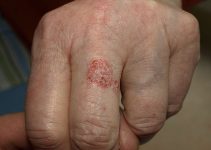
Are you having pea-sized growths under the skin of your neck? You may be suffering from a condition called Pilomatrixoma. Know what is a Pilomatrixoma, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Pilomatrixoma Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Pilomatrixoma Definition
- 2 Pilomatrixoma Meaning
- 3 Pilomatrixoma Location
- 4 Who Gets Pilomatrixoma?
- 5 Symptoms of Pilomatrixoma
- 6 Pilomatrixoma Causes
- 7 Pilomatrixoma Diagnosis
- 8 Pilomatrixoma Differential Diagnosis
- 9 Pilomatrixoma Treatment
- 10 Pilomatrixoma Prognosis
- 11 Does Pilomatrixoma Recur?
- 12 Can You Die From Pilomatrixoma?
- 13 Pilomatrixoma Pictures
Pilomatrixoma is a rare benign tumor that is composed of tissues and originates from the hair follicles. Pilomatrixoma was earlier known as “Calcifying Epithelioma of Malherbe”. It is also called ‘Pilomatricoma’ and ‘Malherbe Calcifying Epithelioma’.
Pilomatrixoma features in the list of rare diseases by the Office of Rare Diseases (ORD) of NIH (National Institute of Health). It affects less than 200,000 people in the United States.
Pilomatrixoma Meaning
The word ‘Pilomatrixoma’ is a fusion of three other terms, ‘pilo’ (meaning “hair”), ‘matrix’ (indicating “intercellular substance”) and ‘oma’ (that means “tumor”). Taken together, the term Pilomatrixoma means a tumor that grows from hair follicles.
“Pilomatrixoma” is pronounced as “Pee-lo-mae-trick-so-maa”.
Pilomatrixoma Location
It usually arises on the scalp, cheek, front area of the ear, eyelids, arms and side of neck. These lesions can also be seen on the upper and lower parts of the body as well as the trunk.
Who Gets Pilomatrixoma?
The bumps are generally seen in kids below 10 years of age and women within 30 years of age. Women are twice as likely to have Pilomatrixoma tumors as men. Pilomatrixoma is found to affect white people more than others. Pilomatrixoma not only affects humans. It can also be seen in animals. Pilomatrixoma in dogs is quite common.
Most Pilomatrixoma cases have been reported in children. Lesions in Pilomatrixoma children are discovered mostly in the first two years of life. The risk of having these lesions reduces with advancing age.
Symptoms of Pilomatrixoma
Pilomatrixoma of Malherbe is mainly characterized by the appearance of firm growths on the skin surface. Sufferers usually have a single bump though multiple Pilomatrixoma growths can also be seen. The lumps are generally small, measuring less than 3 cms in diameter. The skin covering the tumors may get discolored and usually turns faint blue in appearance. The cysts may feel hard to touch.
Pilomatrixoma growths are normally painless but can hurt if they become infected. These grow very slowly in size and are composed of hair matrix that has become calcified. In some cases, these lesions are found to grow as much as 35 mm in a little over 6 months.
In rare cases, pilomatrixoma Calcifying Epithelioma of Malherbe may be associated with conditions like Skull Dysostosis, Gardner Syndrome and Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy.
Pilomatrixoma Causes
Pilomatrixoma cysts develop from an unusual formation of cells that are like hair cells which become calcified or hardened. The hardened cells accumulate under the skin and appear as a bump.
The condition is also supposed to result from hereditary factors. Children having Pilomatrixoma cysts are often seen to have one or more family members with these tumors. This is suggestive of genetic factors at work. Medical research has shown mutations in the CTNNB1 gene in at least 76% of Pilomatrixoma cysts.
Pilomatrixoma Diagnosis
Pilomatrixoma custs are generally diagnosed by physical examination and by taking the medical history of the suffering individual into account. In some cases, the diagnosis may involve a biopsy in which samples of tissues are removed from the tumors with a surgical needle and examined under a microscope. Biopsy helps doctors determine if there is an accumulation of unusual or malignant cells.
In case of Hyperdense Pilomatrixoma CT (Computed Tomography) scan is quite helpful in diagnosis. In complex cases of Pilomatrixoma ultrasound tests may be needed for a proper determination. In a few cases of Pilomatrixoma MRI scans may also be recommended by doctors for an accurate examination of the tumors.
Pilomatrixoma Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for Pilomatrixoma involves differentiating the disease from other similar conditions like Dermoid Cyst, Chondroma, Degenerating Fibroxanthoma, Giant Cell Tumor, Ossifying Hematoma and Sebaceous Cyst.
Pilomatrixoma Treatment
The treatment of Pilomatrixoma depends on the age, health condition and medical history of the patient. If the sufferer happens to be a child, his or her tolerance to specific medicines and therapies also need to be taken into account.
The treatment of Pilomatrixoma mainly involves surgery. Pilomatrixoma excision is generally carried out in body regions such as the head and the neck. The surgical process is short and does not take too much time to complete.
In a few cases, medicines like Amoxicillin have also been found to be effective for treatment. But this should be as per the prescription of an experienced doctor. If the doctor feels you should go for a surgery, it is better not to try any other medications.
Pilomatrixoma Prognosis
The prognosis in Pilomatrixoma tumors is generally very successful. Surgery does not give rise to any adverse outcomes and there is rarely any complication, unless there is malignancy involved. A single surgical operation is usually enough to cure a benign Pilomatrixoma condition.
Does Pilomatrixoma Recur?
Following a proper removal of Pilomatrixoma recurrences are rare. Recurring tumors may be a case of malignant Pilomatrixoma. In ordinary cases, Pilomatrixoma cysts do not recur as a complete resection of these structures is easy.
Can You Die From Pilomatrixoma?
There has not been any reported case of death from Pilomatrixoma. This is usually a benign or non-cancerous condition. But locally invasive tumors of this kind can lead to visceral metastasis in some cases and may result in death. Very large cysts, more than 18 cm in size, can cause serious discomforts in sufferers.
In rare cases, Pilomatrixoma may turn malignant. Pilomatrixoma carcinoma cases can lead to death in some cases.
Pilomatrixoma Pictures
Want to know how Pilomatrixoma cysts on the skin look like? Here are some Pilomatrixoma images that will help you get an idea about the appearance of the condition.
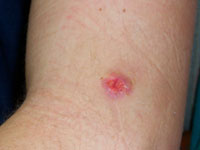
Picture 1 – Pilomatrixoma Photo
Source – blogspot
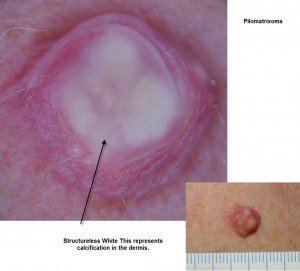
Picture 2 – Pilomatrixoma Image
Source – dermnetnz
If you are having Pilomatrixoma or have anyone in your family suffering from a bump characteristic of this condition, it is better to go for an early diagnosis. It is best not to delay diagnosis as these bumps may turn malignant in rare cases. A timely test will help diagnose the condition and give you relief from future discomforts and possible complications with early treatment.
References:
http://www.lpch.org/DiseaseHealthInfo/HealthLibrary/ent/plmtrixma.html
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-overview
http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/p/pilomatrixoma/basics.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pilomatricoma
http://www.drhull.com/EncyMaster/P/pilomatricoma.html
http://radiopaedia.org/articles/pilomatrixoma
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2636049/
http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/pilomatrixoma