyperthermia
- 11 Homeopathic medications for Hyperthermia
- 12 Expected Duration of Hyperthermia
- 13 When to call a doctor?
- 14 Prognosis
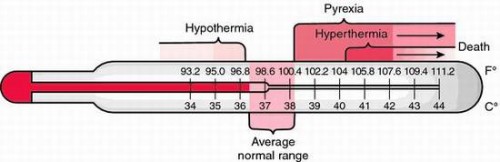
Hyperthermia is a condition that happens due to a steep rise in the body temperature above 104° Fahrenheit or 40° Celsius. It is a kind of heat illness that is common among patients admitted to the emergency department. In this situation, the heat regulation system of the body fails to handle the heat in the surrounding environment.
Difference between Hypothermia & Hyperthermia
Hypothermia is the condition when the body temperature falls extremely low leading to dangerous outcomes. It usually occurs when the body temperature touches or goes below 95°F (35°C).
On the contrary, as mentioned above hyperthermia is a condition when the body temperature rises very high to uncontrollable levels. Both of these are considered as a case of medical emergency.
Hyperthermia often confused with fever
Although, at times it is confused with fever, it is a completely different case. While sick, the body temperature rises to fight out the infectious materials entered into the body and as a result, the temperature is high on the thermometer.
But in case of hyperthermia, the body temperature rises but not on purpose. In this case, the heating and cooling mechanisms of the body become uncontrollable and the body cannot get rid of the heat.
Stages of Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia occurs on many levels. They are:
- Heat Stress: It is a condition when the temperature starts climbing and the affected person is unable to cool himself/herself through sweating. It may lead to serious complications like heat exhaustion or stroke. Dizziness, nausea, weakness, headache and constant thirst are some of the common symptoms. It is advised that in such an event, the patient move to a cooler place and drinks lots of water or fluids that are high on electrolytes. Doing so will keep the body hydrated and help in regulating the heart rate, muscle health and nerve function.
- Heat Fatigue: Working in high heat may cause discomfort or psychological stress and result in heat fatigue. People who are not comfortable to work in hot weather are highly vulnerable to such a situation. Symptoms such as feeling hot, tired and thirsty are coupled with physical strain. It’s advised to get out of the troubled area and drink loads of fluids.
- Heat Syncope: It is a situation when the blood pressure drops considerably followed by reduced blood flow in the brain and accompanied by fainting. Essentially a result of working in a very hot environment, patient is advised to consume beta-blockers for lowering the blood pressure. Lightheadedness and dizziness are the common symptoms before a person faints. It’s best to relax, drink lots of fluids and move to a cooler area.
- Heat cramps: It is a condition that usually occurs after an intense exertion or exercise. It is fallout of electrolyte imbalance that is typically felt around the leg, arm or abdomen region. Moving to a cooler place and drinking lots of fluids rich in electrolytes are essential to get relieved.
- Heat edema: This may happen when a person stands or sits in a heated area for a considerable period of time. The lower legs, ankles and hands tend to swell due to fluid buildup in the extremities. In medical terms, it is defined as a response that involves aldosterone-stimulated re-absorption of sodium in the blood through the kidneys. It spontaneously subsidizes over time once a person gets used to the environment. The best remedy would be to cool down and put the feet up besides keeping the body dehydrated.
- Heat Rash: Actively working in heated conditions for a long period can result in red pimple like bumps on the skin. It mostly develops beneath the clothing that has soaked with sweat. They usually disappear on their own after cooling down and changing clothes.
- Heat exhaustion: Being the most critical stages, it happens when the body is unable to cool on its own. Besides sweating, the common symptoms include dizziness, thirst, weakness, rapid pulse, concentration and coordination issues. It is referred to as the last stage before the heat stroke, hence it’s really important to rest and stay hydrated as soon these symptoms start emerging.
Causes of hyperthermia
Hyperthermia may occur if the standard body temperature control system is not able to regulate the internal temperature levels. Usually, when the outside temperature is remarkably high, the body temperature tends to cool itself through sweating and evaporation of the heat. But at times, the cooling mechanism becomes ineffective resulting in hyperthermic conditions. Consequently in high humid areas, evaporation through sweating will not be possible and the body heat cannot be released easily.
There may be several underlying causes for Hyperthermia which include:
- Overexertion
- Extended exposure to heat
- Underlying medical condition
- Side effects of medicines
- Inadequate fluid intakes
- Excessive loss of fluids
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Dehydration
Symptoms of hyperthermia
- Heat-related illness
- Muscle cramps
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weakness
- Elevated heart rate
- Reddened skin
- Reduced sweating
- Confusion
- Brain damage
- Normal to elevated temperature usually greater than 40.5 degrees
- Dehydration
- Hot, dry skin
- Irritability
- Coordination issues
- Flushed skin
- Weak or rapid pulse beat
Who are at risk?
- Athletes exercising hard in hot climatic conditions
- Older people of 65 years or above
- Infants and small children within four years
- Cardiac patients
- Patients suffering from dehydration
- Patients prone to infection
- Intake of medicines to increase sweat or heat production
- People working in hot environments
- Exposure to heat for a prolonged time
- People working around large ovens
- High-pressure patients
- Diuretics
- Overweight people
- People with mental illness
- Chronically ill people
Diagnosis of hyperthermia
Proper examination should be done to diagnose this disease as most people tend to confuse it with fever. Common tests that doctors often prescribe include:
- CT scan of the head
- Blood tests
- Lumbar puncture
- Urine tests
- Kidney examination
Treatment for hyperthermia
There are two techniques that are commonly used to treat hyperthermia, they are:
- Internal cooling: It involves ice water gastric or rectal lavage, thoracic or peritoneal lavage and extracorporeal blood cooling.
- External cooling: It is a lot easy to implement this method besides being easy to tolerate and is highly effective.
- Direct application of ice baths, ice packs or hypothermic blanket to axillae, groin and neck is the conductive cooling techniques.
- Removal of clothing and moving to a cooler area preferably air-conditioned is referred to as convective technique.
- Alternatively, the evaporative cooling method may also be used by removal of clothing and switching on fan. This needs to be done in conjunction with misting the skin using tepid water or by application of single layer of wet sheet on the body.
Other possible treatments include:
- Flushing the stomach and rectum with cold water
- Cardiopulmonary bypass
- Muscle relaxing medications
- Reducing tissue damage
Home remedies for hyperthermia
- Remove tight and unnecessary clothing
- Wrap the patient in wet sheets
- Spray cool water
- Blow cool air
- Place Ice packs on neck and armpits
- Drink two to three quarts of water daily
- Avoid excessive exercising particularly during very hot times
- Avoid traveling during hot weathers
- Wear hats and loose clothes when outside
- Take cool baths and showers
- Avoid hot meals or drinks
- Avoid alcohol intake
- Stay indoors
- Reduce consumption of caffeine
- Increase intake of salts & minerals
- Apply sunscreen lotions
Homeopathic medications for Hyperthermia
- Nux Vomica
- Petroleum as
- Arsenicum Album
- Sulphur
- Pulsatilla
- Rhus Toxicodendron
- Abrotanum
- Tamus
- Plantago
Expected Duration of Hyperthermia
Typically the patient suffering needs to stay in the hospital for one or more days to detect and avoid the complications. But the effects of it on the body organs stay longer and may recover within two months but can extend up to a year.
When to call a doctor?
Medical attention and seeking emergency help is necessary when the person has been exposed to the heat for quite a long time and has had symptoms like
- Confusion
- Fainting
- Staggering
- Hallucinations
- Unusual agitation
- Coma
Prognosis
Untreated hyperthermia can lead to major consequences such as:
- Kidney damage
- Damage to the liver
- Heart arrhythmias
- congestive heart failures
- Coma
- Death