What is a Heart Attack?
Page Contents
- 1 What is a Heart Attack?
- 2 What is a Massive Heart Attack?
- 3 Outcome of a massive heart attack
- 4 Causes of Massive heart attacks
- 5 Signs and Symptoms of Massive Heart Attack
- 6 Chances of Surviving a Massive Heart Attack
- 7 Diagnosis of a Massive heart attack
- 8 Treatment for Massive heart attack
- 9 Risk factors for heart attack
- 10 Prevalence
- 11 Complications
- 12 When to seek medical attendance?
- 13 Home remedies to relieve heart pain and manage heart palpitations
- 14 Massive Heart Attack Images
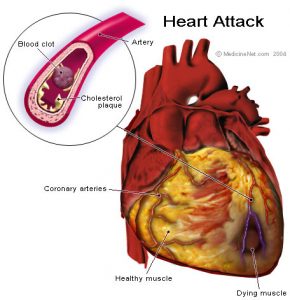
A heart attack is one of the severe health issues around the world and is medically termed as myocardial infarction.
What is a Massive Heart Attack?
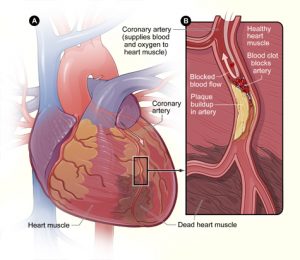
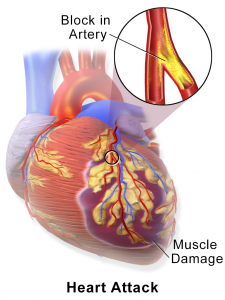
It is a severe form of a heart attack due to lack of oxygen and inadequate blood supply to the heart muscles that causes damage to a large area of the heart. The electrical impulses are mainly responsible for heartbeats and these impulses become weak and irregular as parts of the heart muscles become dead. The oxygenated blood from the ventricle enters the heart and brain causing massive damages.
A massive heart attack affects a significant portion of the heart muscle or causes an enormous amount of heart damage. It can happen if the blockage in a coronary artery occurs in the large artery that supplies blood to a significant portion of the heart. Moreover, it may also be a result of a complete blockage in the blood flow to the heart.
Outcome of a massive heart attack
Heart attacks can lead to:
- Collapses
- Severe cardiac arrest
- Permanent heart damages
These eventually end up causing myocardial arrhythmia, failure of the heart and a chance of a second heart attack. Also, people might get unconscious and in the worst conditions death of the patient occurs. At times, major heart attacks may have a catastrophic outcome on the patient and studies reveal that in 40 to 50% cases there is an increased death risk after the patient is hospitalized.
Causes of Massive heart attacks
There may be several causes underlying the occurrence of massive heart attack-
- Atherosclerosis (coronary heart disease)
- Blockage of arteries
- Abnormal blood circulation, expansion & contraction of the heart
- Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of major heart attacks
- Impaired expansion & contraction of the heart
- Abnormal blood circulation
- Accumulation of fats due to excessive intake of fatty foods
- High blood sugar levels
- High blood pressure
- Excessive consumption of Smoking & alcohol
- Coronary artery spasms(narrowing of the arteries)
- Coronary microvascular disorder (damage to arteries)
- Vasoconstrictors & stimulant drugs
- Emotional stress
- Exposed to cold environments
- Obesity
Signs and Symptoms of Massive Heart Attack
- Chest pain
- Feeling of tightness in chest
- Breathing problems
- Sweating tendency
- Clothes become wet from perspiration
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Cold hands & feet
- Lips, nails & tongue turn blue
- Paleness on the face
- Irregular pulse
- Irregular beating of heart
- Low blood pressure
- Fainting
- Restlessness
- Burning sensation in chest
- Arrhythmia
- Unconsciousness
- Dizziness
- Abdominal pain
- Heartburn
- Clammy skin
Chances of Surviving a Massive Heart Attack
In cases of a heart attack, time is the most vital factor. Even a fraction of minutes can turn out to be very critical for the patients leading to death. The person if admitted in emergency departments has a higher chance of survival than the patient who does not receive medical attention and can get a sudden cardiac arrest and die within minutes. However, survival chances may depend on the following factors:
- Extent of damage to the cardiac tissue
- Rapid and quality of treatment
- Quick opening of the artery within the first 6 hours
- Risk of death increases with age
- Medical history also matters (myocardial infarction, shock, arrhythmia, etc. may cause more damage)
- Chances of survival increases after 48 hours pass
Diagnosis of a Massive heart attack
- ECG is the main diagnostic tool to record the electrical responses of the heart
- Blood test to detect enzymes produced by a damaged heart
- Chest X-rays to examine the heart size and arteries
- Tests to check fluid buildup in lungs
- Angiogram to check for blockage of arteries
- Echocardiogram to check the regular beating of heart through sound waves
- MRI and CT scan to recognize the severity of the heart damage
Treatment for Massive heart attack
Heart attack needs serious and immediate medical attention-
- Aspirin is given while waiting for medical attention to prevent blood clotting
- Nitroglycerin before medical treatment for relieving chest pain
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation or CPR after fainting
- Automatic external defibrillator for restoration of normal heartbeat
- Efforts to save heart muscles after attack
- Regular monitoring of heartbeats
- Adequate oxygen
- Cardioversion in case of arrhythmia
- Anticoagulants for blockage opening
While hospitalized, several medicines may be prescribed to prevent further damages:
- Thrombolytics for dissolving blood clots
- Super aspirins prevents formation of blood clots
- ACE inhibitors saving from further stress
Surgery
- Angioplasty
- Bypass surgery
Risk factors for heart attack
- High cholesterol level
- High blood pressure
- Regular consumption of tobacco
- Diabetes mellitus
- Family history of coronary heart disorders
- Smoking
Prevalence
Unlike females, men are more prone to suffer from massive heart attacks under the age of 75 years. But crossing over, both males and females are equally exposed to cardiac attacks.
Complications
A massive heart attack might have several complications and hazardous impacts:
- Arrhythmia
- Problems in the blood pumping to and from the heart
- Failure of the heart
- Damage to the valves
- Depression or stress
- Fatal rupture of the heart
When to seek medical attendance?
Emergency cases and warning signs of serious problems with heart disease should be considered, and a doctor must be called in when one experiences-
- Severe chest pain
- Serious breathing problems
- Extreme sweating
- Rapid heart rate
- Shortness of breath even during rest
- Arms or legs paralyzed
- Severe headache
- Fainting or being unconscious
Home remedies to relieve heart pain and manage heart palpitations
- Almonds
- Apple cider vinegar
- Having a hot drink
- Application of a cold pack
- Drink lots of water
- Avoid stimulants