Molluscum Contagiosum is a discomforting skin condition affecting many children and adults around the world. Find out more about the condition as well as its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
- 2 Molluscum Contagiosum Symptoms
- 3 Molluscum Contagiosum Causes
- 4 Molluscum Contagiosum Diagnosis
- 5 Molluscum Contagiosum Treatment
- 6 Molluscum Contagiosum Home Remedies
- 7 Molluscum Contagiosum Over-the-Counter Treatment
- 8 Homeopathic Treatment for Molluscum Contagiosum
- 9 Molluscum Contagiosum Prognosis
- 10 Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
- 11 Molluscum Contagiosum in Women
- 12 Genital Molluscum Contagiosum
- 13 Molluscum Contagiosum Complications
- 14 Molluscum Contagiosum Prevention
- 15 Molluscum Contagiosum Pictures
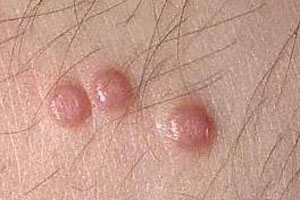
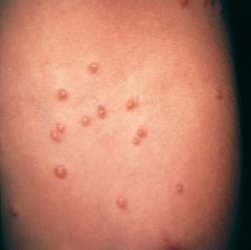
Picture 1 – Molluscum Contagiosum
It is a common viral skin infection that gives rise to painless, hard lumps over the skin surface. The condition mainly affects children.
Molluscum Contagiosum Symptoms
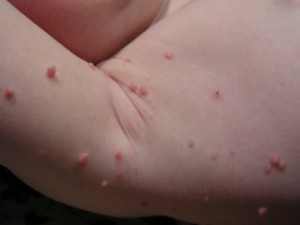
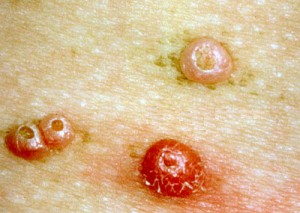
The condition results in the development of tiny, painless papules over the skin of sufferers. The lesions are commonly found to have a central core consisting of a white, waxy substance. Characteristically, there is a tiny dot or indentation at the top of the lumps. In later stages, these bumps may get elevated and become round and flesh-colored in appearance.
Typically, the nodules are 2-5 mm (less than ¼ inch) in diameter and occur in lines. They are often found to arise in skin regions that have been scratched by a person or irritated in some other way. Unlike other skin lesions, these do not generally appear as red or swollen until scratched. If scratched or irritated, the papules get inflamed and occur in lines.
In children, the nodules typically arise on the neck, face, hands, arms and armpits. However, they may develop on any region of the body except for the palms and the soles. In adults, these may appear due to an underlying sexually transmitted disease (STD). The papules are usually located on the genitals, buttocks, inner upper thighs and lower abdomen in grown-ups.
Molluscum Contagiosum Causes
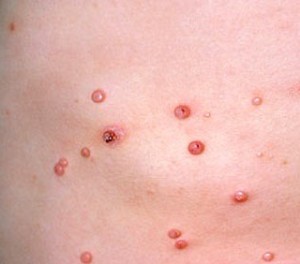
Picture 2 – Molluscum Contagiosum Image
The condition results from an infection by Molluscum Contagiosum Virus. Referred to as MCV, it is a member of the Poxvirus family. The virus can easily spread through:
Direct skin-to-skin contact
The infection occurs when the skin of a child directly comes into contact with a lesion on the body of another child or an adult.
Contact with contaminated objects
The virus may also spread through contact with objects contaminated by the virus, such as towels, toys, clothing, faucet handles or doorknobs.
Sexual contact
The virus also spreads due to sexual contact with an infected person. Initially, nodules arising on the genitalia can be confused with warts or herpetic rashes. Unlike herpetic lesions, however, these lesions are painless.
Irritation
Irritation caused to the lesions due to activities like scratching, rubbing or shaving may spread the virus to adjacent skin. The virus can also spread in a line or in crops (groups).
Weakened immunity
Individuals with a compromised immune system due to underlying disorders, such as AIDS, may suffer from a rapid worsening of MCV.
Molluscum Contagiosum Diagnosis
Physicians usually diagnose the condition by simple observation of the physical appearance of the papules. If they suspect any serious underlying condition, scrapings from the infected skin region may be taken and held under a microscope. A skin biopsy may help in an accurate diagnosis and ruling out the presence of other underlying disorders.
If lumps show up in the genital area, doctors may consider the infection as an STD and carry out further tests. Adults displaying genital molluscum contagiosum rashes should be properly screened for STDs.
An extremely large number of these papules can be indicative of an underlying deficiency of the immune system.
Molluscum Contagiosum Treatment
Physicians often recommend medical cure, particularly for adults. This is mainly due to the fact that MCV infection spreads easily. Treatment for the condition may involve removal of the nodules by:
Non-surgical techniques
MC nodules usually resolve after a period. If they do not, medical techniques may be used for their removal. Removal of individual papules through surgical procedures like freezing, de-coring, needle electrosurgery or scraping has been found to result in scarring (formation of scars in the operated areas). Due to this, the papules are removed with the aid of non-surgical methods like:
- Laser therapy
- Freezing (Cryotherapy)
- Scraping (curettage)
These techniques can be painful for patients. Hence, physicians may prescribe a topical anesthetic to lessen discomfort in sufferers before using non-surgical procedures.
Medications
Topical medications, such as those used to cure psoriasis and acne or remove warts, may be effective in removing the nodules. Imiquimod cream, Tretinoin cream and Cantharidin (commonly referred to as “beetle juice”) are used as standard topical medications for this skin disease. In some cases, a combination of these cures may be used. However, these remedies may result in temporary discoloration of the skin.
Molluscum Contagiosum Home Remedies
Some common home remedies for Molluscum contagiosum include:
Sea Salt Scrub
Combine 2 cups of sea salt with 1/2 cup of olive oil, 1 tablespoon of honey, 2 drops of tea tree essential oil and 1/4 cup of Grapeseed oil. Gently massage the bumps with this solution every day can help you get rid of the lesions. Allow the solution to soak into the skin region for a minute and then wash off with clean water. Use a clean towel to pat the skin dry. Store the mixture in a glass jar to make it last for months.
Salicylic acid application
Directly apply salicylic acid over the lesions to speed up their decomposition. This is a widely popular remedy and is often used as the first treatment for Molluscum.
Tea tree oil application
Tea tree oil has powerful astringent (causes compression of body tissues and canals) properties that are effective in stopping the spread of the lesions. For a more soothing experience, drop the oil in bath-water and soak it in for at least 15 minutes. It is considered to be one of the best natural herbal cures for Molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum Contagiosum Over-the-Counter Treatment
Over-the-counter treatment for this condition include topical remedies, such as
- Aldara
- Betadine Surgical Scrub
- Cantharidin
- Imiquimod cream
- Lemon Myrtle Oil
- Tretinoin (Retin-A)
- Trichloroacetic acid
- 10 percent iodine solution
- 10 percent potassium hydroxide solution
- Zymaderm
In many cases, topical application of these OCD creams and ointments ensures faster recovery and quick resolution of the symptoms.
Homeopathic Treatment for Molluscum Contagiosum
Homeopathic treatment is not only effective in curing the condition but also removing any chance of recurrence of the disease at any time in future. Over-the-counter (OTC) remedies only offer symptomatic relief and do not treat the cause of the condition as such. But homeopathic remedies bring about a permanent relief and not a temporary respite.
The standard homeopathic treatment for the condition is a drug named ‘Thuja’. It is available in most pharmacies and is also used for curing warts. The medicine is completely safe. A patient should be administered with one dose of the drug for two times daily. Usually, the medicine is used in strengths of ’12c’ or ’30c’. The condition usually improves after a few weeks. ‘Thuja’ is one of the best homeopathic remedies for Molluscum Contagiosum.
Molluscum Contagiosum Prognosis
The disease does not give rise to any serious complication. In people with healthy immunity, the condition generally resolves on its own but may take a long time to go away. The nodules may last for a few months or even several years before disappearing completely. They ultimately vanish without leaving any scar, unless the area has been excessively scratched. In most cases, they are seen to go away within 6 – 18 months.
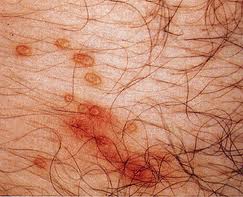
Picture 3 – Molluscum Contagiosum Photo
However, immunosuppressed people (or individuals having a compromised immune system due to conditions like AIDS) may suffer from a rapid worsening of this skin disorder.
In very rare cases, the condition may last longer than two or even five years.
Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
As aforesaid, this condition affects many kids across the world. The MC virus spreads easily and children mostly acquire it from schools or day care centers. The condition is contagious and may spread from direct skin-to-skin contact or touching objects containing virus, such as clothes, toys, bedding and towels. The growths generally develop 2-8 weeks after infection.
MCV infection is common among children aged between 1 and 12 years. However, it is seen most in kids between and 1 and 4 years of age. The condition is characterized by the development of small lesions that are slightly pink or pearly-white in color. For most children, the condition is not too discomforting and goes away naturally with time. The presence of lesions does not affect activities like going to school or taking part in sports.
If left untreated, these may persist for 6 months or a longer duration. Generally, these lesions take anywhere from 1 – 1 ½ years to go away without treatment.
It is generally not a good idea to treat these nodules, especially in children. This is usually because:
- Many of the curative methods, such as application of liquid nitrogen, can be painful for patients
- Some curative techniques have a risk of burning the skin adjoining the lesions
- There can be a minor risk of scarring of the skin due to some treatments
Molluscum Contagiosum in Women
Molluscum Contagiosum is commonly found in women who exercise in gyms, ride bicycles frequently or have multiple sexual partners. They may also get the condition from sexual contact with an MCV-infected male or due to non-sexual viral transmission from children or adult males. The condition is characterized by the development of firm, round bumps over the skin on the sex organs, thighs, pubic region, below the waist or buttocks.
The bumps often heal without treatment.In some cases, however, women may suffer from itchiness or irritation in the lesions. Treatment may be required in such cases. Doctors may scrape the lesions off or treat them with chemical agents.
Women with this condition should abstain from sexual intercourse or have intimacy with only one partner who does not have sex with any other individual. Sexually active women may reduce the risk of suffering from MCV infection or other STDs by using latex barriers such as dental dams, finger cots and condoms.
Genital Molluscum Contagiosum
It is a condition characterized by the development of MCV lesions on the genitals of adults. The problem mainly results from the transmission of the Molluscum virus while having sex. This is an extremely contagious virus and gets transmitted through direct contact with the skin. During sexual activities, the genitals and the pubic regions are exposed and come in direct contact. This makes transmission easy and inevitable.
Men suffering from Genital Molluscum (or MCV lesions on the penis) as well women suspected of having it on their vagina should refrain from having sex until complete resolution of the infection. If sex is continued, there is a high chance that the infected person will transmit the virus to their partner.
Molluscum Contagiosum Complications
In people with severe cases of MCV infection, the nodules and the surrounding skin region turn red and swollen. This condition is referred to as “Molluscum Dermatitis”. This is supposed to occur as an immune response to the viral infection.
If lesions arise on the eyelids, patients may suffer from Conjunctivitis at a later stage. If scratched excessively, the nodules may give rise to secondary bacterial infections on the skin surface. If the skin is irritated, the infection may persist and even spread to adjacent skin areas. There may also be minor problems, such as persistence itchiness in the affected spots.
Molluscum Contagiosum Prevention
The condition can be prevented by measures like:
- Avoiding direct contact with skin lesions of people infected with MCV
- Not sharing towels with infected people.
- Avoiding sex for some time
- Having sex with a single partner known to be non-infected (to prevent molluscum virus as well as other STDs)
- Using condoms with nonoxynol 9 and spermicide. Although they do not offer complete protection from viral infection, they may reduce chances of getting or spreading sexually transmitted conditions.
Molluscum Contagiosum Pictures
Know about the physical appearance of these lesions with these useful Molluscum Contagiosum photos. The Molluscum contagiosum images will help you in getting a true idea about how the condition looks like.
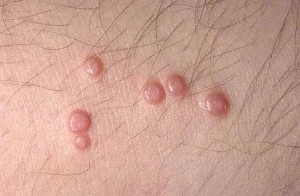
Picture 4 – Molluscum Contagiosum Picture 5 – Molluscum Contagiosum Image
Picture 6 – Molluscum Contagiosum Picture 7 – Photo of Molluscum Contagiosum
If you have symptoms similar to Molluscum Contagiosum, visit your health care provider immediately. This will help you check the condition at the earliest and also prevent development of new symptoms or aggravation of a possible underlying STD.
References:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001829/
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/molluscum-contagiosum/DS00672
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/molluscum_contagiosum/article_em.htm
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000826.htm
http://www.medicinenet.com/molluscum_contagiosum/article.htm
