Myotonia Congenita (MC) is a congenital disease that prevents the muscles from relaxing after a contraction. Find out all about the disorder including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Myotonia Congenita?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Myotonia Congenita?
- 2 Myotonia Congenita Prevalence
- 3 Myotonia Congenita Types
- 4 Myotonia Congenita Causes
- 5 Myotonia Congenita Signs and Symptoms
- 6 Myotonia Congenita Prevention
- 7 Myotonia Congenita Diagnosis
- 8 Myotonia Congenita Differential Diagnosis
- 9 Myotonia Congenita Treatment
- 10 Myotonia Congenita Natural Treatment
- 11 Myotonia Congenita Prognosis
- 12 Myotonia Congenita and Malignant Hyperthermia
- 13 Myotonia Congenita Life Expectancy
- 14 Myotonia Congenita in Animals
- 15 Myotonia Congenita Risk Factors
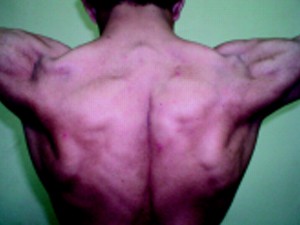
Also known as Congenital Myotonia, this is a genetic neuromuscular condition that affects relaxation of the muscles. As the name suggests, this disease is congenital – meaning an affected individual has it from birth. This disease makes the muscles unable to relax quickly after voluntary contractions.
This condition is sometimes referred to as the “Finnish Heritage Disease” as it is more commonly seen in residents of Finland.
Myotonia Congenita Prevalence
According to studies, one out of every 100000 people is affected by this genetic condition. It is quite common in the northern parts of Scandinavia, where it generally afflicts one out of every ten thousand individuals.
Myotonia Congenita Types
MC is categorized into two different types:
Picture 1 – Myotonia Congenita
- Becker Myotonia
- Thomsen’s Disease
Both these forms are caused by the mutation of the gene CLCN1. However, these are inherited in different ways.
Becker Disease is the most common form of this genetic disease. The inheritance of this disorder occurs in the autosomal recessive pattern. This means an individual with Becker Disease has two copies of altered genes in each cell. Usually, both parents of a patient carry one copy of the mutated gene. However, parents do not generally display any symptoms of the disease.
Thomsen’s Disease or Thomsen Disease is the rarer type of this condition. The inheritance of the condition occurs in the autosomal dominant pattern. This means that a single copy of the mutated gene in all the cells can give rise to the condition. In most cases, an individual suffering from this syndrome has only one parent affected by the condition. Sometimes, the symptoms of Thomsen Disease are so mild that the patients do not even notice them. However, in some rare instances, a person can be severely affected.
SCN4A mutations have recently been identified to be causing another type of Congenital Myotonia which cannot be categorized as either Thomsen’s Disease or Becker Disease. This unusual form of MC is a type of potassium-aggravated Myotonia and is sometimes called Acetazolamide-Responsive Myotonia. Acetazolamide is a type of carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, sold under the brand name of Diamox.
Myotonia Congenita Causes
It is caused by the mutation of the gene that is responsible for the production of a protein that plays an important part in making up the chloride ion channel of the muscles. The gene that undergoes mutation is situated on chromosome 7 (7q35) and is called Gene CLCN. The chloride ion channel is a pore comprising of 2 similar sub-units. It is located in the membranes of the muscle fibres. Under normal circumstances, this pore opens to let the charged chloride ions pass into the cell following a muscle contraction. The chloride ions must flow quickly through the pore so that the difference in the electric charge inside and outside the cell can be restored and maintained. The muscle cannot relax if the function of the chloride channel is impaired in any way. This leads to stiffness of muscles. Researchers have identified over 100 mutations to the gene CLCN1. Various mutations affect the inheritance patterns and the severity of the symptoms.
The underlying pathophysiology of MC first established the significance of sarcolemmal chloride conductance in controlling the excitability muscles.
Myotonia Congenita Signs and Symptoms
This disease is characterized by very early onset of the symptoms. However, the symptoms of MC generally go unnoticed in children aged below 2 to 3 years. The principal symptom of this genetic disorder is the inability of the muscles to relax quickly after every contraction. Some of the common symptoms of MC are:
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Excessive salivation
- Stiffness in movements that improve with repetition
- Frequent falling
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Muscle pain (in some cases)
Myotonia Congenita Prevention
There are no known ways to definitely prevent the condition. However, genetic counseling can help a couple with a history of Congenital Myotonia to have a healthy child.
Myotonia Congenita Diagnosis
A patient has to go through various tests for detection of this disease. Doctors always ask whether a patient has a history of the disorder in his or her family. Proper studying of the family history is very important for an accurate diagnosis. Physicians also perform the following diagnostic tests for confirming MC in patients:
- Genetic testing and reviews
- Electromyography or EMG (testing the electrical activities of muscles)
- Muscle biopsy
Myotonia Congenita Differential Diagnosis
Various other disorders, having Myotonia as a prominent finding, may cause various symptoms similar to those of MC. These conditions include:
- Paramyotonia Congenita
- Potassium-Aggravated Myotonia
- Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (a common type of muscular dystrophy)
Myotonia Congenita Treatment
In some cases, patients of MC do not require treatment as the symptoms are very mild and can be managed without medication. Some individuals do not receive any treatment as the possible side effects of medications actually outweigh the potential benefits of the treatment. The treatment options for more serious instances of Myotonia Congenita include vitamin therapy, hormone therapy and physical therapy. In severe cases, the symptoms can be treated by using medicines and anticonvulsant drugs like:
- Quinine
- Mexiletine
- Carbamazepine
- Phenytoin
Carbamazepine (Tegretol) is sometimes prescribed to people suffering from this disorder.
Myotonia Congenita Natural Treatment
An individual suffering from a mild case of Congenital Myotonia can keep the symptoms in check by doing regular exercise, yoga and physical workouts. This helps the muscles relax better after contractions. Following a healthy and nutritional diet also helps to keep the muscles in proper condition. Eating sodium rich food can help to alleviate the symptoms; however, it is not recommended for people with high blood pressure.
Myotonia Congenita Prognosis
The outcome of the disorder depends on the severity of the symptoms. Proper treatment helps patients to experience a positive result. The symptoms may get better as a patient grows older.
Myotonia Congenita and Malignant Hyperthermia
Malignant Hyperthermia is a genetic condition which causes muscle rigidity and high body temperatures due to use of some anesthetics (such as halothane). It is an associate disorder of Myotonia Congenita. However, there is sufficient amount of controversy regarding their association. Various volatile anesthetics are believed to trigger Malignant Hyperthermia in Congenital Myotonia patients. But there is a lack of evidence as yet to establish the link between these two diseases.
Myotonia Congenita Life Expectancy
MC is not a fatal condition. Regular exercise allows patients to live a normal life and take part in all daily activities just like any normal person.
Myotonia Congenita in Animals
MC can also be seen in many animals apart from humans. It is seen in goats and is hence, sometimes referred to as the Fainting Goat Syndrome. The condition affects canine, feline and cattle species all over the world. It is believed that the form of MC affecting horses is an autosomal recessive condition. The disease has been reported to affect the domestic shorthair cats as a genetic myopathy. Mutated gene in the chloride ion channel also causes this disorder in other animals, including dogs and goats.
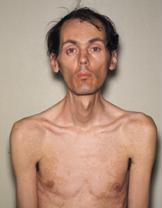
Myotonia Congenita Risk Factors
The risk factors of this disease include:
Picture 2 – Myotonia Congenita Image
Family history
Couples with a family history of the syndrome are likely to have a child suffering from this condition. A newborn child is at high risk of inheriting MC if one parent has the condition. In cases where both parents carry the mutated gene, a child is sure to inherit the disease.
Ritalin
According to some people, Ritalin might cause or promote the symptoms of Congenital Myotonia. Ritalin contains active components of methylphenidate hydrochloride and is used for the treatment of various disorders including Narcolepsy, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, fatigue and depression.
Myotonia Congenita is a rare condition that affects very few people. In most cases, the symptoms are too mild to be noticed while in some cases the condition makes patients suffer from serious symptoms. However, one can easily keep these symptoms in check with regular exercise and proper medications. There are various support groups which provide proper guidelines for the patients of MC and their families regarding the ways to fight the disorder. If you have a MC sufferer at home or having the disorder yourself, you can get in touch with any of these groups for assistance.
References:
http://www.socialstyrelsen.se/rarediseases/myotoniacongenita
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/myotonia-congenita
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001424.htm
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002397/

hello
I am an eighteen-year-old from Iran.
I’m diseases with myotonia congenital
I myself like I did not see anyone in his country.
I like to talk with people who are like me.
I like to know my disease.
In my country I did not have enough information about the disease
Please help me to know myself more